indonesia
SR53_Indonesia_Dec2015
SR53_Indonesia_Dec2015
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
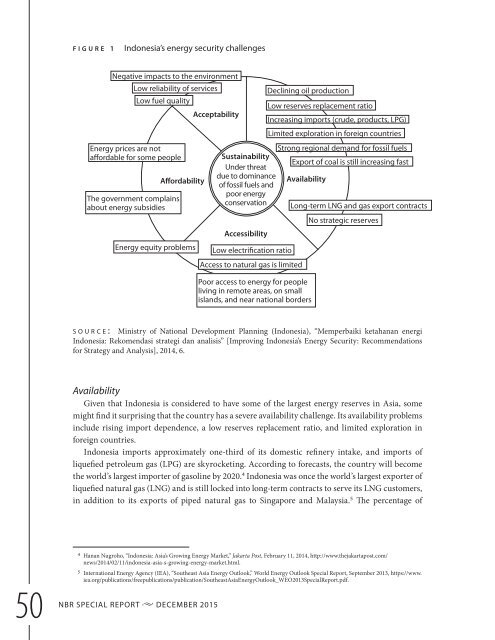
f i g u r e 1<br />
Indonesia’s energy security challenges<br />
Negative impacts to the environment<br />
Low reliability of services<br />
Low fuel quality<br />
Acceptability<br />
Declining oil production<br />
Low reserves replacement ratio<br />
Increasing imports (crude, products, LPG)<br />
Limited exploration in foreign countries<br />
Energy prices are not<br />
affordable for some people<br />
The government complains<br />
about energy subsidies<br />
Affordability<br />
Energy equity problems<br />
Sustainability<br />
Under threat<br />
due to dominance<br />
of fossil fuels and<br />
poor energy<br />
conservation<br />
Accessibility<br />
Low electrification ratio<br />
Access to natural gas is limited<br />
Strong regional demand for fossil fuels<br />
Export of coal is still increasing fast<br />
Availability<br />
Poor access to energy for people<br />
living in remote areas, on small<br />
islands, and near national borders<br />
Long-term LNG and gas export contracts<br />
No strategic reserves<br />
s o u r c e : Ministry of National Development Planning (Indonesia), “Memperbaiki ketahanan energi<br />
Indonesia: Rekomendasi strategi dan analisis” [Improving Indonesia’s Energy Security: Recommendations<br />
for Strategy and Analysis], 2014, 6.<br />
Availability<br />
Given that Indonesia is considered to have some of the largest energy reserves in Asia, some<br />
might find it surprising that the country has a severe availability challenge. Its availability problems<br />
include rising import dependence, a low reserves replacement ratio, and limited exploration in<br />
foreign countries.<br />
Indonesia imports approximately one-third of its domestic refinery intake, and imports of<br />
liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) are skyrocketing. According to forecasts, the country will become<br />
the world’s largest importer of gasoline by 2020. 4 Indonesia was once the world’s largest exporter of<br />
liquefied natural gas (LNG) and is still locked into long-term contracts to serve its LNG customers,<br />
in addition to its exports of piped natural gas to Singapore and Malaysia. 5 The percentage of<br />
50<br />
NBR<br />
4 Hanan Nugroho, “Indonesia: Asia’s Growing Energy Market,” Jakarta Post, February 11, 2014, http://www.thejakartapost.com/<br />
news/2014/02/11/<strong>indonesia</strong>-asia-s-growing-energy-market.html.<br />
5 International Energy Agency (IEA), “Southeast Asia Energy Outlook,” World Energy Outlook Special Report, September 2013, https://www.<br />
iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/SoutheastAsiaEnergyOutlook_WEO2013SpecialReport.pdf.<br />
SPECIAL REPORT u DECEMBER 2015