Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
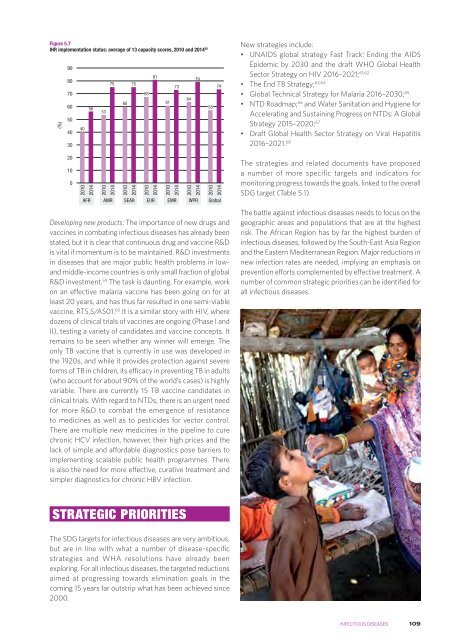
Figure 5.7<br />
IHR implementation status: average of 13 capacity scores, 2010 and 2014 58<br />
(%)<br />
90<br />
80<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
40<br />
56<br />
53<br />
75<br />
60<br />
75<br />
68<br />
81<br />
61<br />
73<br />
64<br />
79<br />
58<br />
74<br />
New strategies include:<br />
• UNAIDS global strategy Fast Track: Ending the AIDS<br />
Epidemic by 2030 and the draft WHO Global Health<br />
Sec<strong>to</strong>r Strategy on HIV 2016–2021; 61,62<br />
• The End TB Strategy; 63,64<br />
• Global Technical Strategy for Malaria 2016–2030; 65<br />
• NTD Roadmap; 66 and Water Sanitation and Hygiene for<br />
Accelerating and Sustaining Progress on NTDs: A Global<br />
Strategy 2015–2020; 67<br />
• Draft Global Health Sec<strong>to</strong>r Strategy on Viral Hepatitis<br />
2016–2021. 68<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
AFR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
AMR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
SEAR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
EUR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
EMR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
WPR<br />
2010<br />
2014<br />
Global<br />
Developing new products: The importance of new drugs and<br />
vaccines in combating infectious diseases has already been<br />
stated, but it is clear that continuous drug and vaccine R&D<br />
is vital if momentum is <strong>to</strong> be maintained. R&D investments<br />
in diseases that are major public health problems in lowand<br />
middle-income countries is only small fraction of global<br />
R&D investment. 59 The task is daunting. For example, work<br />
on an effective malaria vaccine has been going on for at<br />
least 20 years, and has thus far resulted in one semi-viable<br />
vaccine, RTS,S/AS01. 60 It is a similar s<strong>to</strong>ry with HIV, where<br />
dozens of clinical trials of vaccines are ongoing (Phase I and<br />
II), testing a variety of candidates and vaccine concepts. It<br />
remains <strong>to</strong> be seen whether any winner will emerge. The<br />
only TB vaccine that is currently in use was developed in<br />
the 1920s, and while it provides protection against severe<br />
forms of TB in children, its efficacy in preventing TB in adults<br />
(who account for about 90% of the world’s cases) is highly<br />
variable. There are currently 15 TB vaccine candidates in<br />
clinical trials. With regard <strong>to</strong> NTDs, there is an urgent need<br />
for more R&D <strong>to</strong> combat the emergence of resistance<br />
<strong>to</strong> medicines as well as <strong>to</strong> pesticides for vec<strong>to</strong>r control.<br />
There are multiple new medicines in the pipeline <strong>to</strong> cure<br />
chronic HCV infection, however, their high prices and the<br />
lack of simple and affordable diagnostics pose barriers <strong>to</strong><br />
implementing scalable public health programmes. There<br />
is also the need for more effective, curative treatment and<br />
simpler diagnostics for chronic HBV infection.<br />
The strategies and related documents have proposed<br />
a number of more specific targets and indica<strong>to</strong>rs for<br />
moni<strong>to</strong>ring progress <strong>to</strong>wards the goals, linked <strong>to</strong> the overall<br />
SDG target (Table 5.1).<br />
The battle against infectious diseases needs <strong>to</strong> focus on the<br />
geographic areas and populations that are at the highest<br />
risk. The African Region has by far the highest burden of<br />
infectious diseases, followed by the South-East Asia Region<br />
and the Eastern Mediterranean Region. Major reductions in<br />
new infection rates are needed, implying an emphasis on<br />
prevention efforts complemented by effective treatment. A<br />
number of common strategic priorities can be identified for<br />
all infectious diseases.<br />
Prevention: Preventive efforts include: (i) environmental<br />
measures, such as improved water, sanitation and hygiene<br />
<strong>to</strong> reduce transmission of waterborne diseases, hepatitis<br />
STRATEGIC PRIORITIES<br />
The SDG targets for infectious diseases are very ambitious,<br />
but are in line with what a number of disease-specific<br />
strategies and WHA resolutions have already been<br />
exploring. For all infectious diseases, the targeted reductions<br />
aimed at progressing <strong>to</strong>wards elimination goals in the<br />
coming 15 years far outstrip what has been achieved since<br />
2000.<br />
INFECTIOUS DISEASES<br />
109