Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
HEPATITIS<br />
Viral hepatitis is caused by five different viruses, and transmission occurs through contaminated food<br />
or water (hepatitis A and E) or through exposure <strong>to</strong> blood or body fluids (hepatitis B, C, D). Viral hepatitis<br />
infection kills an estimated 1.45 million per year, with approximately 90% of deaths due <strong>to</strong> chronic HBV<br />
and HCV infection, which cause cirrhosis and liver cancer. 12 The majority (85%) of viral hepatitis deaths<br />
occur in Asia, North Africa, East Africa and West Africa. A comprehensive set of hepatitis prevention<br />
interventions exists (Table 5.2) and effective treatment can cure more than 90% of patients with chronic<br />
HCV infection and suppress viral replication of hepatitis B. Despite the high disease burden and available<br />
prevention and treatment interventions, hepatitis has not received the same attention as other diseases<br />
with a comparable burden of disease, such as HIV, TB or malaria.<br />
Table 5.2.<br />
Elements of a comprehensive hepatitis prevention programme<br />
Virus<br />
A E<br />
A<br />
B<br />
B C<br />
B C<br />
B C<br />
A B C<br />
Prevention intervention<br />
Safe water and food<br />
Hepatitis A vaccination according <strong>to</strong> the country's epidemiological<br />
situation<br />
Hepatitis B vaccination for all children and administration of birth dose<br />
Access <strong>to</strong> safe blood (universal screening of all blood donations in<br />
a quality-assured manner)<br />
Access <strong>to</strong> sterile injections and other invasive medical equipment<br />
in formal and informal health settings<br />
Access <strong>to</strong> sterile injection equipment and other harm-reduction<br />
measures for people who inject drugs<br />
Promotion of safe sex practices<br />
ACHIEVEMENTS<br />
Vaccination: The reduction in HBV infections as a result of hepatitis<br />
B vaccination programmes is the greatest achievement in hepatitis<br />
control. By the end of 2014, 194 countries had introduced the vaccine<br />
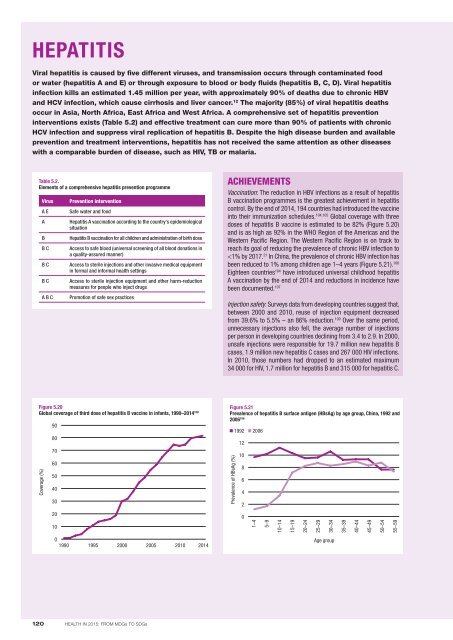
in<strong>to</strong> their immunization schedules. 104,105 Global coverage with three<br />
doses of hepatitis B vaccine is estimated <strong>to</strong> be 82% (Figure 5.20)<br />
and is as high as 92% in the WHO Region of the Americas and the<br />
Western Pacific Region. The Western Pacific Region is on track <strong>to</strong><br />
reach its goal of reducing the prevalence of chronic HBV infection <strong>to</strong><br />