Gibbs adsorption isotherm
Gibbs adsorption isotherm
Gibbs adsorption isotherm
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Gibbs</strong> <strong>adsorption</strong> <strong>isotherm</strong><br />
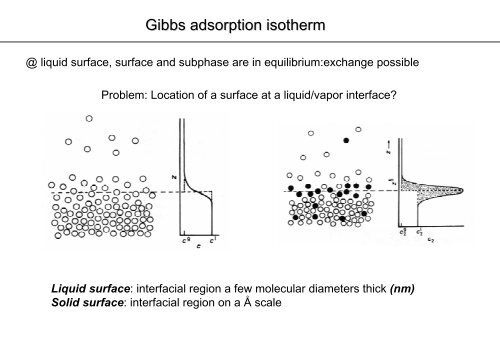
@ liquid surface, surface and subphase are in equilibrium:exchange possible<br />
Problem: Location of a surface at a liquid/vapor interface?<br />
Liquid surface: interfacial region a few molecular diameters thick (nm)<br />
Solid surface: interfacial region on a Å scale
Δ c(z) = c(z) −c<br />
Δ c(z) = c(z) −c<br />
∞<br />
Γ = Γ = − + −<br />
liq<br />
vap<br />
∫ ∫<br />
0<br />
(c(z) c )dz (c(z) c )dz<br />
2 z<br />
2<br />
0<br />
−∞<br />
2<br />
1 H O H O,v H O,liq<br />
∞<br />
∫ ∫<br />
Γ = Γ = − + −<br />
0<br />
(c(z) c )dz (c(z) c )dz<br />
0<br />
−∞<br />
2 SDS<br />
z<br />
SDS,v SDS,liq<br />
c vap ~ 10 -2 (M)<br />
<strong>Gibbs</strong> <strong>adsorption</strong> equation<br />
z<br />
z<br />
∞<br />
∫<br />
∫ ∫<br />
Γ= Δc(z)dz<br />
−∞<br />
∞ ∞<br />
−∞<br />
vap<br />
−∞<br />
liq<br />
Γ= (c(z) − c )dz + (c(z) −c<br />
)dz<br />
= 0<br />
dγ<br />
= −Γ<br />
dμ<br />
SDS<br />
1 dγ<br />
Γ SDS = −<br />
RT d lnc SDS
saturation<br />
below cmc<br />
Surface tension of surfactant solutions<br />
c cmc<br />
Slope<br />
corresponds to<br />
surface density
Surface tension of polyelectrolyt/surfactant solutions
surface tension / mN/m<br />
70 C 12 TAB<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
10 -5<br />
-<br />
10 -4<br />
cac<br />
10 -3<br />
10 -2<br />
-<br />
- +<br />
PSS/C 12TAB 12TAB<br />
5*10 -3<br />
C 12 TAB concentration / mol/l<br />
10 -1<br />
A. Asnacios, R. v. K., D. Langevin, Coll. Surfaces A (2001)
*<br />
A) Polyelectrolytes B) Surfactants (c
C 12 TAB / PAMPS<br />
C 12 TAB / PAMPS<br />
(75 – 750 ppm)<br />
C 12 TAB / PAMPS<br />
+ -<br />
CnTAB TAB / PAMPS<br />
C 12 TAB<br />
C 16 TAB / PAMPS<br />
C16TAB / PAMPS<br />
cac cmc<br />
(75 ppm) cac<br />
KBr / PAMPS<br />
CMC (C 12 TAB) = 15 mM<br />
CMC (C 16 TAB) = 1 mM<br />
PAMPS<br />
C 16 TAB<br />
cmc cmc‘<br />
A. Asnacios, D. Langevin, J.-F. Argillier, Macromolecules (1996)<br />
A. Asnacios, R. v. Klitzing, D. Langevin Coll. Surf. A (2000)
surface tension / mN/m<br />
75<br />
70<br />
65<br />
60<br />
55<br />
50<br />
45<br />
-<br />
Low density<br />
of binding sites<br />
+ -<br />
P(DADMAC-stat<br />
P(DADMAC stat-NMVA)/SDS<br />
NMVA)/SDS<br />
Maximum in density at 50 %<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100<br />
polymer charge density / %<br />
-<br />
Coiled chains<br />
*<br />
C<br />
H 3<br />
Stretched chains<br />
P(DADMAC-stat-NMVA)<br />
-<br />
N +<br />
Cl<br />
CH 3<br />
f<br />
O<br />
n<br />
*<br />
N CH3<br />
CH 3
Langmuir films<br />
Preparation: dissolve insoluble amphiphiles in a volatile organic solvent<br />
and deposit drops of solution onto the air/water interface<br />
S>0 => spreading, evaporation of solvent => monolayer of amphiphiles<br />
Pressure is needed to prevent film from spreading:<br />
0<br />
Π s = γ −γ
Collapse<br />
Langmuir films<br />
G: gas phase<br />
L1: liquid expanded phase<br />
(e.g. saturated unbranched<br />
carbon chains: a 0 ≈30-50Å 2 )<br />
L2: liquid condensed phase<br />
(stronger molecular interactions,<br />
lower compressibilty<br />
S: solid (e.g. alcohols, esters:<br />
a 0 ≈19 Å 2 )<br />
G->L1: typical gas liquid transiton<br />
like in 3D<br />
L1->L2: transition not finally explained.
Effect of polymer charge on lipid/polyelectrolyte complexes @ air/water interface:<br />
DPPA / PDADMAC–co-polymer<br />
Thickness: Ellipsometry<br />
n CP-47 =n CP-73 =1.35<br />
d CP-73 =7.5 nm<br />
d CP-47 =9.0 nm<br />
Kerstin de Meijere et al. Macromolecules 1997
GID (grazing incidence diffraction)
Effect of polymer charge on lipid/polyelectrolyte complexes @ air/water interface:<br />
DPPA / PDADMAC–co-polymer<br />
GID:<br />
α i =0.85α c<br />
in plane<br />
diffraction:<br />
d hk =2π/Q xy<br />
Kerstin de Meijere et al. Macromolecules 1997<br />
DPPA<br />
PDADMAC<br />
Without<br />
PDADMAC<br />
With PDADMAC<br />
Domains of<br />
tilted chains