Foreign Investment in Agriculture in Cambodia CDRI Working Paper ...
Foreign Investment in Agriculture in Cambodia CDRI Working Paper ...
Foreign Investment in Agriculture in Cambodia CDRI Working Paper ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
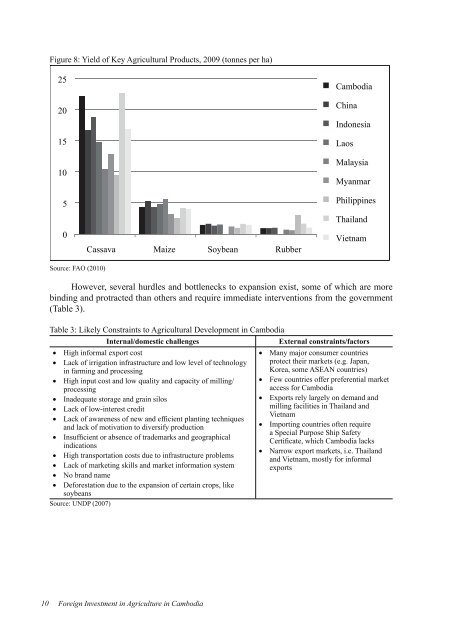
Figure 8: Yield of Key Agricultural Products, 2009 (tonnes per ha)<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
Cassava<br />
Source: FAO (2010)<br />
10 <strong>Foreign</strong> <strong>Investment</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Agriculture</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Cambodia</strong><br />
Maize Soybean Rubber<br />
<strong>Cambodia</strong><br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a<br />
Indonesia<br />
Laos<br />
Malaysia<br />
Myanmar<br />
Philipp<strong>in</strong>es<br />
Thailand<br />
Vietnam<br />
However, several hurdles and bottlenecks to expansion exist, some of which are more<br />
b<strong>in</strong>d<strong>in</strong>g and protracted than others and require immediate <strong>in</strong>terventions from the government<br />
(Table 3).<br />
Table 3: Likely Constra<strong>in</strong>ts to Agricultural Development <strong>in</strong> <strong>Cambodia</strong><br />
Internal/domestic challenges External constra<strong>in</strong>ts/factors<br />
• High <strong>in</strong>formal export cost<br />
• Many major consumer countries<br />
• Lack of irrigation <strong>in</strong>frastructure and low level of technology<br />
<strong>in</strong> farm<strong>in</strong>g and process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
protect their markets (e.g. Japan,<br />
Korea, some ASEAN countries)<br />
• High <strong>in</strong>put cost and low quality and capacity of mill<strong>in</strong>g/<br />
process<strong>in</strong>g<br />
• Few countries offer preferential market<br />
access for <strong>Cambodia</strong><br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
Inadequate storage and gra<strong>in</strong> silos<br />
Lack of low-<strong>in</strong>terest credit<br />
Lack of awareness of new and efficient plant<strong>in</strong>g techniques<br />
and lack of motivation to diversify production<br />
Insufficient or absence of trademarks and geographical<br />
<strong>in</strong>dications<br />
High transportation costs due to <strong>in</strong>frastructure problems<br />
Lack of market<strong>in</strong>g skills and market <strong>in</strong>formation system<br />
No brand name<br />
•<br />
•<br />
•<br />
Exports rely largely on demand and<br />
mill<strong>in</strong>g facilities <strong>in</strong> Thailand and<br />
Vietnam<br />
Import<strong>in</strong>g countries often require<br />
a Special Purpose Ship Safety<br />
Certificate, which <strong>Cambodia</strong> lacks<br />
Narrow export markets, i.e. Thailand<br />
and Vietnam, mostly for <strong>in</strong>formal<br />
exports<br />
• Deforestation due to the expansion of certa<strong>in</strong> crops, like<br />
soybeans<br />
Source: UNDP (2007)