SOYBEAN and BEES
BFhV4z
BFhV4z
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ing region is the throat <strong>and</strong> the flaring outer region is the limb. A sympetalous flower, with<br />
bilateral symmetry with an upper <strong>and</strong> lower lip, is bilabiate. Flowers with connate petals<br />
or sepals may have various shaped corolla or calyx, like campanulate, funnelform, tubular,<br />
urceolate, salverform or rotate (Sattler, 1988).<br />
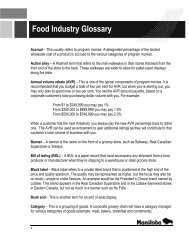
Photos: Decio Luiz Gazzoni<br />
A<br />
B<br />
Ovary<br />
Ovule<br />
Nectaries<br />
Locule<br />
Placente<br />
Receptacle<br />
Pedicel<br />
C<br />
Stigma<br />
D<br />
Stamen<br />
Polen grains<br />
Figure 8. Details of the structure of a perfect flower. A) Cross cut of a perfect flower; B) Details of the ovary <strong>and</strong><br />
the nectaries; C)/D) Side <strong>and</strong> top view of the reprodutory structure.<br />
Many flowers have a symmetry. When the perianth is bisected through the central axis from<br />
any point, symmetrical halves are produced, forming a radial symmetry. These flowers are<br />
also known to be actinomorphic or regular, e.g. rose or trillium. When there is only one line<br />
to bisect flowers that produces symmetrical halves, the flower is said to be irregular or zygomorphic,<br />
e.g. snapdragon or most orchids (Sattler, 1988).<br />
28 SoybeAn <strong>and</strong> bees