FLEISCHWIRTSCHAFT international 2/2018
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
...................... ..........<br />
....................................<br />
68<br />
Fleischwirtschaft <strong>international</strong> 2_<strong>2018</strong><br />
Research &Development Improving the quality of silver carp fillets ...<br />
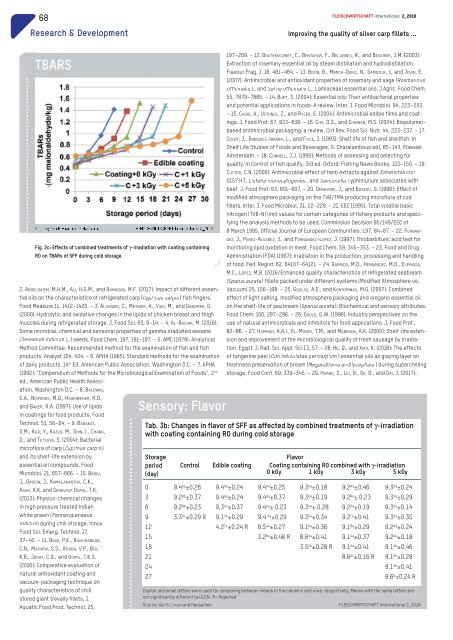
Source: ABD EL-DAIEM and HASSANIEN <strong>FLEISCHWIRTSCHAFT</strong> <strong>international</strong> 2_<strong>2018</strong><br />
Fig. 2c: Effects of combined treatments of γirradiation with coating containing<br />
RO on TBARs of SFF during cold storage<br />
2. ABDELDAIEM,M.H.M., ALI,H.G.M., and RAMADAN,M.F. (2017): Impact of different essential<br />
oils on the characteristics of refrigerated carp (Cyprinus carpio )fishfingers.<br />
Food Measure 11,1412–1420. –3.ALASNIER,C., MEYNIER,A., VIAU,M., and GANDMER,G.<br />
(2000): Hydrolytic and oxidative changes in the lipids of chicken breast and thigh<br />
muscles during refrigerated storage. J. Food Sci. 65, 9–14.–4.AL-BACHIR,M.(2016):<br />
Some microbial, chemical and sensorial properties of gamma irradiated sesame<br />
(Sesamum indicum L.) seeds. Food Chem. 197, 191–197. –5.AMC (1979): Analytical<br />
Method Committee. Recommended method for the examination of fish and fish<br />
products. Analyst 104, 434. –6.APHA(1985): Standard methods for the examination<br />
of dairy products. 14 th Ed. American Public Association, Washington D.C. –7.APHA<br />
(1992): “Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods”, 2 nd<br />
ed., American Public Health Association,<br />
Washington D.C. –8.BALDWIN,<br />
E.A., NISPEROS,M.O., HAGENMAIER,R.D.,<br />
and BAKER,R.A. (1997): Use of lipids<br />
in coatings for food products. Food<br />
Technol. 51, 56–64. –9.BARAKAT,<br />
S.M., KOJI,Y., KAZUO,M., SHIN,I., CHANG,<br />
D., and TETSUYA,S.(2004): Bacterial<br />
microflora of carp (Cyprinus carpio )<br />
and its shelf-life extension by<br />
essential oil compounds. Food<br />
Microbiol. 21,657–666. –10. BINDU,<br />
J., GINSON,J., KAMALAKANTHA,C.K.,<br />
ASHA,K.K. and SRINIVASA GOPAL,T.K.<br />
(2013): Physico-chemical changes<br />
in high pressure treated Indian<br />
white prawn (Fenneropenaeus<br />
indicus)during chill storage. Innov.<br />
Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 17,<br />
37–42. –11. BINSI,P.K., RAVISHANKAR,<br />
C.N., MATHEW,S.S., ATHIRA,V.P., BIJI,<br />
K.B., JOSHY,C.G., and GOPAL,T.K.S.<br />
(2016): Comparative evaluation of<br />
natural antioxidant coating and<br />
vacuum-packaging technique on<br />
quality characteristics of chill<br />
stored giant trevallyfillets. J.<br />
Aquatic Food Prod. Technol. 25,<br />
Sensory: Flavor<br />
197–209. –12. BOUTEKEDJIRET,C., BENTAHAR,F., BELABBES,R., and BESSIERE,J.M. (2003):<br />
Extraction of rosemary essential oil by steam distillation and hydrodistillation.<br />
Flavour Frag. J. 18,481–484. –13. BOZIN,B., MIMICA-DUKIC,N., SAMOJLIK,I., and JOVIN,E.<br />
(2007): Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of rosemary and sage (Rosmarinus<br />
officinalis L. and Salvia officinalis L., Lamiaceae) essential oils. JAgric.Food Chem.<br />
55, 7879–7885. –14. BURT,S.(2004): Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties<br />
and potential applications in foods-A review. Inter.J.Food Microbiol. 94, 223–253.<br />
–15. CAGRI,A., USTUNOL,Z., and RYSER,E.(2004): Antimicrobial edible films and coatings.<br />
J. Food Prot. 67, 833–838. –16. CHA,D.S., and CHINNAN,M.S. (2004): Biopolymerbased<br />
antimicrobial packaging: areview. Crit Rev.Food Sci. Nutr.44, 223–237.–17.<br />
COLBY,J., ENRIQUEZ-IBARRA,L., and FLICK,J.(1993): Shelf life of fish and shellfish. In<br />
Shelf Life Studies of Foods and Beverages, G. Charalambous ed), 85–143, Elsevier,<br />
Amsterdam. –18. CONNELL,J.J. (1990): Methodsofassessing and selecting for<br />
quality.InControl of fish quality, 3rd ed. Oxford: Fishing News Books, 122–150. –19.<br />
CUTTER,C.N. (2000): Antimicrobial effect of herb extracts against Esherichia coli<br />
O157:H7, Listeria monocytogenes ,and Salmonella Typhimurium associated with<br />
beef. J. Food Prot. 63, 601–607. –20. DEBEVERE,J., and BOSKOU,G.(1996): Effect of<br />
modified atmosphere packaging on the TVB/TMA producing microflora of cod<br />
fillets. Inter.J.Food Microbiol. 31, 22–229. –21. EEC (1995): Totalvolatile basic<br />
nitrogen (TVB-N) limit values for certain categories of fishery products and specifying<br />
the analysis methods to be used. Commission Decision 95/149/EEC of<br />
8March 1995. Official Journal of European Communities, L97, 84–87.–22. FERNAN-<br />
DEZ,J., PEREZ-ALVAREZ,J., and FERNANDEZ-LOPEZ,J.(1997): Thiobarbituric acid test for<br />
monitoring lipid oxidation in meat. Food Chem. 59, 345–353. –23. Food and Drug<br />
Administration (FDA) (1997): Irradiation in the production, processing and handling<br />
of food. Fed. Regist. 62, 64107–64121.–24. GARRIDO,M.D., HERNÁNDEZ,M.D., ESPINOSA,<br />
M.C., LÓPEZ,M.B. (2016) Enhanced quality characteristics of refrigerated seabream<br />
(Sparus aurata )fillets packed under different systems (Modified Atmosphere vs.<br />
Vacuum) 25, 156–168. –25. GOULAS,A.E., and KONTOMINAS,M.G. (2007): Combined<br />
effect of light salting, modified atmosphere packaging and oregano essential oil<br />
on the shelf-life of sea bream (Sparus aurata ): Biochemical and sensory attributes.<br />
Food Chem. 100, 287–296. –26. GOULD,G.W. (1996): Industry perspectives on the<br />
use of natural antimicrobials and inhibitors for food applications. J. Food Prot.,<br />
82–86. –27. HAMMAD,A.A.I., EL-MONGY,T.M., and MABROUK,A.K. (2000): Shelf-life extension<br />
and improvement of the microbiological quality of fresh sausage by irradiation.<br />
Egypt. J. Rad. Sci. Appl. Sci 13,57. –28. HE,Q., and XIAO,K.(2016): The effects<br />
of tangerine peel (Citri reticulatae pericarpium )essential oils as glazing layer on<br />
freshness preservation of bream (Megalobrama amblycephala )during superchilling<br />
storage. Food Cont. 69, 339–345. –29. HUANG,S., LIU,B., GE,D., and DAI,J.(2017):<br />
Tab. 3b: Changes in flavor of SFF as affected by combined treatments of γirradiation<br />
with coating containing RO during cold storage<br />
Storage<br />
period<br />
(day)<br />
Flavor<br />
Control Edible coating Coating containing RO combined with γirradiation<br />
0kGy 1kGy 3kGy 5kGy<br />
0 9.4 Aa ±0.26 9.4 Aa ±0.24 9.4 Aa ±0.25 9.3 Aa ±0.18 9.2 Ba ±0.46 9.3 Aa ±0.24<br />
3 9.2 Bb ±0.37 9.4 Aa ±0.24 9.4 Aa ±0.37 9.3 Aa ±0.19 9.2 Ba ±0.23 9.3 Aa ±0.29<br />
6 9.2 Bb ±0.23 9.3 Aa ±0.37 9.4 Aa ±0.23 9.3 Aa ±0.28 9.2 Ba ±0.19 9.3 Aa ±0.14<br />
9 3.3 Dc ±0.29 R 9.1 Cb ±0.29 9.4 Aa ±0.29 9.3 Aa ±0.34 9.2 Ca ±0.41 9.3 Aa ±0.35<br />
12 4.2 Cc ±0.24 R 8.5 Aa ±0.27 9.1 Ba ±0.36 9.1 Ba ±0.29 9.2 Aa ±0.24<br />
15 3.2 Ba ±0.46 R 8.6 Aa ±0.41 9.1 Aa ±0.37 9.2 Aa ±0.18<br />
18 3.5 Cb ±0.28 R 9.1 Aa ±0.41 9.1 Ab ±0.46<br />
21 8.6 Ac ±0.16 R 9.1 Ab ±0.28<br />
24 9.1 Ab ±0.41<br />
27 8.6 d ±0.24 R<br />
Capital and small letters were used for comparing between means in the columns and rows, respectively. Means with the same letters are<br />
not significantlydifferent (p>0.05). R= Rejected<br />
Source: ABD EL-DAIEM andHassanien <strong>FLEISCHWIRTSCHAFT</strong> <strong>international</strong> 2_<strong>2018</strong>