Getting started with IoT
IoT is here and it's time for organisations across the country to take advantage of the transformational benefits of the technologies and expertise available. CENSIS explores IoT for business growth in this IoT starter guide. censis.org.uk
IoT is here and it's time for organisations across the country to take advantage of the transformational benefits of the technologies and expertise available. CENSIS explores IoT for business growth in this IoT starter guide. censis.org.uk
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
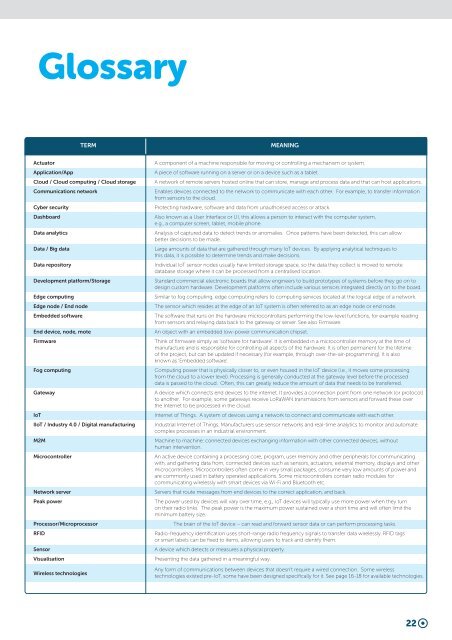
Glossary<br />
TERM<br />
MEANING<br />
Actuator<br />
Application/App<br />
Cloud / Cloud computing / Cloud storage<br />
Communications network<br />
Cyber security<br />
Dashboard<br />
Data analytics<br />
Data / Big data<br />
Data repository<br />
Development platform/Storage<br />
Edge computing<br />
Edge node / End node<br />
Embedded software<br />
End device, node, mote<br />
Firmware<br />
Fog computing<br />
Gateway<br />
<strong>IoT</strong><br />
I<strong>IoT</strong> / Industry 4.0 / Digital manufacturing<br />
M2M<br />
Microcontroller<br />
Network server<br />
Peak power<br />
Processor/Microprocessor<br />
RFID<br />
Sensor<br />
Visualisation<br />
Wireless technologies<br />
A component of a machine responsible for moving or controlling a mechanism or system.<br />
A piece of software running on a server or on a device such as a tablet.<br />
A network of remote servers hosted online that can store, manage and process data and that can host applications.<br />
Enables devices connected to the network to communicate <strong>with</strong> each other. For example, to transfer information<br />
from sensors to the cloud.<br />
Protecting hardware, software and data from unauthorised access or attack.<br />
Also known as a User Interface or UI, this allows a person to interact <strong>with</strong> the computer system,<br />
e.g., a computer screen, tablet, mobile phone.<br />
Analysis of captured data to detect trends or anomalies. Once patterns have been detected, this can allow<br />
better decisions to be made.<br />
Large amounts of data that are gathered through many <strong>IoT</strong> devices. By applying analytical techniques to<br />
this data, it is possible to determine trends and make decisions.<br />
Individual <strong>IoT</strong> sensor nodes usually have limited storage space, so the data they collect is moved to remote<br />
database storage where it can be processed from a centralised location.<br />
Standard commercial electronic boards that allow engineers to build prototypes of systems before they go on to<br />
design custom hardware. Development platforms often include various sensors integrated directly on to the board.<br />
Similar to fog computing, edge computing refers to computing services located at the logical edge of a network.<br />
The sensor which resides at the edge of an <strong>IoT</strong> system is often referred to as an edge node or end node.<br />
The software that runs on the hardware microcontrollers performing the low-level functions, for example reading<br />
from sensors and relaying data back to the gateway or server. See also Firmware.<br />
An object <strong>with</strong> an embedded low-power communication chipset.<br />
Think of firmware simply as ‘software for hardware’. It is embedded in a microcontroller memory at the time of<br />
manufacture and is responsible for controlling all aspects of the hardware. It is often permanent for the lifetime<br />
of the project, but can be updated if necessary (for example, through over-the-air-programming). It is also<br />
known as ‘Embedded software’.<br />
Computing power that is physically closer to, or even housed in the <strong>IoT</strong> device (i.e., it moves some processing<br />
from the cloud to a lower level). Processing is generally conducted at the gateway level before the processed<br />
data is passed to the cloud. Often, this can greatly reduce the amount of data that needs to be transferred.<br />
A device which connects end devices to the internet. It provides a connection point from one network (or protocol)<br />
to another. For example, some gateways receive LoRaWAN transmissions from sensors and forward these over<br />
the Internet to be processed in the cloud.<br />
Internet of Things. A system of devices using a network to connect and communicate <strong>with</strong> each other.<br />
Industrial Internet of Things. Manufacturers use sensor networks and real-time analytics to monitor and automate<br />
complex processes in an industrial environment.<br />
Machine to machine: connected devices exchanging information <strong>with</strong> other connected devices, <strong>with</strong>out<br />
human intervention.<br />
An active device containing a processing core, program, user memory and other peripherals for communicating<br />
<strong>with</strong>, and gathering data from, connected devices such as sensors, actuators, external memory, displays and other<br />
microcontrollers. Microcontrollers often come in very small packages, consume very low amounts of power and<br />
are commonly used in battery operated applications. Some microcontrollers contain radio modules for<br />
communicating wirelessly <strong>with</strong> smart devices via Wi-Fi and Bluetooth etc.<br />
Servers that route messages from end devices to the correct application, and back.<br />
The power used by devices will vary over time, e.g., <strong>IoT</strong> devices will typically use more power when they turn<br />
on their radio links. The peak power is the maximum power sustained over a short time and will often limit the<br />
minimum battery size.<br />
The brain of the <strong>IoT</strong> device – can read and forward sensor data or can perform processing tasks.<br />
Radio-frequency identification uses short-range radio frequency signals to transfer data wirelessly. RFID tags<br />
or smart labels can be fixed to items, allowing users to track and identify them.<br />
A device which detects or measures a physical property.<br />
Presenting the data gathered in a meaningful way.<br />
Any form of communications between devices that doesn’t require a wired connection. Some wireless<br />
technologies existed pre-<strong>IoT</strong>, some have been designed specifically for it. See page 16-18 for available technologies.<br />
22