Leadership in Organizations
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
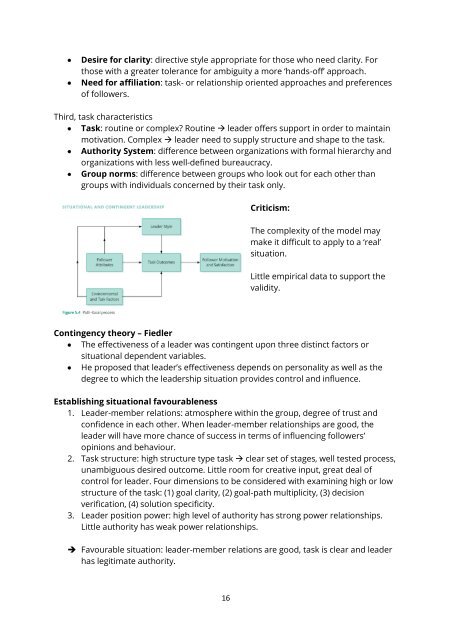
• Desire for clarity: directive style appropriate for those who need clarity. For<br />
those with a greater tolerance for ambiguity a more ‘hands-off’ approach.<br />
• Need for affiliation: task- or relationship oriented approaches and preferences<br />
of followers.<br />
Third, task characteristics<br />
• Task: rout<strong>in</strong>e or complex? Rout<strong>in</strong>e → leader offers support <strong>in</strong> order to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><br />
motivation. Complex → leader need to supply structure and shape to the task.<br />
• Authority System: difference between organizations with formal hierarchy and<br />
organizations with less well-def<strong>in</strong>ed bureaucracy.<br />
• Group norms: difference between groups who look out for each other than<br />
groups with <strong>in</strong>dividuals concerned by their task only.<br />
Criticism:<br />
The complexity of the model may<br />
make it difficult to apply to a ‘real’<br />
situation.<br />
Little empirical data to support the<br />
validity.<br />
Cont<strong>in</strong>gency theory – Fiedler<br />
• The effectiveness of a leader was cont<strong>in</strong>gent upon three dist<strong>in</strong>ct factors or<br />
situational dependent variables.<br />
• He proposed that leader’s effectiveness depends on personality as well as the<br />
degree to which the leadership situation provides control and <strong>in</strong>fluence.<br />
Establish<strong>in</strong>g situational favourableness<br />
1. Leader-member relations: atmosphere with<strong>in</strong> the group, degree of trust and<br />
confidence <strong>in</strong> each other. When leader-member relationships are good, the<br />
leader will have more chance of success <strong>in</strong> terms of <strong>in</strong>fluenc<strong>in</strong>g followers’<br />
op<strong>in</strong>ions and behaviour.<br />
2. Task structure: high structure type task → clear set of stages, well tested process,<br />
unambiguous desired outcome. Little room for creative <strong>in</strong>put, great deal of<br />
control for leader. Four dimensions to be considered with exam<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g high or low<br />
structure of the task: (1) goal clarity, (2) goal-path multiplicity, (3) decision<br />
verification, (4) solution specificity.<br />
3. Leader position power: high level of authority has strong power relationships.<br />
Little authority has weak power relationships.<br />
➔ Favourable situation: leader-member relations are good, task is clear and leader<br />
has legitimate authority.<br />
16