- Page 2:
SPECIALTY CUT FLOWERS
- Page 5 and 6:
Photographs by Allan M. Armitage un
- Page 7 and 8:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 9 and 10:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 11 and 12:
10 PREFACE and eggplant would be co
- Page 13 and 14:
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The information con
- Page 15 and 16:
14 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Ed Pincus, Third
- Page 17 and 18:
16 INTRODUCTION increase if they ar
- Page 19 and 20:
18 INTRODUCTION market outlets. Spe
- Page 21 and 22:
POSTHARVEST CARE Whether flowers ar
- Page 23 and 24:
22 POSTHARVEST CARE later in this s
- Page 25 and 26:
24 POSTHARVEST CARE dangerously hig
- Page 27 and 28:
26 POSTHARVEST CARE Aquilegia hybri
- Page 29 and 30:
28 POSTHARVEST CARE extends vase li
- Page 31 and 32:
DRYING AND PRESERVING Dried flowers
- Page 33 and 34:
32 DRYING AND PRESERVING longer to
- Page 35 and 36:
34 DRYING AND PRESERVING freeze-dry
- Page 37 and 38:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 39 and 40:
38 ACHILLEA ‘CORONATION GOLD’ P
- Page 41 and 42:
40 ACHILLEA FILIPENDULINA Stage of
- Page 43 and 44:
42 ACHILLEA MILLEFOLIUM AND HYBRIDS
- Page 45 and 46:
44 ACHILLEA MILLEFOLIUM AND HYBRIDS
- Page 47 and 48:
46 ACHILLEA MILLEFOLIUM AND HYBRIDS
- Page 49 and 50:
48 ACHILLEA MILLEFOLIUM AND HYBRIDS
- Page 51 and 52:
50 ACHILLEA PTARMICA Environmental
- Page 53 and 54:
52 ACONITUM Reading Armitage, A. M.
- Page 55 and 56:
54 ACONITUM A cold period of 32-35F
- Page 57 and 58:
56 ACONITUM Variety’ and ‘Kelms
- Page 59 and 60:
58 AGASTACHE FOENICULUM Agastache f
- Page 61 and 62:
60 AGERATUM HOUSTONIANUM ‘Apricot
- Page 63 and 64:
62 AGERATUM HOUSTONIANUM but if acc
- Page 65 and 66:
64 AGERATUM HOUSTONIANUM Pests and
- Page 67 and 68:
66 AGROSTEMMA GITHAGO 12-hour day m
- Page 69 and 70:
68 ALLIUM Grower Comments “Spacin
- Page 71 and 72:
Allium christophii
- Page 73 and 74:
72 ALLIUM GIGANTEUM Field Performan
- Page 75 and 76:
Allium sphaerocephalon
- Page 77 and 78:
76 ALLIUM SPHAEROCEPHALON Allium at
- Page 79 and 80:
78 ALSTROEMERIA Alstroemeria Peruvi
- Page 81 and 82:
80 ALSTROEMERIA Photoperiod: Long d
- Page 83 and 84:
82 ALSTROEMERIA Cultivars Most of t
- Page 85 and 86:
84 AMARANTHUS CAUDATUS Propagation
- Page 87 and 88:
86 AMARANTHUS CAUDATUS of 8-10 hour
- Page 89 and 90:
88 AMARANTHUS CAUDATUS ‘Flaming F
- Page 91 and 92:
90 AMMI MAJUS Harvesting of Ammi ma
- Page 93 and 94:
92 AMMI MAJUS Cultivars ‘Queen of
- Page 95 and 96:
Anemone ‘De Caen White’ and ‘
- Page 97 and 98:
96 ANEMONE CORONARIA The effect of
- Page 99 and 100:
98 ANEMONE CORONARIA Mona Lisa Grou
- Page 101 and 102:
Antirrhinum majus ‘Potomac Yellow
- Page 103 and 104:
102 ANTIRRHINUM MAJUS Field Perform
- Page 105 and 106:
104 ANTIRRHINUM MAJUS light intensi
- Page 107 and 108:
106 ANTIRRHINUM MAJUS Pests and Dis
- Page 109 and 110: 108 ARTEMISIA Reid, M., M. Cantwell
- Page 111 and 112: 110 ARTEMISIA LUDOVICIANA Stage of
- Page 113 and 114: 112 ASCLEPIAS TUBEROSA Asclepias tu
- Page 115 and 116: 114 ASCLEPIAS TUBEROSA Field Perfor
- Page 117 and 118: 116 ASTER Wilt is caused by Pythium
- Page 119 and 120: 118 ASTER Propagation Most cultivar
- Page 121 and 122: 120 ASTER Pinching: Plants may be p
- Page 123 and 124: 122 ASTER used for late spring and
- Page 125 and 126: 124 ASTER Stage of Harvest Cut stem
- Page 127 and 128: 126 ASTER ‘Winston Churchill’ w
- Page 129 and 130: 128 ASTILBE ×ARENDSII Leaf nematod
- Page 131 and 132: 130 ASTILBE ×ARENDSII forced at 65
- Page 133 and 134: 132 ASTILBE ×ARENDSII Cultivar Pla
- Page 135 and 136: 134 ASTRANTIA MAJOR Reading Beattie
- Page 137 and 138: 136 ASTRANTIA MAJOR nitrogen result
- Page 139 and 140: 138 BAPTISIA AUSTRALIS Vaughan, M.
- Page 141 and 142: 140 BAPTISIA AUSTRALIS Germination
- Page 143 and 144: 142 BUDDLEIA DAVIDII plants ‘last
- Page 145 and 146: 144 BUDDLEIA DAVIDII Stage of Harve
- Page 147 and 148: 146 BUDDLEIA DAVIDII Additional Spe
- Page 149 and 150: 148 CALLICARPA Seed: Seed should be
- Page 151 and 152: 150 CALLICARPA ing. The fruit falls
- Page 153 and 154: 152 CALLISTEPHUS CHINENSIS Calliste
- Page 155 and 156: 154 CALLISTEPHUS CHINENSIS in the f
- Page 157 and 158: 156 CALLISTEPHUS CHINENSIS Dried: H
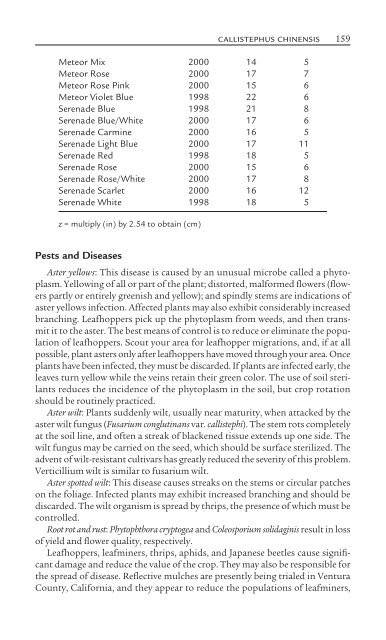
- Page 159: 158 CALLISTEPHUS CHINENSIS in trial
- Page 163 and 164: 162 CAMPANULA Temperature: All pere
- Page 165 and 166: 164 CAMPANULA ‘Moerheimii’ bear
- Page 167 and 168: 166 CARTHAMUS TINCTORIUS Wiel, A. v
- Page 169 and 170: 168 CARTHAMUS TINCTORIUS Greenhouse
- Page 171 and 172: 170 CARYOPTERIS ×CLANDONENSIS Fiel
- Page 173 and 174: 172 CARYOPTERIS INCANA Propagation
- Page 175 and 176: 174 CARYOPTERIS INCANA in the “re
- Page 177 and 178: 176 CELOSIA ARGENTEA flower heads m
- Page 179 and 180: 178 CELOSIA ARGENTEA Harvesting: Fl
- Page 181 and 182: 180 CELOSIA ARGENTEA Cultivars Chil
- Page 183 and 184: 182 CELOSIA ARGENTEA Year of Stem S
- Page 185 and 186: 184 CENTAUREA AMERICANA, C. CYANUS,
- Page 187 and 188: 186 CENTAUREA AMERICANA, C. CYANUS,
- Page 189 and 190: 188 CENTAUREA MACROCEPHALA Florence
- Page 191 and 192: 190 CENTAUREA MACROCEPHALA Environm
- Page 193 and 194: 192 CENTRANTHUS RUBER Laurie, A., a
- Page 195 and 196: 194 CIRSIUM JAPONICUM Pests and Dis
- Page 197 and 198: 196 CIRSIUM JAPONICUM Environmental
- Page 199 and 200: 198 CLARKIA Nau, J. 1999. Ball Cult
- Page 201 and 202: 200 CLARKIA (60 cm) centers, depend
- Page 203 and 204: 202 CLARKIA Postharvest Fresh: In w
- Page 205 and 206: 204 CONSOLIDA plants come and go. C
- Page 207 and 208: 206 CONSOLIDA (21C). The elongation
- Page 209 and 210: 208 CONSOLIDA stem for fresh flower
- Page 211 and 212:
210 CONSOLIDA root bound, so as soo
- Page 213 and 214:
212 COREOPSIS, RUDBECKIA, LEUCANTHE
- Page 215 and 216:
214 COREOPSIS, RUDBECKIA, LEUCANTHE
- Page 217 and 218:
216 CORNUS people ask when it will
- Page 219 and 220:
218 CORNUS FLORIDA A few cultivars
- Page 221 and 222:
220 COSMOS BIPINNATUS Additional Sp
- Page 223 and 224:
222 COSMOS BIPINNATUS Propagation S
- Page 225 and 226:
224 COSMOS BIPINNATUS Greenhouse Pe
- Page 227 and 228:
226 COSMOS BIPINNATUS Greenhouse st
- Page 229 and 230:
228 CROCOSMIA HYBRIDS although that
- Page 231 and 232:
230 CROCOSMIA HYBRIDS Corms did not
- Page 233 and 234:
232 DAHLIA HYBRIDS Reading Armitage
- Page 235 and 236:
234 DAHLIA HYBRIDS Growing-on Trans
- Page 237 and 238:
236 DAHLIA HYBRIDS Pinching: As wit
- Page 239 and 240:
238 DELPHINIUM HYBRIDS Moser, B. C.
- Page 241 and 242:
240 DELPHINIUM HYBRIDS moved outdoo
- Page 243 and 244:
242 DELPHINIUM HYBRIDS sulphate, if
- Page 245 and 246:
244 DELPHINIUM HYBRIDS Phoma xanthi
- Page 247 and 248:
246 DIANTHUS BARBATUS can be vernal
- Page 249 and 250:
248 DIANTHUS BARBATUS ‘Hollandia
- Page 251 and 252:
250 DIGITALIS PURPUREA Grower Comme
- Page 253 and 254:
252 DIGITALIS PURPUREA greenhouse o
- Page 255 and 256:
254 ECHINACEA PURPUREA the next Jun
- Page 257 and 258:
256 ECHINACEA PURPUREA Propagation
- Page 259 and 260:
258 ECHINACEA PURPUREA ‘Bravado
- Page 261 and 262:
260 ECHINOPS BANNATICUS Propagation
- Page 263 and 264:
262 ECHINOPS BANNATICUS Shelley McG
- Page 265 and 266:
264 EMILIA JAVANICA Emilia javanica
- Page 267 and 268:
266 EREMURUS all sides. The inflore
- Page 269 and 270:
268 EREMURUS dried out, soak them f
- Page 271 and 272:
270 ERYNGIUM PLANUM placed in the s
- Page 273 and 274:
272 ERYNGIUM PLANUM are guidelines
- Page 275 and 276:
Eryngium alpinum
- Page 277 and 278:
276 EUPHORBIA MARGINATA Growth of E
- Page 279 and 280:
278 EUPHORBIA MARGINATA hour photop
- Page 281 and 282:
280 EUSTOMA GRANDIFLORUM Eustoma gr
- Page 283 and 284:
282 EUSTOMA GRANDIFLORUM Field Perf
- Page 285 and 286:
284 EUSTOMA GRANDIFLORUM problems.
- Page 287 and 288:
286 EUSTOMA GRANDIFLORUM mately 2'
- Page 289 and 290:
288 EUSTOMA GRANDIFLORUM Reading Al
- Page 291 and 292:
290 FREESIA ×HYBRIDA Freesia ×hyb
- Page 293 and 294:
292 FREESIA ×HYBRIDA Stage of Harv
- Page 295 and 296:
294 GLADIOLUS CALLIANTHUS per corm,
- Page 297 and 298:
296 GLADIOLUS CALLIANTHUS Postharve
- Page 299 and 300:
Gladiolus hybrid
- Page 301 and 302:
300 GLADIOLUS HYBRIDS 29C) for 10-1
- Page 303 and 304:
302 GLADIOLUS HYBRIDS drained and s
- Page 305 and 306:
304 GOMPHRENA GLOBOSA comments of o
- Page 307 and 308:
306 GOMPHRENA GLOBOSA Temperature:
- Page 309 and 310:
308 GOMPHRENA GLOBOSA Additional Sp
- Page 311 and 312:
310 GONIOLIMON TATARICUM ers, where
- Page 313 and 314:
312 GYPSOPHILA PANICULATA Reading H
- Page 315 and 316:
314 GYPSOPHILA PANICULATA Rooted cu
- Page 317 and 318:
316 GYPSOPHILA PANICULATA ‘Bristo
- Page 319 and 320:
318 GYPSOPHILA PANICULATA Additiona
- Page 321 and 322:
Helianthus annuus ‘Sunrich Orange
- Page 323 and 324:
322 HELIANTHUS ANNUUS strong to car
- Page 325 and 326:
324 HELIANTHUS ANNUUS been trialed
- Page 327 and 328:
326 HELIANTHUS ANNUUS ‘Red Treasu
- Page 329 and 330:
328 HELIANTHUS ANNUUS Additional Sp
- Page 331 and 332:
330 HELIANTHUS ANNUUS “The ‘Sun
- Page 333 and 334:
332 HELICHRYSUM BRACTEATUM Growing-
- Page 335 and 336:
334 HELICHRYSUM BRACTEATUM Cultivar
- Page 337 and 338:
336 HELLEBORUS ORIENTALIS Helleboru
- Page 339 and 340:
338 HELLEBORUS ORIENTALIS Stage of
- Page 341 and 342:
340 HYDRANGEA MACROPHYLLA Hydrangea
- Page 343 and 344:
342 HYDRANGEA MACROPHYLLA Shade: Hy
- Page 345 and 346:
344 HYDRANGEA MACROPHYLLA ‘Nikko
- Page 347 and 348:
346 HYDRANGEA MACROPHYLLA Hydrangea
- Page 349 and 350:
348 HYPERICUM Pinching: Plants shou
- Page 351 and 352:
350 ILEX Ilex deciduous holly Aquif
- Page 353 and 354:
352 ILEX “gatherers,” with thei
- Page 355 and 356:
354 IRIS use a method similar to th
- Page 357 and 358:
356 IRIS XIPHIUM Iris xiphium group
- Page 359 and 360:
358 IRIS XIPHIUM weeks of 48F (9C).
- Page 361 and 362:
360 IRIS XIPHIUM Ideal Group 50-60
- Page 363 and 364:
362 IRIS XIPHIUM Max. Plant Bulb gr
- Page 365 and 366:
364 LATHYRUS ODORATUS taken them to
- Page 367 and 368:
366 LATHYRUS ODORATUS If sowing in
- Page 369 and 370:
368 LATHYRUS ODORATUS Houck fertili
- Page 371 and 372:
370 LAVATERA TRIMESTRIS Propagation
- Page 373 and 374:
372 LAVATERA TRIMESTRIS ‘Loveline
- Page 375 and 376:
374 LIATRIS SPICATA Liatris spicata
- Page 377 and 378:
376 LIATRIS SPICATA Three weeks’
- Page 379 and 380:
378 LIATRIS SPICATA Additional Spec
- Page 381 and 382:
380 LILIUM HYBRIDS Zieslin, N. 1985
- Page 383 and 384:
382 LILIUM HYBRIDS Growing-on Bulbs
- Page 385 and 386:
384 LILIUM HYBRIDS peratures, the p
- Page 387 and 388:
386 LILIUM HYBRIDS Lilium formosanu
- Page 389 and 390:
388 LIMONIUM HYBRIDS species are us
- Page 391 and 392:
390 LIMONIUM PEREZII Environmental
- Page 393 and 394:
Limonium sinuatum ‘Sunset Blue’
- Page 395 and 396:
394 LIMONIUM SINUATUM The effect of
- Page 397 and 398:
396 LIMONIUM SINUATUM Stem quality:
- Page 399 and 400:
398 LIMONIUM SINUATUM New Wonder se
- Page 401 and 402:
400 LIMONIUM TETRAGONUM a lot of my
- Page 403 and 404:
402 LIMONIUM TETRAGONUM of flower b
- Page 405 and 406:
404 LOBELIA Lobelia Campanulaceae a
- Page 407 and 408:
406 LOBELIA ‘Russian Princess’
- Page 409 and 410:
408 LOBELIA field or 4" (10 cm) con
- Page 411 and 412:
410 LYSIMACHIA CLETHROIDES Reading
- Page 413 and 414:
412 LYSIMACHIA CLETHROIDES Two-year
- Page 415 and 416:
Greenhouse schedules for Lysimachia
- Page 417 and 418:
416 MATTHIOLA INCANA ally seen in n
- Page 419 and 420:
418 MATTHIOLA INCANA The effect of
- Page 421 and 422:
420 MATTHIOLA INCANA Approximately
- Page 423 and 424:
422 MATTHIOLA INCANA Vegmo series o
- Page 425 and 426:
424 NARCISSUS Post, K. 1942. Effect
- Page 427 and 428:
426 NARCISSUS Planting time: In cli
- Page 429 and 430:
428 NIGELLA DAMASCENA veins. The di
- Page 431 and 432:
430 NIGELLA DAMASCENA Environmental
- Page 433 and 434:
432 ORNITHOGALUM ARABICUM Nigella s
- Page 435 and 436:
434 ORNITHOGALUM ARABICUM temperatu
- Page 437 and 438:
436 ORNITHOGALUM ARABICUM Storage:
- Page 439 and 440:
Paeonia ‘Bowl of Beauty’ (Japan
- Page 441 and 442:
440 PAEONIA HYBRIDS Garden Flowers
- Page 443 and 444:
442 PAEONIA HYBRIDS sistently produ
- Page 445 and 446:
444 PAEONIA HYBRIDS Cultivars Many
- Page 447 and 448:
446 PAEONIA HYBRIDS dwarfed. Dwarfi
- Page 449 and 450:
448 PAPAVER NUDICAULE container can
- Page 451 and 452:
450 PAPAVER NUDICAULE Papaver somni
- Page 453 and 454:
452 PHLOX PANICULATA Phlox panicula
- Page 455 and 456:
454 PHLOX PANICULATA Field Performa
- Page 457 and 458:
456 PHLOX PANICULATA Purple, lavend
- Page 459 and 460:
458 PHYSALIS ALKEKENGI Growing-on P
- Page 461 and 462:
460 PHYSOSTEGIA VIRGINIANA Physoste
- Page 463 and 464:
462 PHYSOSTEGIA VIRGINIANA LD plant
- Page 465 and 466:
464 PHYSOSTEGIA VIRGINIANA day/nigh
- Page 467 and 468:
466 PLATYCODON GRANDIFLORUS Kelly,
- Page 469 and 470:
468 PLATYCODON GRANDIFLORUS pot cul
- Page 471 and 472:
470 POLIANTHES TUBEROSA Song, C. Y.
- Page 473 and 474:
472 POLIANTHES TUBEROSA however, wa
- Page 475 and 476:
474 POLIANTHES TUBEROSA The effect
- Page 477 and 478:
Ranunculus asiaticus ‘Tecolote’
- Page 479 and 480:
478 RANUNCULUS ASIATICUS As Mike Me
- Page 481 and 482:
480 SALIX Horovitz, A. 1985. Ranunc
- Page 483 and 484:
Salix chaenomeloides
- Page 485 and 486:
484 SALVIA Reading Dirr, M. A. 1998
- Page 487 and 488:
486 SALVIA LEUCANTHA date. This can
- Page 489 and 490:
488 SALVIA LEUCANTHA wide with deep
- Page 491 and 492:
490 SCABIOSA ATROPURPUREA Ore., pla
- Page 493 and 494:
492 SCABIOSA CAUCASICA Scabiosa cau
- Page 495 and 496:
494 SCABIOSA CAUCASICA Forcing: Fie
- Page 497 and 498:
496 SOLIDAGO HYBRIDS, ×SOLIDASTER
- Page 499 and 500:
498 SOLIDAGO HYBRIDS, ×SOLIDASTER
- Page 501 and 502:
500 SOLIDAGO HYBRIDS, ×SOLIDASTER
- Page 503 and 504:
502 SOLIDAGO HYBRIDS, ×SOLIDASTER
- Page 505 and 506:
504 THALICTRUM Thalictrum delavayi
- Page 507 and 508:
506 THALICTRUM mately 18 months. Cr
- Page 509 and 510:
508 TRACHELIUM CAERULEUM ters consi
- Page 511 and 512:
510 TRACHELIUM CAERULEUM Overwinter
- Page 513 and 514:
512 TRACHELIUM CAERULEUM ‘Merii B
- Page 515 and 516:
514 TRITELEIA Planting time: Corms
- Page 517 and 518:
516 TULIPA De Hertogh, A. A. 1996.
- Page 519 and 520:
518 TULIPA Field Performance Bulb s
- Page 521 and 522:
520 TULIPA significant differences
- Page 523 and 524:
522 TWEEDIA CAERULEA Many thanks to
- Page 525 and 526:
524 TWEEDIA CAERULEA Light: High li
- Page 527 and 528:
526 VERBENA BONARIENSIS Two to 3" (
- Page 529 and 530:
528 VERONICA Reading Nau, J. 1999.
- Page 531 and 532:
530 VERONICA field-grown plants are
- Page 533 and 534:
532 VERONICA Postharvest Fresh: Flo
- Page 535 and 536:
Veronicastrum virginicum
- Page 537 and 538:
536 ZANTEDESCHIA Shade: Shading is
- Page 539 and 540:
Zantedeschia aethiopica
- Page 541 and 542:
540 ZANTEDESCHIA eral, horns are pr
- Page 543 and 544:
542 ZANTEDESCHIA 64/61F (18/16C) da
- Page 545 and 546:
544 ZANTEDESCHIA ‘Cameo’ produc
- Page 547 and 548:
546 ZINNIA ELEGANS Post, K. 1936. F
- Page 549 and 550:
548 ZINNIA ELEGANS Postharvest Fres
- Page 551 and 552:
550 ZINNIA ELEGANS Additional Speci
- Page 553 and 554:
This page intentionally left blank
- Page 555 and 556:
554 REFERENCES A delightful book wr
- Page 557 and 558:
556 REFERENCES ber of seeds needed
- Page 559 and 560:
558 REFERENCES Excellent catalogs a
- Page 561 and 562:
560 STAGE OF HARVEST Ageratum houst
- Page 563 and 564:
562 STAGE OF HARVEST when the folli
- Page 565 and 566:
564 STAGE OF HARVEST Physalis Harve
- Page 567 and 568:
566 ADDITIONAL PLANTS SUITABLE FOR
- Page 569 and 570:
568 ADDITIONAL PLANTS SUITABLE FOR
- Page 571 and 572:
570 ADDITIONAL PLANTS SUITABLE FOR
- Page 573 and 574:
U.S.D.A. HARDINESS MAP
- Page 575 and 576:
574 INDEX OF BOTANICAL NAMES [Amara
- Page 577 and 578:
576 INDEX OF BOTANICAL NAMES [Delph
- Page 579 and 580:
578 INDEX OF BOTANICAL NAMES [Limon
- Page 581 and 582:
580 INDEX OF BOTANICAL NAMES [Trite
- Page 583 and 584:
582 INDEX OF COMMON NAMES calendula
- Page 585 and 586:
584 INDEX OF COMMON NAMES Michaelma
- Page 587:
586 INDEX OF COMMON NAMES willow 48