Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Sales Data <strong>Exchange</strong> System Specification and Implementation Guide Sections 1–6: General Information<br />
Section 4.2 File Structure to <strong>ATPCO</strong><br />
Section 4.2.1 TCN File Structure<br />
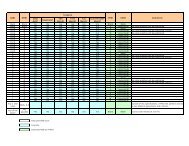
The file structure of TCN transmissions inbound to <strong>ATPCO</strong> Sales Data <strong>Exchange</strong> consists of one<br />
Transmission Header Record followed by detail ticket records.<br />
Address<br />
Transmission<br />
Header Transmission Record<br />
Header Record<br />
Detail <strong>Ticket</strong><br />
Record Detail <strong>Ticket</strong> #1<br />
Record #1<br />
Address<br />
Detail <strong>Ticket</strong><br />
Record Detail <strong>Ticket</strong> #2<br />
Record #2<br />
Address<br />
Detail <strong>Ticket</strong><br />
Record Detail <strong>Ticket</strong> #3<br />
Record #3<br />
Address<br />
Figure 4-A: Input Records into <strong>ATPCO</strong> Sales Data <strong>Exchange</strong><br />
Detail <strong>Ticket</strong><br />
Record Detail to <strong>Ticket</strong> #n<br />
Record to #n<br />
On the inbound transmission to the <strong>ATPCO</strong> Sales Data <strong>Exchange</strong> from a system provider, carrier, or<br />
ticketing system, the first record must always be the Transmission Header Record. This Transmission<br />
Header Record contains information to allow <strong>ATPCO</strong> to identify the type of data and where the data<br />
originated, and provides for additional controls.<br />
After the Transmission Header Record, the rest of the transmission can be considered a simple postal<br />
system. The system provider or the ISR/TCN Codeshare Table at <strong>ATPCO</strong> determines where the<br />
data is sent. <strong>ATPCO</strong> addresses the recipient carriers in the Address Label and attaches the ticketing<br />
data. <strong>ATPCO</strong> generates and propagates ticketing records by encoding the Address Label to codesharing<br />
and alliance partners upon instructions from the marketing carrier. An envelope is considered a complete<br />
ticketing transaction addressed to one or more addressee. <strong>ATPCO</strong>, upon receiving the envelope, reads<br />
the addressees and sends a copy of the envelope to each. The Address Label has the ability to send the<br />
envelope to up to 14 different carriers. As <strong>ATPCO</strong> retransmits the envelope, it drops the Address Label.<br />
The system provider, carrier, or ticketing system has the prime responsibility for the addressing of the<br />
Address Label. <strong>ATPCO</strong>’s codesharing service has secondary responsibility for addressing the Address<br />
Label on certain tickets, if there is proper authority from the marketing carrier (initiated by the presence of<br />
a signed TCN Codeshare and Data Agreement). The system provider, carrier, or ticketing system is<br />
responsible for identifying carriers eligible to receive the ticketing data (validating carrier, any carrier in the<br />
routing, possible codesharing or alliance carriers, and any carrier participating as the credit card vendor,<br />
or the accounting carrier). The system provider populates the 42-byte Address Label with codes of<br />
eligible carriers with whom they have a bilateral agreement and attaches the Address Label to the data in<br />
the envelope.<br />
10 November 2007