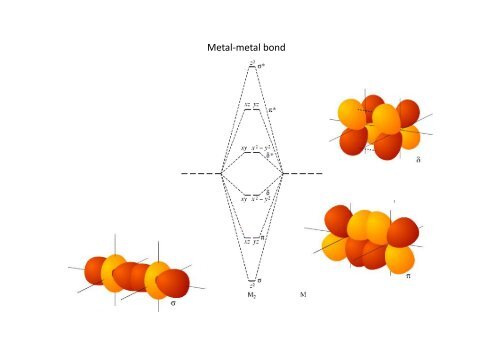
Metal-metal bond
Metal-metal bond
Metal-metal bond
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> <strong>bond</strong>
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> <strong>bond</strong>
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
M L<br />
M<br />
M L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
σ∗ σ<br />
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> <strong>bond</strong> (M 2L 8)<br />
π∗ M-M anti<strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
δ∗<br />
z d yz dxyy d xy d yz z<br />
d z 2 d z 2<br />
d xz<br />
the dx2- y2, s and px,y<br />
orbitals are not shown<br />
since they are used<br />
for M-ligand M ligand <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
δ<br />
d xz<br />
π M-M <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
σ<br />
orbitals d yz<br />
d z 2 σ<br />
d xz<br />
d xy δ<br />
the dx2- y2orbitals<br />
(not shown) are used for M-L <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
π
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> <strong>bond</strong> (M 2L 8)<br />
Electron Count Resulting M-M Bond<br />
d1 -d1 Single <strong>bond</strong><br />
d2 -d2 Double <strong>bond</strong><br />
d3 -d3 Triple <strong>bond</strong><br />
d4 -d4 Quadruple <strong>bond</strong> optimum<br />
d5 -d5 Triple <strong>bond</strong><br />
d6 -d6 Double <strong>bond</strong><br />
d7 -d7 Single <strong>bond</strong><br />
d8 - d8 No <strong>bond</strong> (symmetry interaction)<br />
H 3C CH 3<br />
H 3C<br />
Re<br />
CH 3<br />
H H3CC CH CH3 H 3C<br />
RRe<br />
CH 3<br />
2-<br />
PR3 Cl Re Cl<br />
R3P Re<br />
R 3P Cl<br />
Cl PR 3<br />
Me<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
M<br />
M<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
σ∗<br />
π∗ M-M anti<strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
δ∗<br />
dz2 dyz dxy dxy dyz dz2 dxz dxz the dx2- y2, s and px,y<br />
orbitals are not shown<br />
since they are used<br />
for M-ligand <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
Re-Re = 22.18 18 Å CCr-Cr C =1.85 1 85 Å<br />
Eclipsed conformations<br />
O<br />
δ<br />
π M-M <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
σ<br />
O<br />
Cr Cr<br />
Me<br />
4
‐2<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
M<br />
M<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
L<br />
σ∗<br />
π∗ M-M anti<strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
δ∗<br />
δ<br />
dz2 dyz dxy dxy dyz dz2 dxz dxz the dx2- y2, s and px,y<br />
orbitals are not shown<br />
since they are used<br />
for M-ligand <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
π M-M <strong>bond</strong>ing<br />
orbitals<br />
σ
p z<br />
L L<br />
M M<br />
L L<br />
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> <strong>bond</strong> d 8 case<br />
L L ‐2<br />
CNR<br />
L L<br />
σ∗<br />
σ<br />
σ∗<br />
p z<br />
d z 2 d z 2<br />
σ<br />
RNC Ir CNR<br />
RN<br />
C<br />
R R3P 3P Cl<br />
Ir<br />
NC<br />
C<br />
R<br />
NR CNR<br />
RNC Ir CNR<br />
RN<br />
C<br />
‐2<br />
‐2<br />
‐2<br />
‐2
<strong>Metal</strong>‐<strong>metal</strong> quintuple <strong>bond</strong>
Isolobal analogy<br />
http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1981/hoffman‐lecture.pdf
Isolobal analogy<br />
‐Simplification
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Isolobal analogy
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
Ligand dissociation / coordination<br />
Me Me3Al 3Al + NMe 3<br />
6e 8e<br />
Mo(CO) 6<br />
18e 16e<br />
Me Me3Al-NMe 3Al-NMe 3<br />
Mo(CO) 5 + CO
Β‐Elimination<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
‐Alkyl group with a β‐hydrogen<br />
‐Coordination vacant on the <strong>metal</strong><br />
or an easy to dissociate ligand in<br />
cis‐ position<br />
‐An empty orbital at the <strong>metal</strong><br />
‐Feasible approach of the β‐<br />
hd hydrogen to the<strong>metal</strong> h l<br />
‐A full orbital at the <strong>metal</strong>
OC<br />
Β‐Elimination<br />
OC<br />
Fe<br />
Ph 3P<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
O<br />
N<br />
Co<br />
N N<br />
H2O O O<br />
H<br />
H O<br />
N<br />
‐Alkyl group with a β‐hydrogen<br />
‐Coordination vacant on the <strong>metal</strong><br />
or an easy to dissociate ligand in<br />
cis‐ position<br />
‐An empty orbital at the <strong>metal</strong><br />
‐Feasible approach of the β‐<br />
PPh PPh3 hd hydrogen to the<strong>metal</strong> h l<br />
Pt<br />
O<br />
BF 4<br />
‐A full orbital at the <strong>metal</strong>
Β‐Elimination<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
Pb<br />
‐Alkyl group with a β‐hydrogen<br />
‐Coordination vacant on the <strong>metal</strong><br />
or an easy to dissociate ligand in<br />
cis‐ position<br />
‐An empty orbital at the <strong>metal</strong><br />
‐Feasible approach of the β‐<br />
hd hydrogen to the<strong>metal</strong> h l<br />
‐A full orbital at the <strong>metal</strong>
Β‐Elimination<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
PPh 3<br />
H3N Pd Me<br />
‐Alkyl group with a β‐hydrogen<br />
‐Coordination vacant on the <strong>metal</strong><br />
or an easy to dissociate ligand in<br />
cis‐ position<br />
‐An empty orbital at the <strong>metal</strong><br />
‐Feasible approach of the β‐<br />
hd hydrogen to the<strong>metal</strong> h l<br />
‐A full orbital at the <strong>metal</strong>
Β‐Elimination<br />
P<br />
P<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
Cl<br />
Ti<br />
Cl<br />
Agostic g<br />
interaction<br />
Cl<br />
H<br />
‐Alkyl group with a β‐hydrogen<br />
‐Coordination vacant on the <strong>metal</strong><br />
or an easy to dissociate ligand in<br />
cis‐ position<br />
‐An empty orbital at the <strong>metal</strong><br />
‐Feasible approach of the β‐<br />
hd hydrogen to the<strong>metal</strong> h l<br />
‐A full orbital at the <strong>metal</strong>
Β‐Elimination<br />
Cr<br />
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
OC<br />
WMe 6<br />
H<br />
Ir<br />
Ph 3P<br />
Au<br />
N<br />
N<br />
Fe
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
Migratory i iinsertion/Elimination i /lii i
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
Reallya ll migration i i or an iinsertion? i ?
Elementary steps in organo<strong>metal</strong>lic chemistry<br />
‐Two oxidation steps separated by two units are necessary.<br />
‐For the oxidative addition a full and an empty orbitals on the <strong>metal</strong> are required. It is<br />
favored by strong donating ligands (R‐X compounds are good sustrates)<br />
‐Reductive elimination is favored by π‐acceptor, high oxidation states and bulky<br />
lligands d ( (R‐R, R‐H and d R‐CHO groups are easily l eliminated)<br />
l d)
Heck reaction
Olefin reduction
Hydroformylation