- Page 1: NUTRITION IN SPORT VOLUME VII OF TH
- Page 4 and 5: IOC MEDICAL COMMISSION SUB-COMMISSI
- Page 6 and 7: © 2000 by Blackwell Science Ltd Ed
- Page 8 and 9: vi contents 18 Gastrointestinal Fun
- Page 11 and 12: List of Contributors K.P. AULINMD,
- Page 13: Quaker Oats Company, 617 West Main
- Page 17 and 18: Preface At an international Consens
- Page 19: PART 1 NUTRITION AND EXERCISE
- Page 22 and 23: 4 nutrition and exercise Table 1.1
- Page 24 and 25: 6 nutrition and exercise athlete ca
- Page 26 and 27: 8 nutrition and exercise tion and t
- Page 28 and 29: 10 nutrition and exercise aerobic m
- Page 30 and 31: 12 nutrition and exercise completel
- Page 32 and 33: 14 nutrition and exercise season, t
- Page 34 and 35: 16 nutrition and exercise skeletal
- Page 36 and 37: 18 nutrition and exercise coplasmic
- Page 38 and 39: 20 nutrition and exercise Table 2.1
- Page 40 and 41: 22 nutrition and exercise O 2 Fats
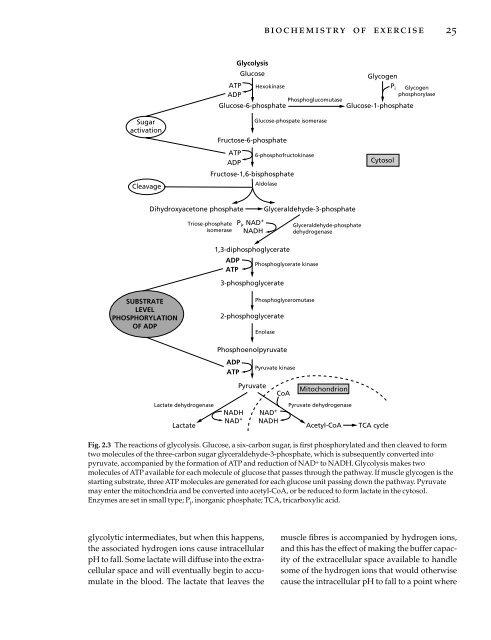
- Page 44 and 45: 26 nutrition and exercise it would
- Page 46 and 47: 28 nutrition and exercise Pyruvate
- Page 48 and 49: 30 nutrition and exercise stores be
- Page 50 and 51: 32 nutrition and exercise A key reg
- Page 52 and 53: 34 nutrition and exercise ATP resyn
- Page 54 and 55: 36 nutrition and exercise glycogen
- Page 56 and 57: 38 nutrition and exercise skeletal
- Page 58 and 59: 40 nutrition and exercise Table 3.1
- Page 60 and 61: 42 nutrition and exercise and conti
- Page 62 and 63: 44 nutrition and exercise Potential
- Page 64 and 65: 46 nutrition and exercise volume tr
- Page 66 and 67: ∆ VO2max (ml . kg -1. min -1 . )
- Page 68 and 69: 50 nutrition and exercise not assoc
- Page 70 and 71: 52 nutrition and exercise walking f
- Page 72 and 73: 54 nutrition and exercise the term
- Page 74 and 75: 56 nutrition and exercise model by
- Page 76 and 77: 58 nutrition and exercise state. RQ
- Page 78 and 79: 60 nutrition and exercise running a
- Page 80 and 81: 62 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 82 and 83: 64 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 84 and 85: 66 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 86 and 87: 68 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 88 and 89: 70 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 90 and 91: 72 nutrition and exercise kJ·h-1·
- Page 92 and 93:
74 nutrition and exercise Table 5.1
- Page 94 and 95:
76 nutrition and exercise Table 5.2
- Page 96 and 97:
78 nutrition and exercise Table 5.3
- Page 98 and 99:
80 nutrition and exercise Table 5.4
- Page 100 and 101:
82 nutrition and exercise 65-70% of
- Page 102 and 103:
84 nutrition and exercise Holt, S.,
- Page 104 and 105:
86 nutrition and exercise Table 6.1
- Page 106 and 107:
88 nutrition and exercise entering
- Page 108 and 109:
90 nutrition and exercise In practi
- Page 110 and 111:
92 nutrition and exercise Muscle fi
- Page 112 and 113:
94 nutrition and exercise Conclusio
- Page 114 and 115:
96 nutrition and exercise Nosek, T.
- Page 116 and 117:
98 nutrition and exercise and maint
- Page 118 and 119:
100 nutrition and exercise tional i
- Page 120 and 121:
102 nutrition and exercise Glycogen
- Page 122 and 123:
104 nutrition and exercise resynthe
- Page 124 and 125:
106 nutrition and exercise increase
- Page 126 and 127:
108 nutrition and exercise causes s
- Page 128 and 129:
110 nutrition and exercise with hum
- Page 130 and 131:
Chapter 8 Carbohydrate Replacement
- Page 132 and 133:
114 nutrition and exercise Hepatic
- Page 134 and 135:
116 nutrition and exercise availabi
- Page 136 and 137:
118 nutrition and exercise vs. soli
- Page 138 and 139:
120 nutrition and exercise NH 3 Asp
- Page 140 and 141:
122 nutrition and exercise rats in
- Page 142 and 143:
124 nutrition and exercise summary,
- Page 144 and 145:
126 nutrition and exercise ferase r
- Page 146 and 147:
128 nutrition and exercise substant
- Page 148 and 149:
130 nutrition and exercise Banister
- Page 150 and 151:
132 nutrition and exercise Wagenmak
- Page 152 and 153:
(a) (b) 134 nutrition and exercise
- Page 154 and 155:
136 nutrition and exercise estimate
- Page 156 and 157:
138 nutrition and exercise 1991; La
- Page 158 and 159:
140 nutrition and exercise Nitrogen
- Page 160 and 161:
142 nutrition and exercise Leucine
- Page 162 and 163:
144 nutrition and exercise plus min
- Page 164 and 165:
146 nutrition and exercise studies
- Page 166 and 167:
148 nutrition and exercise in older
- Page 168 and 169:
150 nutrition and exercise muscle g
- Page 170 and 171:
152 nutrition and exercise brain 5-
- Page 172 and 173:
154 nutrition and exercise Non-esse
- Page 174 and 175:
156 nutrition and exercise occur. F
- Page 176 and 177:
Table 11.2 A comparison of studies
- Page 178 and 179:
160 nutrition and exercise liferati
- Page 180 and 181:
162 nutrition and exercise longed e
- Page 182 and 183:
164 nutrition and exercise sive tra
- Page 184 and 185:
166 nutrition and exercise which de
- Page 186 and 187:
168 nutrition and exercise and risk
- Page 188 and 189:
170 nutrition and exercise S.M. She
- Page 190 and 191:
172 nutrition and exercise CNS fati
- Page 192 and 193:
174 nutrition and exercise various
- Page 194 and 195:
176 nutrition and exercise were inf
- Page 196 and 197:
178 nutrition and exercise dopamine
- Page 198 and 199:
180 nutrition and exercise was foun
- Page 200 and 201:
182 nutrition and exercise Reviews
- Page 202 and 203:
Chapter 13 Fat Metabolism during Ex
- Page 204 and 205:
186 nutrition and exercise palmitat
- Page 206 and 207:
188 nutrition and exercise the mito
- Page 208 and 209:
190 nutrition and exercise Referenc
- Page 210 and 211:
Chapter 14 Adaptations to a High Fa
- Page 212 and 213:
194 nutrition and exercise tigated
- Page 214 and 215:
196 nutrition and exercise Plasma F
- Page 216 and 217:
198 nutrition and exercise 210kJ ·
- Page 218 and 219:
200 nutrition and exercise (averagi
- Page 220 and 221:
202 nutrition and exercise Helge, J
- Page 222 and 223:
204 nutrition and exercise cost. Ai
- Page 224 and 225:
206 nutrition and exercise The abil
- Page 226 and 227:
208 nutrition and exercise Water lo
- Page 228 and 229:
210 nutrition and exercise during t
- Page 230 and 231:
212 nutrition and exercise both the
- Page 232 and 233:
214 nutrition and exercise electrol
- Page 234 and 235:
Chapter 16 Effects of Dehydration a
- Page 236 and 237:
218 nutrition and exercise rehydrat
- Page 238 and 239:
220 nutrition and exercise drated.
- Page 240 and 241:
222 nutrition and exercise cacy of
- Page 242 and 243:
224 nutrition and exercise Kubica,
- Page 244 and 245:
Chapter 17 Water and Electrolyte Lo
- Page 246 and 247:
228 nutrition and exercise Sweat ra
- Page 248 and 249:
230 nutrition and exercise the volu
- Page 250 and 251:
232 nutrition and exercise 1994). T
- Page 252 and 253:
234 nutrition and exercise Potassiu
- Page 254 and 255:
236 nutrition and exercise ent carb
- Page 256 and 257:
238 nutrition and exercise of gastr
- Page 258 and 259:
240 nutrition and exercise gene tra
- Page 260 and 261:
242 nutrition and exercise a U-shap
- Page 262 and 263:
244 nutrition and exercise The fact
- Page 264 and 265:
246 nutrition and exercise 15min, a
- Page 266 and 267:
248 nutrition and exercise Table 18
- Page 268 and 269:
250 nutrition and exercise nausea a
- Page 270 and 271:
252 nutrition and exercise an infre
- Page 272 and 273:
254 nutrition and exercise Peters,
- Page 274 and 275:
Chapter 19 Rehydration and Recovery
- Page 276 and 277:
258 nutrition and exercise with a h
- Page 278 and 279:
260 nutrition and exercise tion bev
- Page 280 and 281:
262 nutrition and exercise Table 19
- Page 282 and 283:
264 nutrition and exercise drinking
- Page 284 and 285:
Chapter 20 Vitamins: Metabolic Func
- Page 286 and 287:
268 nutrition and exercise Function
- Page 288 and 289:
270 nutrition and exercise times th
- Page 290 and 291:
272 nutrition and exercise Marginal
- Page 292 and 293:
274 nutrition and exercise toxicity
- Page 294 and 295:
276 nutrition and exercise metaboli
- Page 296 and 297:
278 nutrition and exercise Brubache
- Page 298 and 299:
280 nutrition and exercise Telford,
- Page 300 and 301:
282 nutrition and exercise ciencies
- Page 302 and 303:
284 nutrition and exercise Table 21
- Page 304 and 305:
286 nutrition and exercise processe
- Page 306 and 307:
288 nutrition and exercise these vi
- Page 308 and 309:
290 nutrition and exercise Belko, A
- Page 310 and 311:
Chapter 22 Exercise-induced Oxidati
- Page 312 and 313:
294 nutrition and exercise nic rese
- Page 314 and 315:
296 nutrition and exercise study wh
- Page 316 and 317:
298 nutrition and exercise Total gl
- Page 318 and 319:
300 nutrition and exercise Formatio
- Page 320 and 321:
302 nutrition and exercise tion of
- Page 322 and 323:
304 nutrition and exercise nium def
- Page 324 and 325:
306 nutrition and exercise making u
- Page 326 and 327:
308 nutrition and exercise however,
- Page 328 and 329:
310 nutrition and exercise kidney a
- Page 330 and 331:
312 nutrition and exercise macokine
- Page 332 and 333:
314 nutrition and exercise (1997) B
- Page 334 and 335:
316 nutrition and exercise enduranc
- Page 336 and 337:
Chapter 23 Minerals: Calcium KARIN
- Page 338 and 339:
320 nutrition and exercise if some
- Page 340 and 341:
322 nutrition and exercise Fig. 23.
- Page 342 and 343:
324 nutrition and exercise Drinkwat
- Page 344 and 345:
Chapter 24 Minerals: Iron E. RANDY
- Page 346 and 347:
328 nutrition and exercise the trai
- Page 348 and 349:
330 nutrition and exercise suggests
- Page 350 and 351:
332 nutrition and exercise tive’.
- Page 352 and 353:
334 nutrition and exercise immediat
- Page 354 and 355:
336 nutrition and exercise Haematol
- Page 356 and 357:
338 nutrition and exercise Rogers,
- Page 358 and 359:
340 nutrition and exercise letes ha
- Page 360 and 361:
342 nutrition and exercise ing a ro
- Page 362 and 363:
344 nutrition and exercise Because
- Page 364 and 365:
346 nutrition and exercise Summary
- Page 366 and 367:
348 nutrition and exercise weight.
- Page 368 and 369:
350 nutrition and exercise suggest
- Page 370 and 371:
352 nutrition and exercise requirem
- Page 372 and 373:
354 nutrition and exercise vanadyl
- Page 374 and 375:
Chapter 26 Nutritional Ergogenic Ai
- Page 376 and 377:
358 nutrition and exercise lean bod
- Page 378 and 379:
360 nutrition and exercise function
- Page 380 and 381:
362 nutrition and exercise strate u
- Page 382 and 383:
364 nutrition and exercise efficacy
- Page 384 and 385:
366 nutrition and exercise Nissen,
- Page 386 and 387:
368 nutrition and exercise Diet Blo
- Page 388 and 389:
370 nutrition and exercise appear t
- Page 390 and 391:
372 nutrition and exercise testinal
- Page 392 and 393:
374 nutrition and exercise change).
- Page 394 and 395:
376 nutrition and exercise the incr
- Page 396 and 397:
378 nutrition and exercise turnover
- Page 398 and 399:
380 nutrition and exercise Caffeine
- Page 400 and 401:
382 nutrition and exercise to incre
- Page 402 and 403:
384 nutrition and exercise on porti
- Page 404 and 405:
386 nutrition and exercise simply h
- Page 406 and 407:
388 nutrition and exercise indirect
- Page 408 and 409:
390 nutrition and exercise Conclusi
- Page 410 and 411:
392 nutrition and exercise Cederbla
- Page 412 and 413:
394 nutrition and exercise Table 29
- Page 414 and 415:
396 nutrition and exercise acidic a
- Page 416 and 417:
398 nutrition and exercise letes ar
- Page 418 and 419:
400 nutrition and exercise each of
- Page 420 and 421:
402 nutrition and exercise Donaldso
- Page 422 and 423:
404 nutrition and exercise influenc
- Page 424 and 425:
406 nutrition and exercise survey o
- Page 426 and 427:
408 nutrition and exercise has been
- Page 428 and 429:
410 nutrition and exercise Furtherm
- Page 430 and 431:
412 nutrition and exercise Research
- Page 432 and 433:
414 nutrition and exercise Houmard,
- Page 435 and 436:
Chapter 31 The Female Athlete KATHE
- Page 437 and 438:
given to athletes. It is also expec
- Page 439 and 440:
10 g CHO kg BW ¥ 60 kg BW = 600 g
- Page 441 and 442:
ecommended level of 0.016. The resu
- Page 443 and 444:
effects of trace mineral supplement
- Page 445 and 446:
Related Diseases in Europe. WHO Reg
- Page 447 and 448:
Chapter 32 The Young Athlete VISWAN
- Page 449 and 450:
always commence with ‘simple’ d
- Page 451 and 452:
et al. 1989), suggesting that the s
- Page 453 and 454:
directed eating from the child’s
- Page 455 and 456:
Fig. 32.4 Net body weight changes t
- Page 457 and 458:
pretation of the data with normal g
- Page 459 and 460:
physical dimensions of children. An
- Page 461 and 462:
against their carnivorous counterpa
- Page 463 and 464:
of epidemiological research are tra
- Page 465 and 466:
term adherents to a strict uncooked
- Page 467 and 468:
exercise increases zinc loss from t
- Page 469 and 470:
cantly decreased in the vegetarian
- Page 471 and 472:
non-vegetarian and 8 non-Seventh Da
- Page 473 and 474:
and omnivorous women. Journal of St
- Page 475 and 476:
Chapter 34 The Diabetic Athlete JØ
- Page 477 and 478:
concentration of glucose in the blo
- Page 479 and 480:
Henriksson 1992). Too high a glucos
- Page 481 and 482:
Fig. 34.3 Glycogen synthesis in IDD
- Page 483 and 484:
content impedes this. The reduced g
- Page 485:
PART 3 PRACTICAL ISSUES
- Page 488 and 489:
470 practical issues Beals & Manore
- Page 490 and 491:
472 practical issues (grams per day
- Page 492 and 493:
474 practical issues 11% of the var
- Page 494 and 495:
476 practical issues 33±14 years;
- Page 496 and 497:
478 practical issues certain amount
- Page 498 and 499:
480 practical issues accompany seve
- Page 500 and 501:
482 practical issues energy balance
- Page 502 and 503:
Chapter 36 The Travelling Athlete A
- Page 504 and 505:
486 practical issues bars. Other at
- Page 506 and 507:
488 practical issues content may be
- Page 508 and 509:
490 practical issues immune system.
- Page 510 and 511:
Chapter 37 Overtraining: Nutritiona
- Page 512 and 513:
494 practical issues Overtraining s
- Page 514 and 515:
496 practical issues overload train
- Page 516 and 517:
498 practical issues (Febbraio et a
- Page 518 and 519:
500 practical issues feine (Vallera
- Page 520 and 521:
502 practical issues Glycogen (mmol
- Page 522 and 523:
504 practical issues and ingested h
- Page 524 and 525:
506 practical issues recommendation
- Page 526 and 527:
508 practical issues ability and te
- Page 528 and 529:
Chapter 39 Eating Disorders in Athl
- Page 530 and 531:
512 practical issues 1987; Burckes-
- Page 532 and 533:
514 practical issues Weight loss an
- Page 534 and 535:
516 practical issues the importance
- Page 536 and 537:
518 practical issues weight history
- Page 538 and 539:
520 practical issues Throughout thi
- Page 540 and 541:
522 practical issues ballet school.
- Page 542 and 543:
524 practical issues (National Rese
- Page 544 and 545:
526 practical issues include ‘con
- Page 546 and 547:
528 practical issues researched of
- Page 548 and 549:
530 practical issues growth-enhanci
- Page 551:
PART 4 SPORT-SPECIFIC NUTRITION
- Page 554 and 555:
536 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 556 and 557:
538 sport-specific nutrition subjec
- Page 558 and 559:
540 sport-specific nutrition ample
- Page 560 and 561:
542 sport-specific nutrition tion o
- Page 562 and 563:
544 sport-specific nutrition have s
- Page 564 and 565:
546 sport-specific nutrition immuno
- Page 566 and 567:
548 sport-specific nutrition Nevill
- Page 568 and 569:
Chapter 42 Distance Running JOHN A.
- Page 570 and 571:
552 sport-specific nutrition see Ha
- Page 572 and 573:
554 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 574 and 575:
556 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 576 and 577:
558 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 578 and 579:
560 sport-specific nutrition Asher,
- Page 580 and 581:
Chapter 43 Cycling ASKER E. JEUKEND
- Page 582 and 583:
564 sport-specific nutrition remark
- Page 584 and 585:
566 sport-specific nutrition the mu
- Page 586 and 587:
568 sport-specific nutrition additi
- Page 588 and 589:
570 sport-specific nutrition 10 Aft
- Page 590 and 591:
572 sport-specific nutrition Refere
- Page 592 and 593:
Chapter 44 Team Sports JENS BANGSBO
- Page 594 and 595:
576 sport-specific nutrition the hi
- Page 596 and 597:
578 sport-specific nutrition A B C
- Page 598 and 599:
580 sport-specific nutrition Glycog
- Page 600 and 601:
582 sport-specific nutrition minera
- Page 602 and 603:
584 sport-specific nutrition ence t
- Page 604 and 605:
586 sport-specific nutrition liquid
- Page 606 and 607:
Chapter 45 Gymnastics DAN BENARDOT
- Page 608 and 609:
(a) (b) 590 sport-specific nutritio
- Page 610 and 611:
592 sport-specific nutrition summar
- Page 612 and 613:
594 sport-specific nutrition The an
- Page 614 and 615:
596 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 616 and 617:
598 sport-specific nutrition of ske
- Page 618 and 619:
(a) (b) 600 sport-specific nutritio
- Page 620 and 621:
602 sport-specific nutrition Table
- Page 622 and 623:
604 sport-specific nutrition snacks
- Page 624 and 625:
606 sport-specific nutrition over 1
- Page 626 and 627:
608 sport-specific nutrition Webste
- Page 628 and 629:
610 sport-specific nutrition an ave
- Page 630 and 631:
612 sport-specific nutrition traini
- Page 632 and 633:
614 sport-specific nutrition drate
- Page 634 and 635:
616 sport-specific nutrition cantly
- Page 636 and 637:
618 sport-specific nutrition RBC (1
- Page 638 and 639:
620 sport-specific nutrition in fem
- Page 640 and 641:
622 sport-specific nutrition is zer
- Page 642 and 643:
624 sport-specific nutrition The tw
- Page 644 and 645:
626 sport-specific nutrition progra
- Page 646 and 647:
628 sport-specific nutrition betwee
- Page 648 and 649:
630 sport-specific nutrition effect
- Page 650 and 651:
Chapter 48 Racquet Sports MARK HARG
- Page 652 and 653:
634 sport-specific nutrition (Ellio
- Page 654 and 655:
636 sport-specific nutrition Reilly
- Page 656 and 657:
638 sport-specific nutrition Weight
- Page 658 and 659:
640 sport-specific nutrition which
- Page 660 and 661:
642 sport-specific nutrition been p
- Page 662 and 663:
644 sport-specific nutrition months
- Page 664 and 665:
Chapter 50 Skating ANN C. SNYDER AN
- Page 666 and 667:
648 sport-specific nutrition Energy
- Page 668 and 669:
650 sport-specific nutrition be ach
- Page 670 and 671:
652 sport-specific nutrition improv
- Page 672 and 673:
654 sport-specific nutrition hours
- Page 674 and 675:
Chapter 51 Cross-country Skiing BJO
- Page 676 and 677:
658 sport-specific nutrition The hi
- Page 678 and 679:
660 sport-specific nutrition breath
- Page 680 and 681:
662 sport-specific nutrition Saltin
- Page 682 and 683:
664 index alcohol consumption (Cont
- Page 684 and 685:
666 index carbohydrate ingestion (C
- Page 686 and 687:
668 index dry skating 647, 649 dura
- Page 688 and 689:
670 index fluid intake (Cont.) chil
- Page 690 and 691:
672 index high fat diet 192-201 end
- Page 692 and 693:
674 index maximum aerobic power (Co
- Page 694 and 695:
676 index protein metabolism (Cont.
- Page 696 and 697:
678 index swimming (Cont.) iron sta
- Page 698:
680 index weight restriction (Cont.