MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 mRNA and Protein Expression in ...
MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 mRNA and Protein Expression in ...
MDR1/P-glycoprotein and MRP-1 mRNA and Protein Expression in ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
suggests that almost 61% of cases had no detectable mdr1<br />
<strong>mRNA</strong>, but expressed <strong>MDR1</strong> P-gp prote<strong>in</strong>. Chi-squared<br />
analysis showed no significant (p=0.636) correlation<br />
between mdr1 <strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>MDR1</strong> P-gp prote<strong>in</strong> expression<br />
<strong>in</strong> the NSCLC specimens analysed <strong>in</strong> this study.<br />
In the case of <strong>MRP</strong>-1, ~ 17% of NSCLC were found to<br />
co-express mrp1 <strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>MRP</strong>-1 prote<strong>in</strong>, with 8.3% not<br />
express<strong>in</strong>g <strong>MRP</strong>-1 at all (Table IV (B)). Approximately<br />
71% of specimens were found to transcribe, but not to<br />
translate, <strong>MRP</strong>1; while 4.2% of cases had detectable levels<br />
of <strong>MRP</strong>-1 prote<strong>in</strong>, but the correspond<strong>in</strong>g gene transcripts<br />
could not be detected follow<strong>in</strong>g 30 cycles of RT-PCR. No<br />
significant (p=0.569) correlation was found between mrp1<br />
<strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>MRP</strong>-1 prote<strong>in</strong> expression.<br />
Discussion<br />
Resistance to chemotherapy is a major obstacle <strong>in</strong> the<br />
cl<strong>in</strong>ical management of lung cancer. While, at the time of<br />
diagnosis, most small cell lung carc<strong>in</strong>omas (SCLCs) are<br />
responsive to chemotherapy, the majority of NSCLCs (which<br />
constitute ~ 85% of all lung cancers) are <strong>in</strong>tr<strong>in</strong>sically<br />
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 27: 1325-1330 (2007)<br />
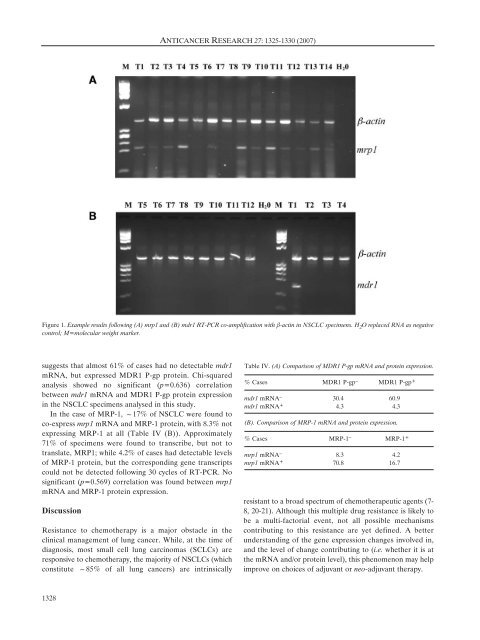
Figure 1. Example results follow<strong>in</strong>g (A) mrp1 <strong>and</strong> (B) mdr1 RT-PCR co-amplification with ‚-act<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> NSCLC specimens. H 2 O replaced RNA as negative<br />
control; M=molecular weight marker.<br />
1328<br />
Table IV. (A) Comparison of <strong>MDR1</strong> P-gp <strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong> prote<strong>in</strong> expression.<br />
% Cases <strong>MDR1</strong> P-gp – <strong>MDR1</strong> P-gp +<br />
mdr1 <strong>mRNA</strong> – 30.4 60.9<br />
mdr1 <strong>mRNA</strong> + 4.3 4.3<br />
(B). Comparison of <strong>MRP</strong>-1 <strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong> prote<strong>in</strong> expression.<br />
% Cases <strong>MRP</strong>-1 – <strong>MRP</strong>-1 +<br />
mrp1 <strong>mRNA</strong> – 8.3 4.2<br />
mrp1 <strong>mRNA</strong> + 70.8 16.7<br />
resistant to a broad spectrum of chemotherapeutic agents (7-<br />
8, 20-21). Although this multiple drug resistance is likely to<br />
be a multi-factorial event, not all possible mechanisms<br />
contribut<strong>in</strong>g to this resistance are yet def<strong>in</strong>ed. A better<br />
underst<strong>and</strong><strong>in</strong>g of the gene expression changes <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong>,<br />
<strong>and</strong> the level of change contribut<strong>in</strong>g to (i.e. whether it is at<br />
the <strong>mRNA</strong> <strong>and</strong>/or prote<strong>in</strong> level), this phenomenon may help<br />
improve on choices of adjuvant or neo-adjuvant therapy.