Low-Valent Titanium Induced Carbonyl Coupling Reactions
Low-Valent Titanium Induced Carbonyl Coupling Reactions
Low-Valent Titanium Induced Carbonyl Coupling Reactions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
60<br />
C<br />
H 3<br />
NH<br />
O<br />
O<br />
O<br />
Ti/Graphite in DME<br />
CH 3<br />
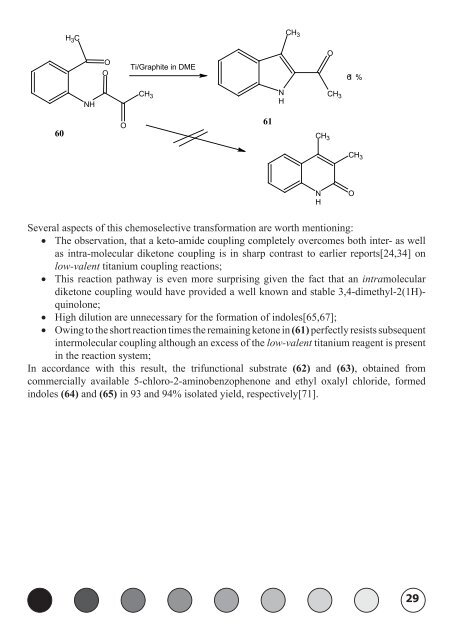
Several aspects of this chemoselective transformation are worth mentioning:<br />
• The observation, that a keto-amide coupling completely overcomes both inter- as well<br />
as intra-molecular diketone coupling is in sharp contrast to earlier reports[24,34] on<br />
low-valent titanium coupling reactions;<br />
• This reaction pathway is even more surprising given the fact that an intramolecular<br />
diketone coupling would have provided a well known and stable 3,4-dimethyl-2(1H)quinolone;<br />
• High dilution are unnecessary for the formation of indoles[65,67];<br />
• Owing to the short reaction times the remaining ketone in (61) perfectly resists subsequent<br />
intermolecular coupling although an excess of the low-valent titanium reagent is present<br />
in the reaction system;<br />
In accordance with this result, the trifunctional substrate (62) and (63), obtained from<br />
commercially available 5-chloro-2-aminobenzophenone and ethyl oxalyl chloride, formed<br />
indoles (64) and (65) in 93 and 94% isolated yield, respectively[71].<br />
61<br />
N<br />
H<br />
CH 3<br />
CH 3<br />
N<br />
H<br />
O<br />
CH 3<br />
61 %<br />
CH 3<br />
O<br />
29