Análisis Diferencial de la Curva Involuta de un C´ırculo.
Análisis Diferencial de la Curva Involuta de un C´ırculo.
Análisis Diferencial de la Curva Involuta de un C´ırculo.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
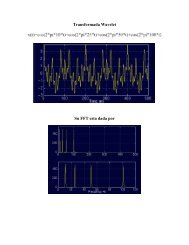
<strong>de</strong>terminarán <strong>la</strong>s seg<strong>un</strong>das <strong>de</strong>rivadas <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong>s coor<strong>de</strong>nadas <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong> curva involutad 2 xdψ 2 = rå d Cosψ− Senψdψ θå= dr Cosψè− Senψ − rå Senψè+ Cosψ + Cosψ dθdψ θθθ 2 (22)dψDebe notarse que, <strong>de</strong> <strong>la</strong>s ecuaciones (12, 13), se tiene queèdθdψ = dθ dφdφdψ = Sec2 φtan 2 φ = 1Sen 2 φSustituyendo <strong>la</strong>s ecuaciones (14, 23, 3) en <strong>la</strong> ecuación (22), se tiene queåd 2 xdψ 2 = r Cosψè− Senψ − rå Senψè+ Cosψ + Cosψθ θθθ 2 Sen 2 φå 2 Senψ è= −r + Cosψ 1+ 1 θθ 4Simi<strong>la</strong>rmente, <strong>la</strong> seg<strong>un</strong>da <strong>de</strong>rivada <strong>de</strong> y está dadapord 2 ydψ 2 = rå d Senψè+ Cosψdψ θå= dr Senψè+ Cosψ + rå Cosψ− Senψ − Senψ dθdψ θθθ 2 dψå= r Senψè+ Cosψ + rå Cosψè− Senψ −Senψθ θθθ 2 Sen 2 φå 2 Cosψ è= r − Senψ 1+ 1 θθ 4è(23)(24)(25)De <strong>la</strong> figura 1, el vector <strong>un</strong>itario normal, a <strong>la</strong> curva involuta, en el p<strong>un</strong>to P ,está dadoporê n = −Senθî + Cosθĵ. (26)Por lo tanto, <strong>la</strong> aceleración normal está dada pora n d2 x=dψ 2 î + d2 ydψ 2 ĵ · ê n = − d2 xdψ 2 Senθ + d2 ydψ 2 Cosθ= rå 2 Senψ è+ Cosψ 1+ 1 θθ 4 Senθ + rå 2 CosψθRecordando <strong>la</strong>s i<strong>de</strong>ntida<strong>de</strong>s trogonométricas− SenψSenφ = Sen(θ − ψ) =SenθCosψ − Cosθ SenψCosφ = Cos(θ − ψ) =CosθCosψ + SenθSenψ è1+ 1 θ 4 Cosθ5