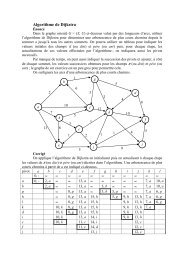
Langages de l'informatique
Langages de l'informatique
Langages de l'informatique
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Machine p. 124 - virtuelle Licence <strong>de</strong>s droits d’usage en page 2.<br />
Sémantique opérationnelle<br />
<strong>Langages</strong> <strong>de</strong> l’informatique<br />
Patrick Bellot<br />
Introduction<br />
Les langages<br />
Les paradigmes<br />
Modèle impératif abstrait<br />
Boehm et Jacopini<br />
Programmation impérative<br />
Programmation fonctionnelle<br />
Programmation en logique<br />
Gestion <strong>de</strong> la mémoire<br />
Quatre types <strong>de</strong> mémoire<br />
Gérer sa mémoire<br />
Comptage <strong>de</strong> référence<br />
Syntaxe et sémantique<br />
Sémantiques<br />
Analyse lexicale<br />
Analyse syntaxique<br />
Dans ce type <strong>de</strong> sémantique, on décrit une machine<br />
abstraite, un genre d’ordinateur parfait.<br />
On définit comment les instructions du langage<br />
<strong>de</strong>vraient s’exécuter sur cette machine abstraite.<br />
Cela peut donner une bonne idée <strong>de</strong> ce que font les<br />
programmes mais ce type <strong>de</strong> sémantique n’est ni très<br />
maniable ni très utile d’un point <strong>de</strong> vue théorique.<br />
Exemple: on pourrait compiler les instructions du<br />
langage dans le modèle impératif abstrait.<br />
Compilation<br />
Interprétation