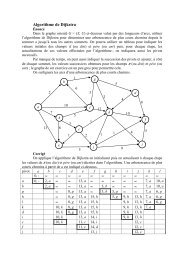
Langages de l'informatique
Langages de l'informatique
Langages de l'informatique
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Machine p. 126 - virtuelle Licence <strong>de</strong>s droits d’usage en page 2.<br />
Sémantique axiomatique<br />
<strong>Langages</strong> <strong>de</strong> l’informatique<br />
Patrick Bellot<br />
Introduction<br />
Les langages<br />
Les paradigmes<br />
Modèle impératif abstrait<br />
Boehm et Jacopini<br />
Programmation impérative<br />
Programmation fonctionnelle<br />
Programmation en logique<br />
Gestion <strong>de</strong> la mémoire<br />
Quatre types <strong>de</strong> mémoire<br />
Gérer sa mémoire<br />
Comptage <strong>de</strong> référence<br />
Syntaxe et sémantique<br />
Sémantiques<br />
Analyse lexicale<br />
Analyse syntaxique<br />
Compilation<br />
En sémantique axiomatique, on décrit l’état d’un<br />
programme par un ensemble <strong>de</strong> formules logiques.<br />
Puis l’effet <strong>de</strong> chaque instruction est décrit par une<br />
règle <strong>de</strong> logique basée sur les notions <strong>de</strong> pré et<br />
post-conditions.<br />
Exemples<br />
{x ≥ 0} x++ {x > 0}<br />
Si {P ∧test} I {Q}<br />
et {P ∧¬test} J {Q}<br />
alors {P} if test then I else J {Q}<br />
La sémantique s’obtient <strong>de</strong> la même manière qu’une<br />
démonstration en logique, ce qui est assez compliqué.<br />
Interprétation