Distributeurs | Préleveurs | Fournitures pour le ... - Bürkle GmbH
Distributeurs | Préleveurs | Fournitures pour le ... - Bürkle GmbH
Distributeurs | Préleveurs | Fournitures pour le ... - Bürkle GmbH
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
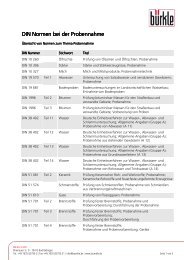
Les matières plastiques, propriétés physiques | Indications sur la compatibilité chimiqueE-CTFE Etylène-Chlorotrifluoroéthylène-Copolymère (Halar ® )FEP Tetrafluoroéthylène perfluorpropylène(Téflon ® FEP)FPM Fluoro-Polymère (Viton ® )HDPE Polyéthylène haute densitéLDPE Polyéthylène basse densitéPA PolyamidePC PolycarbonatePFA Polymère perfluoroalkoxy (Teflon ® PFA)PMP Polyméthylpentène (TPX ® )PP PolypropylènePS PolystyrènePSF PolysulfonePTFE Polytétrafluoroéthylène (Teflon ® )PVC Polychlorure de viny<strong>le</strong>PVDF Polyfluorure de viny<strong>le</strong>SAN Copolymère de Styrène-acrylonitri<strong>le</strong>SI Caoutchouc siliconéMatières plastiques Températures admises Stérilisation 5) Apparence F<strong>le</strong>xibilité Poids AbsorptionSig<strong>le</strong>s max. °C min °C Vapeur 4) Gaz Rayons gamma Chimique spécifique d‘eau1) 2) 121°C Oxyde d‘éthylène 2,5 kGy Formaline,Ethanol g/cm3 %E-CTFE + 150° - 100° oui oui non oui transparent moyenne 1,70 < 0,10FEP + 205° - 255° oui oui non oui transparent remarquab<strong>le</strong> 2,15 < 0,01FPM + 200° - 20° noir bonne 1,90HDPE + 110° - 50° non oui oui oui transparent rigide 0,95 0,01LDPE + 95° - 50° non oui oui oui transparent excel<strong>le</strong>nte 0,92 0,01PA + 90° - 0° non oui oui oui transparent rigide 1,13 1,30PC + 135° - 135° oui oui oui oui clair inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,20 0,35PFA + 250° - 270° oui oui non oui transparent excel<strong>le</strong>nte 2,15 0.03PMP + 175° - 150° oui oui oui oui translucide inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 0,83 0,01PP + 135° 5° oui oui non oui transparent inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 0,90 0,02PS + 70° - 20° non non oui oui translucide inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,05 0,05PSU + 165° - 100° oui oui oui clair rigide 1,24 0,30PTFE + 270° - 270° oui oui non oui opaque excel<strong>le</strong>nte 2,25 < 0,01PVC + 70° - 30° non 3) oui non oui clair inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,35 0,06PVDF + 160° - 4° oui oui oui oui transparent inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,78 0,04SAN + 95° - 40° non oui non oui translucide inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,03 0,05SI + 180° - 60° oui oui non oui transparent excel<strong>le</strong>nte 1,10PETG + 70° + 5° non k.A. k.A. oui translucide inf<strong>le</strong>xib<strong>le</strong> 1,78 0,701)supérieures si exposition brève2)température de fragilisation3)Sauf <strong>le</strong>s tubes en PVC, qui résistent à une stérilisation à la vapeur de 121 °C.4)Une stérilisation à la vapeur fréquente provoque une perte de solidité !5)rincer préalab<strong>le</strong>ment <strong>le</strong>s appareils à l‘eau distillée (on écarte ainsi <strong>le</strong>s risques de corrosion liésaux tensions). Pour des récipients à fermeture, il est conseillé de retirer ou d‘ouvrir partiel<strong>le</strong>mentl‘obturateur, qu‘on ne revissera qu‘après refroidissement.Groupes de substances à 20 °C ABS ECTFE HDPE LDPE PA PC PMP PP PS PTFE/FEP/PFA PVC SAN SIAldéhydes - + + + 0 0 0 + - + - - 0Alcools aliphatiques + + + + 0 + + + + + + + +Esters - + 0 0 + - 0 0 - + - - 0Ethers - + 0 - + - - - - + - - -Cétones - 0 0 0 + - 0 0 - + - -Hydrocarburesaliphathiques - + + 0 + 0 0 + - + + - -aromatiques - + + 0 + - - 0 - + - - -halogénés - + 0 - 0 - - 0 - + - - -Acides, faib<strong>le</strong>s/dilués 0 + + + 0 0 + + 0 + + 0 0Acides, forts/concentrés - + + + - - + + 0 + + - -Acides, oxydants - 0 0 0 - - 0 0 - + - - -Lessives alcalines 0 + + + 0 - + + + + + ++ = Résistance chimique excel<strong>le</strong>nteL‘exposition constante au milieu ne provoque aucunedétèrioration de la matière plastique dans <strong>le</strong>s 30 jours. Lamatière plastique peut demeurer résistante pendant desannées.0 = Résistance chimique bonne à restreinteL‘exposition constante au milieu provoque de faib<strong>le</strong>sdétériorations entre 7 et 30 jours, qui sont en partieréversib<strong>le</strong>s (ramollissement, gonf<strong>le</strong>ment, dégradation descaractéristiques mécaniques, colorations).- = Résistance chimique faib<strong>le</strong>Déconseillées <strong>pour</strong> une exposition constante au milieu. Lesdétériorations peuvent être immédiates (dégradation descaractéristiques mécaniques, déformations, colorations,fissures, dissolution, danger de rupture).243