Download full issue - PanamJAS
Download full issue - PanamJAS
Download full issue - PanamJAS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
296<br />
A. R. GHIDINI ET AL.<br />
composed mainly by pastureland (Andreoli &<br />
Carneiro 2005).<br />
Iraí Reservoir was built in 2001 and its<br />
morphometrical and hydrological features have been<br />
causing Cyanobacteria proliferation since its filling,<br />
complicating water treatment and reducing water<br />
quality (Andreoli & Carneiro 2005).<br />
One of the four main tributaries (Timbú<br />
River) is characterized by an elevated nutrient load,<br />
especially of phosphorus and nitrogen, due to the<br />
disordered urban occupation of the drainage basin.<br />
This fact, associated to the high residence time and<br />
low dept of the reservoir favored the development of<br />
blooms of Cyanobacteria, as Anabaena sp.,<br />
Cylindrospermopsis sp., and Microcystis sp.,<br />
promoting significantly changes in the water quality<br />
of the reservoir (Bollmann & Andreoli 2005).<br />
Field work, samples and data analyses.<br />
The samples were obtained monthly from<br />
March/2002 to July/2003 in six stations in the<br />
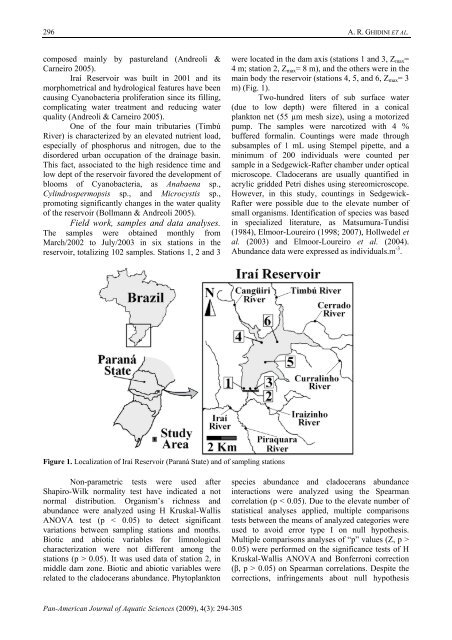
reservoir, totalizing 102 samples. Stations 1, 2 and 3<br />
were located in the dam axis (stations 1 and 3, Z max =<br />
4 m; station 2, Z max = 8 m), and the others were in the<br />
main body the reservoir (stations 4, 5, and 6, Z max = 3<br />
m) (Fig. 1).<br />
Two-hundred liters of sub surface water<br />
(due to low depth) were filtered in a conical<br />
plankton net (55 µm mesh size), using a motorized<br />
pump. The samples were narcotized with 4 %<br />
buffered formalin. Countings were made through<br />
subsamples of 1 mL using Stempel pipette, and a<br />
minimum of 200 individuals were counted per<br />
sample in a Sedgewick-Rafter chamber under optical<br />
microscope. Cladocerans are usually quantified in<br />
acrylic gridded Petri dishes using stereomicroscope.<br />
However, in this study, countings in Sedgewick-<br />
Rafter were possible due to the elevate number of<br />
small organisms. Identification of species was based<br />
in specialized literature, as Matsumura-Tundisi<br />
(1984), Elmoor-Loureiro (1998; 2007), Hollwedel et<br />
al. (2003) and Elmoor-Loureiro et al. (2004).<br />
Abundance data were expressed as individuals.m -3 .<br />
Figure 1. Localization of Iraí Reservoir (Paraná State) and of sampling stations<br />
Non-parametric tests were used after<br />
Shapiro-Wilk normality test have indicated a not<br />
normal distribution. Organism’s richness and<br />
abundance were analyzed using H Kruskal-Wallis<br />
ANOVA test (p < 0.05) to detect significant<br />
variations between sampling stations and months.<br />
Biotic and abiotic variables for limnological<br />
characterization were not different among the<br />
stations (p > 0.05). It was used data of station 2, in<br />
middle dam zone. Biotic and abiotic variables were<br />
related to the cladocerans abundance. Phytoplankton<br />
species abundance and cladocerans abundance<br />
interactions were analyzed using the Spearman<br />
correlation (p < 0.05). Due to the elevate number of<br />
statistical analyses applied, multiple comparisons<br />
tests between the means of analyzed categories were<br />
used to avoid error type I on null hypothesis.<br />
Multiple comparisons analyses of “p” values (Z, p ><br />
0.05) were performed on the significance tests of H<br />
Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA and Bonferroni correction<br />
(β, p > 0.05) on Spearman correlations. Despite the<br />
corrections, infringements about null hypothesis<br />
Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences (2009), 4(3): 294-305