Transformada de Fourier de Sinais Discretos
Transformada de Fourier de Sinais Discretos
Transformada de Fourier de Sinais Discretos
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
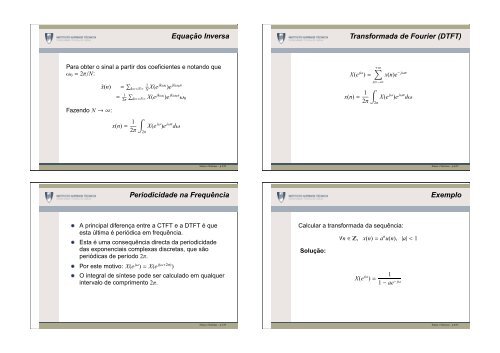
Equação Inversa<br />
<strong>Transformada</strong> <strong>de</strong> <strong>Fourier</strong> (DTFT)<br />
Para obter o sinal a partir dos coeficientes e notando que<br />
ω 0 = 2π/N:<br />
˜x(n)<br />
Fazendo N → ∞:<br />
= ∑ k= 1 X(e jkω 0<br />
)e jkω 0n<br />
N<br />
∑<br />
k= X(e jkω 0<br />
)e jkω0n ω 0<br />
= 1<br />
2π<br />
x(n) = 1<br />
2π<br />
∫<br />
2π<br />
X(e jω )e jωn dω<br />
X(e jω ) =<br />
x(n) = 1<br />
2π<br />
∫<br />
+∞∑<br />
n=−∞<br />
2π<br />
x(n)e − jωn<br />
X(e jω )e jωn dω<br />
.<br />
.<br />
<strong>Sinais</strong> e Sistemas – p.5/35<br />
<strong>Sinais</strong> e Sistemas – p.6/35<br />
Periodicida<strong>de</strong> na Frequência<br />
Exemplo<br />
A principal diferença entre a CTFT e a DTFT é que<br />
esta última é periódica em frequência.<br />
Esta é uma consequência directa da periodicida<strong>de</strong><br />
das exponenciais complexas discretas, que são<br />
periódicas <strong>de</strong> período 2π.<br />
Por este motivo: X(e jω ) = X(e j(ω+2π) )<br />
O integral <strong>de</strong> síntese po<strong>de</strong> ser calculado em qualquer<br />
intervalo <strong>de</strong> comprimento 2π.<br />
Calcular a transformada da sequência:<br />
∀n ∈ , x(n) = a n u(n), |a| < 1<br />
Solução:<br />
X(e jω ) =<br />
1<br />
1 − ae − jω <strong>Sinais</strong> e Sistemas – p.8/35<br />
.<br />
.<br />
<strong>Sinais</strong> e Sistemas – p.7/35