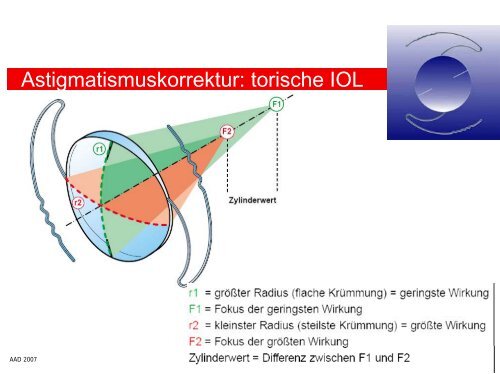
Astigmatismuskorrektur: torische IOL
Astigmatismuskorrektur: torische IOL
Astigmatismuskorrektur: torische IOL
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
<strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong>: <strong>torische</strong> <strong>IOL</strong><br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Rayner Surgical<br />
T-flex 571T<br />
single piece, hydorphiles Acrylat<br />
Optik-Durchmesser: 5,75 mm<br />
bis 11 dpt. Zylinder u. Sonderanfertigungen<br />
<strong>torische</strong> Oberfläche auf der Rückfläche der <strong>IOL</strong><br />
T-flex 623T<br />
wie 571T<br />
Optik-Durchmesser: 6,25 mm<br />
<strong>torische</strong> Oberfläche auf der Vorderseite der <strong>IOL</strong><br />
<strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong>: 1,5 – 11,0 dpt. (0,25 dpt.)<br />
bis sphärisches Äquivalent von 25 dpt.<br />
Inzisionsbreite: 2,5 – 3,2 mm<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Humanoptics<br />
MicroSil Toric MS 6116 TU<br />
faltbare, dreiteilige Silikon-<strong>IOL</strong><br />
Optik-Durchmesser: 6,0 mm<br />
Z-Haptik<br />
<strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong>: 2,0 – 12,0 dpt. (1 dpt.)<br />
MicroSil Toric MS 6116 T-Y<br />
mit Blaulichtfilter<br />
MicroSil Toric MS 614 T<br />
Sulcusimplantation<br />
C-Haptik<br />
MicroSil Toric MS 714 TPB TU<br />
Piggy-Back-Implantation<br />
C-Haptik, Optik-Durchmesser: 7,0 mm<br />
<strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong>: 1,0 – 6,0 dpt. (1 dpt.)<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Humanoptics<br />
sphärische Vorderseite, Torus auf Rückseite<br />
3-fach optimiert für Haigis (a0, a1, a2)<br />
Implantation mittels Pinzette<br />
Inzisionsbreite: >(3,2) 4,0 mm<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Acritec<br />
*Acri.Smart 646TLC/643TLC<br />
hydratisiertes Acrylat mit hydrophober Oberfläche<br />
single piece, Plattenhaptik<br />
bitorisch<br />
Vorteile: geringere Mittendicke, bessere<br />
Abbildungsqualität<br />
aberrationskorrigiert<br />
Optik-Durchmesser: 6,0 mm<br />
Gesamtdurchmesser: 11,0 mm<br />
sph 0,0 bis 32,0 (40,0) dpt.<br />
cyl 0,0 bis 12,0 dpt.<br />
Inzisionsbreite: 1,8 bis 2,0 mm<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen<br />
STAAR: Toric-<strong>IOL</strong> AA4203 TF/TL<br />
erste FDA-zugelassene <strong>IOL</strong>: 11-98<br />
single piece, Silikon, Plattenhaptik<br />
in 2 Zylinderstärken: 2 dpt. (corneal: 1,5 dpt.)<br />
und 3,5 dpt. (corneal: 2,25 dpt.)<br />
Gesamtdurchmesser: 10, 8 – 11,2 mm<br />
Optik: 6 mm<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff<br />
Chang DF. Pearls on implanting the Staar toric <strong>IOL</strong>. Video report. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001;85(Jan)
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Indikationen<br />
AAD 2007<br />
cornealer Astigmatismus > 3 dpt.<br />
regulärer Astigmatismus<br />
stabiler Astigmatismus-Befund über 6 Monate<br />
stabiler Kapselsack: Ausschluß Cat. traumatica<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen<br />
AAD 2007<br />
OP-Voraussetzungen:<br />
- KL-Karenz von 2 Wochen<br />
- präoperative Diagnostik<br />
- Kostenübernahmeantrag: „Sonderlinse“ an<br />
die GKV<br />
bei med. Indikation ab 5 dpt. laut BVA (1-<br />
2007)<br />
- cave,explizit: Übernahme der Kosten <strong>IOL</strong><br />
- cave: je nach Astigmatismus<br />
Produktionszeitraum von bis zu 6 Wochen<br />
beachten<br />
Anmerkung: Sonderlinsen im Sinne des EBM nach Einschätzung des<br />
BVA: <strong>IOL</strong> mit Zusatzfunktionen, die über die Parameter monofokale,<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: prä-OP Diagnostik<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Brillenrefraktion, objektive Refraktion<br />
Keratometerie<br />
Hornhauttopographie<br />
cave: Ausschluß Keratokonus<br />
ACD: cave: epi- oder endothelseitig<br />
axiale Bulbuslänge: akustisch/optisch<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: prä-OP Diagnostik<br />
Brillenrefraktion, objektive Refraktion<br />
Keratometerie<br />
Hornhauttopographie<br />
cave: Ausschluß Keratokonus<br />
ACD: cave: epi- oder endothelseitig<br />
axiale Bulbuslänge: akustisch/optisch<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> <strong>IOL</strong>:<br />
Keratometerwerte:<br />
- Geräteangabe<br />
Bulbuslänge:<br />
AAD 2007<br />
- akustisch/optisch<br />
J. Wolff
AAD 2007<br />
Präoperative Markierung<br />
Horizontal-Achsenmarkierer n. Gerten (Geuder)<br />
0° oder „on axis“ Achsenmarkierung im Ocular der SPL (Zeiss)<br />
0°-Grad Markierung im Sitzen:<br />
- Tropfanästhesie<br />
- bei Geradeausblick<br />
- Methylenblau<br />
J. Wolff
Markierung der prä-OP Astigmatismuslage<br />
AAD 2007<br />
90°<br />
0°<br />
on axis<br />
J. Wolff
Markierung der prä-OP Astigmatismuslage<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Methylenblau Markierung<br />
der Conjunctiva/Cornea<br />
oder Fotodokumentation<br />
prominentes Skleragefäß<br />
Stichinzision paralimbär<br />
Argon-LK paralimbär<br />
J. Wolff
absolute Zyklorotation (intraoperativ)<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Prozent [%]<br />
40%<br />
35%<br />
30%<br />
25%<br />
20%<br />
15%<br />
10%<br />
5%<br />
0%<br />
0-1<br />
1-2<br />
2-3<br />
3-4<br />
4-5<br />
5-6<br />
Zyklorotation [°]<br />
J. Wolff et al., 2004<br />
22,7% > 4°<br />
6-7<br />
7-8<br />
8-9<br />
9-10<br />
Total: 88<br />
MW: 2,7°<br />
Std: 2,0<br />
Min: 0,1°<br />
Max 8,7°<br />
J. Wolff
AAD 2007<br />
Cyclotorsion: Seated - Supine<br />
Author year n mean rotation range special<br />
Smith et al. 1994 50 0.2° +/- 1.2 0° - 16° p = .41<br />
Suzuki et al. 1997 38 4.4° +/- 2.8 0° - 14° 14% no change in<br />
axis<br />
Swami et al. 2002 240 4.1° +/- 3.7 0°– 14.5° 8% > 20°<br />
Taylor N. 2002 3.7° 14% > 5°<br />
Becker et al. 2004 15 13% -20% > 13°<br />
Chernyak D. 2004 51 OD: 2.0° +/- 2.9<br />
OS: 2.2° +/- 3.0<br />
0° - 7°<br />
0° - 9°<br />
SMI GmbH 2.8° +/- 3.6 0° - 9.4°<br />
21% > 5°<br />
J. Wolff
Iris Recognition 3-D Eyetracker<br />
AAD 2007<br />
theoretical effects of axis misalignement on astigmatism<br />
correction*<br />
• 4° => 14% undercorrection of astigmatism<br />
• 6° => 20% undercorrection of astigmatism<br />
• 8° => 25% undercorrection of astigmatism<br />
• 16° => 50% undercorrection of astigmatism<br />
=> 30° off = keine Wirkung der <strong>torische</strong>n <strong>IOL</strong><br />
* Stevens JD., EJCRS 1994;4:310-318<br />
J. Wolff
Implantationstechnik<br />
AAD 2007<br />
temp. Schnitt 2,8 mm<br />
Rhexisgröße 5,5 mm<br />
High Vacuum Phakoemulsifikation<br />
Implantation der <strong>IOL</strong> mit Injektor<br />
Rotation der <strong>IOL</strong> auf gewünschte Markierung:<br />
Methylenblaumarkierung, Fotodokumentation, Bildschirmfolie,<br />
Astigmatismusscheibe nach Hartmann<br />
Rhexis sollte komplett der Linsenvorderfläche aufliegen<br />
J. Wolff
Implantationstechnik<br />
Positionierung der <strong>IOL</strong>:<br />
Mendez Marker<br />
Bildschirmfolie<br />
Astigmatismusscheibe<br />
AAD 2007<br />
n. Hartmann<br />
J. Wolff
Prinzip der <strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong><br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
Torische <strong>IOL</strong>: Rayner 571 T<br />
Astigmatismus PräOP / PostOP (6 Wochen)<br />
Astigmatismus<br />
AAD 2007<br />
8<br />
7<br />
6<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
1 2 3 4 5<br />
Patient<br />
PräOP<br />
PostOP<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Rayner <strong>IOL</strong>:<br />
- Rotationsstabilität nach 1 Monat:<br />
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Humanoptics <strong>IOL</strong> MS 6116 TU (58 Augen)<br />
- Rotationsstabilität nach >3 Mo. u. 10° Grad<br />
- Nachrotation in 5% nach 3-6 Wochen<br />
G. Gerten: Torische Intraokularlinsen, Ophthalmochirurgie 17: 191-198 (2005)<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen<br />
AAD 2007<br />
Acritec Toric:<br />
- Rotationsstabilität 5-9 Monaten:<br />
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Literatur<br />
Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: Correcting astigmatism while<br />
controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994;20:523-526.<br />
Patel CK, Ormonde S, Rosen PH, Bron AJ. Postoperative intraocular lens rotation: A<br />
randomized comparison of plate and loop haptic implants. Ophthalmology.<br />
1999;106:2190-2196.<br />
Ruhswurm I, et al. Astigmatism correction with foldable toric intraocular lens in cataract<br />
patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:1022-1027.<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
<strong>torische</strong> Intraokularlinsen: Literatur<br />
• De Silva DJ, Ramkissoon YD et al. Evaluation of a toric intraocular lens with a Z-haptic.<br />
J Cataract Refract Surg 2006; 32:1492-1498<br />
• Warlo I, Krummenauer F et al. Rotational stability in intraocular lenses with C-loop haptics<br />
versus Z haptics in cataract surgery Prospektiver randomisierter Vergleich. Ophthalmologe<br />
2005; 102 (10): 987-92<br />
• Gerten G. Torische Intraokularlinsen Patientenauswahl, Ergebnisse,<br />
Komplikationsmanagement. Ophthalmo-Chirurgie 2005; 17: 191-198<br />
• Viestenz A, Küchle M et al. Torische Kunstlinsen zur Korrektur eines persistierenden<br />
kornealen Astigmatismus nach perforierender Keratoplastik. Ophthalmologe 2005;<br />
102(2):148-52<br />
• Buchwald H-J, Lang G K et al. Kataraktoperation mit Implantation <strong>torische</strong>r Silikonlinsen bei<br />
hohem Astigmatismus nach Keratoplastik. Klein Montasbl Augenheilkd 2004;221: 489-494<br />
AAD 2007<br />
J. Wolff
AAD 2007<br />
Zusammenfassung<br />
effektive <strong>Astigmatismuskorrektur</strong><br />
hoch zufriedene Patienten<br />
Nachteil <strong>torische</strong> <strong>IOL</strong>: hohe Kosten<br />
postoperative Drehung ist abhängig von:<br />
Rhexisgröße, Kapselsackgröße, Linsenkonfiguration<br />
J. Wolff