- Seite 1:
Kabelkatalog Cable Catalogue
- Seite 5 und 6:
Sehr geehrte Damen und Herren, Sie
- Seite 7 und 8:
In der TKD KABEL GmbH vereinigt sic
- Seite 9 und 10:
Hinter unserem Erfolg steht die sta
- Seite 11 und 12:
FI IE GB BE FR ES PT NL DK EE LT PL
- Seite 13 und 14:
Weltweit sind Leistungsbeweise der
- Seite 15 und 16:
Zum Start der Suche werden Artikeln
- Seite 17:
“Don’t waste a lot of time sear
- Seite 20 und 21:
Inhalt 01 Flexible Maschinensteuerl
- Seite 22 und 23:
Inhalt 03 BUS-, LAN-, Koax- ,Video-
- Seite 24 und 25:
Inhalt 05 Systemorientierte Leitung
- Seite 26 und 27:
Inhalt 08 Temperaturbeständige Lei
- Seite 28 und 29:
Inhalt Contents 14 Spiralkabel 14 S
- Seite 30 und 31:
Stichwortverzeichnis Seite Installa
- Seite 32 und 33:
Stichwortverzeichnis Seite Schwere
- Seite 34 und 35:
Index H K page Halogen-free single
- Seite 36:
Index SiF/GL page 08.04.01 SiFv 08.
- Seite 40 und 41:
01 Flexible Maschinensteuerleitunge
- Seite 42 und 43:
ÖPVC-JB/OB Anwendung als Energie,
- Seite 44 und 45:
ÖPVC-JB/OB-YCY Anwendung als Energ
- Seite 46 und 47:
ÖPVC-JB/OB-YSY Anwendung als Energ
- Seite 48 und 49:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ ÖPVC-JZ/OZ Anwendung a
- Seite 50 und 51:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ-YCY Anwendung als Energ
- Seite 52 und 53:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ-CY Anwendung als Energi
- Seite 54 und 55:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ-YSY Anwendung als Energ
- Seite 56 und 57:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ ÖPVC-JZ/OZ 0,6/1kV sch
- Seite 58 und 59:
ÖPVC-JZ/OZ-YCY 0,6/1kV schwarz sch
- Seite 60 und 61:
2YSL(St)CY-J 0,6/1 kV EMV, transpar
- Seite 62 und 63:
2YSL(St)CY-J 0,6/1 kV EMV-3 PLUS, t
- Seite 64 und 65:
H05VV5-F H05VV5-F Anwendung als Ene
- Seite 66 und 67:
H05VVC4V5-K Anwendung als Energie-,
- Seite 68 und 69:
Multinorm H05VV5-F HAR/UL/CSA Anwen
- Seite 70 und 71:
Multinorm-CY H05VVC4V5-K H05VVC4V5-
- Seite 72 und 73:
2-Norm (H)05VV5-F UL/CSA Anwendung
- Seite 74 und 75:
2-Norm-CY (H)05VVC4V5-K (H)05VVC4V5
- Seite 76 und 77:
FLAME-JZ/OZ-H FRNC FRNC Anwendung a
- Seite 78 und 79:
FLAME-JZ/OZ-CH FRNC FRNC Anwendung
- Seite 80 und 81:
PUR (N)YMH11YÖ (N)YMH11YÖ GRAU /
- Seite 82 und 83:
H05BQ-F, H07BQ-F Anwendung als Ger
- Seite 84 und 85:
Highflex LiFY Anwendung als hochfle
- Seite 86 und 87:
ESUY Kupfer-Erdungsseil Anwendung a
- Seite 88 und 89:
SOLAIRFLEX - S - 150H FRNC + UV 0,6
- Seite 90 und 91:
SOLAIRFLEX - ECO - 120H FRNC + UV 0
- Seite 93 und 94:
Kapitelbezeichnung Elektronikleitun
- Seite 95 und 96:
Inhalt 02 Elektronikleitungen (NF),
- Seite 97 und 98:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 99 und 100:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 101 und 102:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 103 und 104:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 105 und 106:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 107 und 108:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 109 und 110:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 111 und 112:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 113 und 114:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 115 und 116:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 117 und 118:
Abmessung n x AWG mm² dimension n
- Seite 119 und 120:
Abmessung n x AWG mm² dimension n
- Seite 121 und 122:
Abmessung n x 2 x AWG mm² dimensio
- Seite 123 und 124:
Abmessung n x 2 x AWG mm² dimensio
- Seite 125 und 126:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 127 und 128:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 129 und 130:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 131 und 132:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 133 und 134:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 135 und 136:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 137 und 138:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 139 und 140:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 141 und 142:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 143 und 144:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C / 300
- Seite 145 und 146:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C / 300
- Seite 147 und 148:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C +90°C
- Seite 149 und 150:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C +90°C
- Seite 151 und 152:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C +90°C
- Seite 153 und 154:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C / 300
- Seite 155 und 156:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C +90°C
- Seite 157 und 158:
Instrumentationskabel +90°C / 300
- Seite 159 und 160:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 161 und 162:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 163 und 164:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 165 und 166:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 167:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm dimension n x
- Seite 170 und 171:
03 BUS-, LAN-, Koax-, Video-Leitung
- Seite 172 und 173:
INTERBUS und INTERBUS HYBRID (RBC)
- Seite 174 und 175:
INTERBUS und INTERBUS HYBRID (RBC)
- Seite 176 und 177:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® L2-D 100 -
- Seite 178 und 179:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® für Erdver
- Seite 180 und 181:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® für Energi
- Seite 182 und 183:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® für feste
- Seite 184 und 185:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® für Energi
- Seite 186 und 187:
PROFIBUS ® PROFIBUS ® 2462 C-PVC-
- Seite 188 und 189:
SAFETY-BUS C-H-UL 3 x 0,75 mm² 3 x
- Seite 190 und 191:
Profinet ® Profinet ® PVC cUL 100
- Seite 192:
Profinet ® Profinet ® SK-PUR FC F
- Seite 195 und 196:
für normale Anwendung Abmessung n
- Seite 197 und 198:
für Energieführungsketten Abmessu
- Seite 199 und 200:
für feste Verlegung - Trunk & Drop
- Seite 201 und 202:
für Energieführungsketten - Trunk
- Seite 204 und 205:
LAN-Kabel CAT.5 - PVC, 100 MHz für
- Seite 206 und 207:
LAN-Kabel CAT.7-H, 600 MHz für str
- Seite 208 und 209:
RG Koaxial-Kabel 50 Ω nach UL-Sta
- Seite 210 und 211:
RG Koaxial-Kabel TEFLON ® 50/75/95
- Seite 212 und 213:
Video Koaxial-Kabel 75 Ω Anwendun
- Seite 214:
Video Koaxial-Kabel TEFLON ® 50/75
- Seite 217 und 218:
n x AWG 2807 Abmessung n x AWG dime
- Seite 219 und 220:
n x AWG 2807 RFBL UL Abmessung n x
- Seite 221 und 222:
Kapitelbezeichnung Steuerschlepplei
- Seite 223 und 224:
Inhalt 04 Steuer- und Datenleitunge
- Seite 225 und 226:
schleppkettentauglich capable for d
- Seite 228 und 229:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 230 und 231:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für erhöh
- Seite 232 und 233:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 234 und 235:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 236 und 237:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für erhöh
- Seite 238 und 239:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 240 und 241:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 242 und 243:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 244 und 245:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ®
- Seite 246 und 247:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für erhöh
- Seite 248 und 249:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 250 und 251:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für erhöh
- Seite 252 und 253:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 254 und 255:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ®
- Seite 256 und 257:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 258 und 259:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 260 und 261:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 262 und 263:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 264 und 265:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 266 und 267:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 268 und 269:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für normal
- Seite 270 und 271:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 272 und 273:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 274 und 275:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 276 und 277:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 278 und 279:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 280 und 281:
Systemorientierte Leitungen (auch m
- Seite 282 und 283:
05 Systemorientierte Leitungen (auc
- Seite 284 und 285:
Übersicht schleppkettentauglich ca
- Seite 286 und 287:
Übersicht schleppkettentauglich ca
- Seite 288:
Übersicht Einsatzparameter in Ener
- Seite 291 und 292:
für normale Anforderungen Abmessun
- Seite 293 und 294:
für flexible und feste Verlegung,
- Seite 295 und 296:
für hohe Anforderungen nach SIEMEN
- Seite 297 und 298:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 299 und 300:
für hohe Anforderungen 4 Versorgun
- Seite 301 und 302:
KAWEFLEX ® KAWEFLEX ® für hohe A
- Seite 303 und 304:
für hohe Anforderungen 4 Versorgun
- Seite 305 und 306:
für hohe Anforderungen 4 Versorgun
- Seite 307 und 308:
für hohe Anforderungen 4 Versorgun
- Seite 309 und 310:
für flexiblen Einsatz und feste Ve
- Seite 311 und 312:
für hohe Anforderungen schleppkett
- Seite 313 und 314:
für hohe Anforderungen schleppkett
- Seite 315 und 316:
nach SIEMENS Standard 6FX8008-1BD81
- Seite 317 und 318:
für erhöhte Anforderungen schlepp
- Seite 319 und 320:
Kapitelbezeichnung PVC-Flachleitung
- Seite 321 und 322:
Inhalt 06 Kran-, Fördermittel- und
- Seite 323 und 324:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 325 und 326:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 327 und 328:
YFLY KYFLY Abmessung n x mm² dimen
- Seite 329 und 330:
YCFLY Abmessung n x mm² dimension
- Seite 331 und 332:
H05VVD3H6-F KYFLTY KYFLTFY Abmessun
- Seite 333 und 334:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 335 und 336:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 337 und 338:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 339 und 340:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 341 und 342:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 343 und 344:
KYSTY KYSTUY Abmessung n x mm² dim
- Seite 345 und 346:
YSSTY YSSTCY Abmessung n x 2 x mm²
- Seite 347 und 348:
KYSSTUY KYSTCY KYSTCUY Abmessung n
- Seite 349 und 350:
Abmessung n x 2 x AWG mm² dimensio
- Seite 351 und 352:
KHSTUH K12YSTU11Y Abmessung n x mm
- Seite 353 und 354:
K12YSTCU11Y Abmessung n x mm² dime
- Seite 355 und 356:
Abmessung n x 2 x AWG mm² dimensio
- Seite 357 und 358:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 359 und 360:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 361 und 362:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 363 und 364:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 365 und 366:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 367 und 368:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 369 und 370:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 371 und 372:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 373 und 374:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 375 und 376:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 377 und 378:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 379 und 380:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 381 und 382:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 383 und 384:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 385 und 386:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 387 und 388:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 389 und 390:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 391 und 392:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 393 und 394:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 395 und 396:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 397 und 398:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 399 und 400:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 401 und 402:
Kapitelbezeichnung Leichte- und mit
- Seite 403 und 404:
Inhalt 07 Gummischlauchleitungen 07
- Seite 405 und 406:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 407 und 408:
H07RN-F Abmessung n x mm² dimensio
- Seite 409 und 410:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 411 und 412:
halogenfrei Abmessung n x mm² dime
- Seite 413 und 414:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 415 und 416:
H01N2-D H01N2-E Abmessung n x mm²
- Seite 417 und 418:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 419 und 420:
für Nutzwasser, rund Abmessung n x
- Seite 421 und 422:
für Nutzwasser, flach Abmessung n
- Seite 423 und 424:
für Trinkwasser, rund Abmessung n
- Seite 425:
für Trinkwasser, flach Abmessung n
- Seite 428 und 429:
08 Temperaturbeständige Leitungen
- Seite 430 und 431:
H05/07G-K Anwendung als wärmebest
- Seite 432 und 433:
SiD; SiD/GL; SiF; SiF/GL; SiF/GL; S
- Seite 434 und 435:
ZKSi, HZLSi, SiL ZKSi Zündkabel, H
- Seite 436 und 437:
SIHF-J Anwendung als wärme- und k
- Seite 438 und 439:
SIHF-J+C SIHF-J+C Anwendung als wä
- Seite 440 und 441:
SIHF-J / GLP Anwendung als wärme-
- Seite 442 und 443:
H05SS-F Anwendung als harmonisierte
- Seite 444 und 445:
THERM-205-FEP-EA Anwendung als wär
- Seite 446 und 447:
THERM-205-FEP Anwendung als wärme-
- Seite 448 und 449:
THERM-205-FEP+C Anwendung als wärm
- Seite 450 und 451:
THERM-205-FEP/GL Anwendung als wär
- Seite 452 und 453:
THERM-205-FEP/GLP Anwendung als wä
- Seite 454 und 455:
THERM-260-PTFE-EA Anwendung als wä
- Seite 456 und 457:
THERM-260-PTFE Anwendung als wärme
- Seite 458 und 459:
THERM-260-PTFE+C Anwendung als wär
- Seite 460 und 461:
THERM-260-PTFE/GL Anwendung als wä
- Seite 462 und 463:
THERM-260-PTFE/GLP Anwendung als w
- Seite 464 und 465:
THERM-350-GLI/GL-EA Anwendung als w
- Seite 466 und 467:
THERM-350-GLH/GL Anwendung als wär
- Seite 468 und 469:
THERM-350-GLH/GLP Anwendung als wä
- Seite 470 und 471:
THERM-1250-GLI/GA-EA Anwendung als
- Seite 472 und 473:
THERM-1250-GLIGAHGLI/GAP Anwendung
- Seite 474 und 475:
THERM-1550-FLAME Anwendung als wär
- Seite 477 und 478:
Kapitelbezeichnung PVC-Verdrahtungs
- Seite 479 und 480:
Inhalt 09 Kabel und Leitungen für
- Seite 481 und 482:
LiYvz H05V-K H07V-K Abmessung mm²
- Seite 483 und 484:
Abmessung mm² dimension mm² Auße
- Seite 485 und 486:
Abmessung AWG mm² dimension AWG mm
- Seite 487 und 488:
LiHvz H05Z-K H07Z-K H05Z-U Abmessun
- Seite 489 und 490:
Abmessung mm² dimension mm² Auße
- Seite 491 und 492:
NYM-J NYM-O Abmessung n x mm² dime
- Seite 493 und 494:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 495 und 496:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 497 und 498:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 499 und 500:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 501 und 502:
heizleitung tkd 0915 hl-S Typenbeis
- Seite 503 und 504:
heizleitung tkd 0915 hl-l Typenbeis
- Seite 505 und 506:
heizleitung tkd 0915 hl-M Typenbeis
- Seite 507 und 508:
Frost protection +5 °C for self-re
- Seite 509 und 510:
Loss of heat on pipes in W/m at 10
- Seite 511 und 512:
Accessories for heating cables 09.1
- Seite 513 und 514:
Kapitelbezeichnung Datenübertragun
- Seite 515 und 516:
Inhalt 10 Kraftstoffbeständige Lei
- Seite 517 und 518:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 519 und 520:
Außen-Ø mm outer Ø mm Cu-Zahl kg
- Seite 521 und 522:
LIYCYÖ Abmessung n x mm² dimensio
- Seite 523 und 524:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 525 und 526:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 527 und 528:
Abmessung n x 2 x mm² dimension n
- Seite 529:
Abmessung n x mm² dimension n x mm
- Seite 532 und 533:
11 Schiffs- und Marinekabel Ship an
- Seite 534 und 535:
Schiffs- und Marinekabel 11.2 MARIN
- Seite 536 und 537:
12 Lichtwellenleiterkabel (LWL) Fib
- Seite 538:
POF SIMPLEX PE 980/1000 Anwendung D
- Seite 541 und 542:
Fibre optics cables, coding as per
- Seite 543 und 544:
TWENOPTO Auszug aus unserem Lieferp
- Seite 545 und 546:
Inhalt TWENKARAIL Bahn-, Nachrichte
- Seite 547 und 548:
Inhalt Spiralkabel Seite Kapitelbez
- Seite 549 und 550:
aus H05VV-F Abmessung n x mm² dime
- Seite 551 und 552:
aus H05RN-F und H07RN-F Abmessung n
- Seite 553 und 554:
aus H05BQ-F / H07BQ-F Leiterklasse
- Seite 555 und 556:
aus H05BQ-F / H07BQ-F Leiterklasse
- Seite 557 und 558:
Li12Y11Y - ungeschirmt Abmessung n
- Seite 559 und 560:
Li12YD11Y - geschirmt Abmessung n x
- Seite 561 und 562:
Inhalt Überblick TEKAPLUS ® Kabel
- Seite 563 und 564:
15.20.xx 15.21.xx 15.22.xx 15.16.xx
- Seite 565 und 566:
15.30.xx 15.31.xx 15.32.xx 15.30.xx
- Seite 567 und 568:
15.55.xx 15.56.xx 15.57.xx 15.55.xx
- Seite 569 und 570:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 571 und 572:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 573 und 574:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 575 und 576:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 577 und 578:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 579:
Aufzugkomponenten Elevator componen
- Seite 582 und 583:
Technischer Anhang Kurzzeichen Kabe
- Seite 584 und 585:
Technischer Anhang Kurzzeichen Fern
- Seite 586 und 587:
Technischer Anhang Kurzzeichen Star
- Seite 588 und 589:
Technischer Anhang Kurzzeichen Harm
- Seite 590 und 591:
Technischer Anhang Kurzzeichen Harm
- Seite 592 und 593:
Technischer Anhang Aderkennzeichnun
- Seite 594 und 595:
Technischer Anhang Aderkennzeichnun
- Seite 596 und 597:
Technischer Anhang Aderkennzeichnun
- Seite 598 und 599:
Technischer Anhang Aderkennzeichnun
- Seite 600 und 601:
Technischer Anhang Drähte und Litz
- Seite 602 und 603:
Technischer Anhang Drähte und Litz
- Seite 604 und 605:
Technischer Anhang Belastbarkeit Gr
- Seite 606 und 607:
Technischer Anhang Belastbarkeit Re
- Seite 608 und 609:
Technischer Anhang Eigenschaften Ei
- Seite 610 und 611:
Technischer Anhang Chemische Bestä
- Seite 612 und 613:
Technischer Anhang Biegeradien Klei
- Seite 614 und 615:
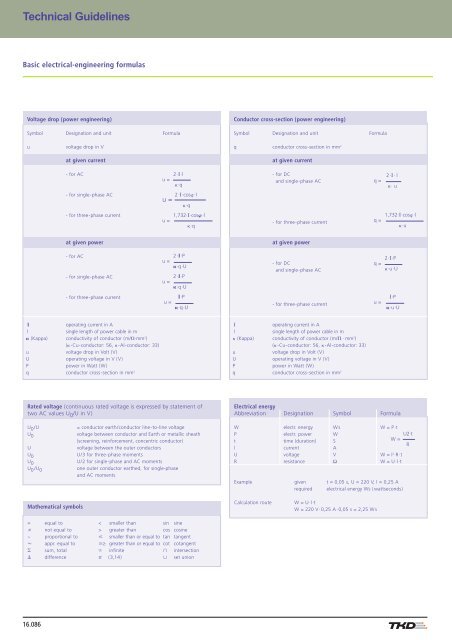
Technischer Anhang Grundformeln der
- Seite 616 und 617: Technischer Anhang Stichwortverzeic
- Seite 618 und 619: Technischer Anhang Stichwortverzeic
- Seite 620 und 621: Technischer Anhang Stichwortverzeic
- Seite 622 und 623: Technischer Anhang Britische und US
- Seite 624 und 625: Technischer Anhang Übersicht von H
- Seite 626 und 627: Technischer Anhang Registrierte War
- Seite 628 und 629: Technischer Anhang Einbauempfehlung
- Seite 630 und 631: Technischer Anhang Montage-Hinweise
- Seite 632 und 633: Technischer Anhang Allgemeine Zahlu
- Seite 634 und 635: Technical Guidelines Codes Cables A
- Seite 636 und 637: Technical Guidelines Codes Telecomm
- Seite 638 und 639: Technical Guidelines Codes High-vol
- Seite 640 und 641: Technical Guidelines Codes Harmoniz
- Seite 642 und 643: Technical Guidelines Codes Harmoniz
- Seite 644 und 645: Technical Guidelines Core marking C
- Seite 646 und 647: Technical Guidelines Core marking M
- Seite 648 und 649: Technical Guidelines Core coding TK
- Seite 650 und 651: Technical Guidelines Core marking C
- Seite 652 und 653: Technical Guidelines Wires and stra
- Seite 654 und 655: Technical Guidelines Wires and stra
- Seite 656 und 657: Technical Guidelines Current-carryi
- Seite 658 und 659: Technical Guidelines Current-carryi
- Seite 660 und 661: Technical Guidelines Properties Pro
- Seite 662 und 663: Technical Guidelines Chemical Resis
- Seite 664 und 665: Technical Guidelines Bending radii
- Seite 668 und 669: Technical Guidelines Index Definiti
- Seite 670 und 671: Technical Guidelines Index Definiti
- Seite 672 und 673: Technical Guidelines Index, Determi
- Seite 674 und 675: Technical Guidelines British and US
- Seite 676 und 677: Technical Guidelines KTG Cable Drum
- Seite 678 und 679: Technical Guidelines Registered Tra
- Seite 680 und 681: Technical Guidelines Recommendation
- Seite 682 und 683: Technical Guidelines Assembly detai
- Seite 684: Technical Guidelines Terms of Deliv