DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY ABDUL WALI KHAN ... - AWKUM
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY ABDUL WALI KHAN ... - AWKUM
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY ABDUL WALI KHAN ... - AWKUM
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>DEPARTMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
<strong>ABDUL</strong> <strong>WALI</strong> <strong>KHAN</strong> UNIVERSITY, MARDAN, PALOSA<br />
CAMPUS CHARSADDA<br />
Scheme of Studies for BS Chemistry Four Years Program<br />
1
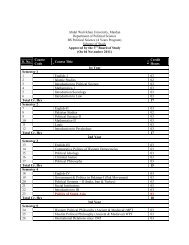
SCHEME <strong>OF</strong> STUDIES, BS (4-YEAR) PROGRAM IN <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Department of Chemistry Palosa Campus Charsadda, <strong>AWKUM</strong><br />
Course Title Credit hours<br />
Semester - I Theory Practical<br />
ENG-100 English-I<br />
(Functional)<br />
3 0<br />
GEN-100 General-I 3 0<br />
GEN-101 General-II<br />
MATH-100<br />
3 0<br />
Mathematics-I<br />
Mathematics-<br />
3 0<br />
I/Functional Biology<br />
COMP-100 Computer<br />
and Its Applications in<br />
Chemistry<br />
3 0<br />
CHEM-151 Inorganic<br />
Chemistry<br />
3 1<br />
Total 18 1<br />
Semester - II Theory Practical<br />
ENG-200 English-II<br />
(Functional)<br />
3 0<br />
GEN-200 Islamic<br />
Studies / Ethics<br />
2 0<br />
GEN-201 General-III<br />
MATH-200<br />
Mathematics-<br />
3 0<br />
II/Functional<br />
Biology/University<br />
Optional<br />
3 0<br />
STAT-100 Statistics 3 0<br />
CHEM-161 Organic<br />
Chemistry<br />
3 1<br />
Total 17 1<br />
Semester - III Theory Practical<br />
ENG-300 English-III<br />
(Report Writing)<br />
3 0<br />
GEN-300 Pakistan<br />
Studies<br />
2 0<br />
GEN-301 General-IV 3 0<br />
GEN-302 General-V<br />
CHEM-141<br />
3 0<br />
Environmental<br />
Chemistry<br />
2 0<br />
CHEM-171 Physical<br />
Chemistry<br />
3 1<br />
Total 16 1<br />
Semester - IV Theory Practical<br />
ENG-400 English-IV /<br />
University Optional<br />
3 0<br />
2
GEN-400 General-VI 3 0<br />
GEN-401 General-VII 3 0<br />
CHEM-111 Analytical<br />
Chemistry<br />
2 0<br />
CHEM-121 Industrial<br />
2 0<br />
Chemistry<br />
CHEM-131<br />
Biochemistry<br />
2 0<br />
Total 15 0<br />
Course Title Credit hours<br />
Semester - V Theory Practical<br />
CHEM-251 Inorganic Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-261 Organic Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-271 Physical Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-211 Analytical-/<br />
CHEM-231 Bio-Chemistry<br />
3 1<br />
Total 12 4<br />
Semester - VI Theory Practical<br />
CHEM-351 Inorganic Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-361 Organic Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-371 Physical Chemistry 3 1<br />
CHEM-311 Analytical-/<br />
CHEM-331 Bio- Chemistry<br />
3 1<br />
Total<br />
Semester - VII: Specialization<br />
12 4<br />
(Inorganic/<br />
Organic/Physical/Applied/<br />
Analytical/Bio Chemistry)<br />
Theory Practical<br />
Paper-I 3 0<br />
Paper-II 3 0<br />
Paper-III 3 0<br />
Practical-I 0 1<br />
Elective Course-I (other than the<br />
field of specialization)<br />
Research Project / Advanced<br />
3 0<br />
Practical /<br />
Position Paper (literature survey)<br />
0 2<br />
Total<br />
Semester - VIII : Specialization<br />
12 3<br />
(Inorganic/ Organic/Physical/<br />
Applied/<br />
Analytical-/Bio-Chemistry<br />
Theory Practical<br />
Paper - IV 3 0<br />
Paper - V 3 0<br />
Paper - VI 3 0<br />
Practical - II 0 1<br />
Elective Course - II (other than the<br />
field of specialization)<br />
3 0<br />
3
Research Project / Advanced<br />
Practical / Position Paper (write-<br />
up)<br />
0 2<br />
Total 12 3<br />
Total Credit Hours: 131<br />
The list of general courses was also reviewed and approved as follows:<br />
List of General Courses:<br />
(Proposed in NCRC special meeting in Chemistry)<br />
1. Social Psychology<br />
2. Community Development<br />
3. Environmental Sciences<br />
4. Principles of management<br />
5. Logic and Reasoning<br />
6. Teaching and Learning<br />
7. Social Issues of Pakistan<br />
8. Entrepreneurship<br />
9. Human Resource Management<br />
10. Basic Financial Management<br />
11. History of Human Civilization<br />
12. History of Science<br />
Any other, including supportive science courses other than chemistry, depending upon the<br />
expertise available.<br />
OR<br />
4
<strong>DEPARTMENT</strong> <strong>OF</strong> <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
PALOSA CAMPUS <strong>ABDUL</strong> <strong>WALI</strong> <strong>KHAN</strong> UNIVERSITY<br />
MARDAN<br />
Scheme of Studies for M.Sc Two Years Program<br />
6
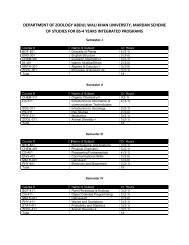
SCHEME <strong>OF</strong> STUDIES M.Sc TWO YEARS PROGRAM IN <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong>,<br />
PALOSA CAMPUS <strong>AWKUM</strong><br />
Semester-I Semester-II<br />
S.NO Paper Cr. Hrs S.NO Paper Cr. Hrs<br />
1 Analytical Chem. paper-I 2-0 1 Analytical Chem. paper-II 2-1<br />
2 Biochemistry paper-I 2-0 2 Biochemistry paper-II 2-1<br />
3 Inorganic Chem. paper-I 3-1 3 Inorganic Chem. paper-II 3-1<br />
4 Organic Chem. paper-I 3-1 4 Organic Chem. paper-II 3-1<br />
5 Physical Chem. paper-I 3-1 5 Physical Chem. paper-II 3-1<br />
6 Mathematics 2-0<br />
Total 18 Total 18<br />
Semester-III (Specialization) Semester-IV (Specialization)<br />
S.NO Paper Cr. Hrs S.NO Paper Cr. Hrs<br />
1 Env. /Computational Chem.<br />
Paper-I<br />
2-1 1 Env. /Computational<br />
Chem. Paper-II<br />
2 Specialization Paper-I 3 2 Specialization Paper-V 3<br />
3 Specialization Paper-II 3 3 Specialization Paper-VI 3<br />
4 Specialization Paper-III 3 4 Specialization Paper-VII 3<br />
5 Specialization Paper-IV 3 5 Specialization Paper-VIII 3<br />
6 Special practical/research 3 6 Special practical/research 3<br />
Total 18 Total 18<br />
Specialization papers: Inorganic/analytical, Biochemistry, Organic and Physical<br />
Chemistry, the student will have to opt for one field of Specialization.<br />
7<br />
03
COURSE OUTLINES <strong>OF</strong> M.Sc TWO YEARS PROGRAM IN <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong>,<br />
<strong>AWKUM</strong><br />
M.Sc. 1 st –Year, Semester -I<br />
Course Title: Analytical Chemistry Paper-I Code: CHEM-511<br />
Credit Hours: 02 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Introduction to Analytical Chemistry, Classical methods of analysis, Analytical<br />
Sampling: Data handling: Stoichiometric calculations, Chemical Equilibrium, acid/base,<br />
Solubility and Complexation equilibria, Electroanalytical techniques, Classifications of<br />
Electroanalytical techniques, Potentiometry and conductometry with applications,<br />
Introduction to spectroscopic techniques.<br />
Analytical Chemistry Practical Cr. Hrs: 01<br />
1. To determine the exact weight of materials and to analyze replicate measurement<br />
statistically.<br />
2. To calibrate Volumetric Apparatus and to investigate errors in delivered volume.<br />
3. To determine the concentration of strong acid solution by conductometric<br />
titration.<br />
4. To determine the individual concentration of acid in the given binary mixture of<br />
strong/weak acid condutometrically.<br />
5. To evaluate Ksp for lead iodate by conductance method.<br />
6. To determine the solubility product of Cadmium iodate titrimetrically.<br />
7. To determine the constancy of the solubility product.<br />
8. To estimate Ca ++ concentration in drinking water by EDTA Complexometric<br />
titration.<br />
9. To determine the concentration of strong acid potentiometrically using first and<br />
second derivative method.<br />
10. To determine pKa for the given set weak acids by potentiometric method.<br />
11. To show independence of solubility on the amount of undissolved species.<br />
12. To establish the stochiometric relation for the precipitation of silver chloride.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
� Gary D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons.<br />
� Douglas A. Skoog, Donald M. West, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch,<br />
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Reinhote, New York.<br />
� Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Chemical Analysis,<br />
� I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
� David Harvey, Modern Analytical Chemistry<br />
Course Title: Biochemistry Paper-I Code: CHEM- 531<br />
Credit Hours: 02 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Introduction, Importance and the scope of Biochemistry. Forms, functions and<br />
8
ief classification of prokaryotes. Cellular architecture and diversity of eukaryotes.<br />
Physical aspects of biochemistry<br />
Water, ionization of water, pH, Acid-base reactions, Buffers.<br />
Water<br />
Structure, physical properties & importance of water. Unique properties of carbon.<br />
Nature of organic matter. Isomerism. General reactions of different functional groups.<br />
Biologically important organic compounds / Solvents.<br />
Biomolecules<br />
Overview of Biomolecules and their structures including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids<br />
and nucleic acids.<br />
Nucleic Acids<br />
Nucleosides and Nucleotides, Purines and Pyrimidines. Introduction to DNA, RNA.<br />
Metabolism Pathways<br />
Glycolysis, Tricarboxylic acid Cycle, Gluconeogenesis.<br />
Evolution of life<br />
Prebiotic molecular evolution and rise of living systems. Review of the variety and<br />
ecology of the living world. Use and significance of Radioisotopes in Biochemistry.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Voet, D. and J. G. Voet,. Biochemistry, John Wiley and Sons, New York (2001).<br />
2. Text Book of Biochemistry (1970) by E. West & W. Todd Macmillan.<br />
3. Biochemistry. (1999) 3rd Ed. by C. K. Mathews, K. E. Van Holde, & K.G. Ahern.<br />
Prentice Hall.<br />
4. Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry, 27th Ed. by R.K. Murray, D.K. Grannar, V.W.<br />
Rodwell. McGraw Hill.<br />
5. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (2008) 5th Ed. by D. L. Nelson, M. M. Cox. W.<br />
H. Freeman Publishers<br />
Biochemistry Practical Credit Hours: 01<br />
Marks: 50<br />
1. Preparation of solutions<br />
� Preparation of Percent solutions (W/V, V/V and milligram percent).<br />
9
� Preparation of Molar Solutions.<br />
� Preparation of Normal / equivalent solutions.<br />
� Preparation of Molal solutions.<br />
� Preparation of ppm and ppb solutions.<br />
� Preparation of solution from given stock solution by dilution method.<br />
2. Standardization of given solution.<br />
3. Determination of pH of different samples and body fluids.<br />
(pH meter, pH strip/paper and Titrimetric method)<br />
4. Preparation of Buffers:Phosphate buffer, Acetate buffer, Citrate buffer, Universal<br />
buffer<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Wilson, A. Practical Biochemistry: Principle and techniques (2000).<br />
2. Swotzer, Experiment Biochemistry theory and exercises in fundamental method<br />
(2000).<br />
3. Dryer, R. L. and G. F. Lata, Experimental Biochemistry, Oxford University Press.<br />
4. Plummer, D. T., Introduction to Practical Biochemistry, , McGraw Hill Book Co.,<br />
New York (1986).<br />
5. Alexander, R. R., J. M Griggiths and M. L. Wikinson, Basic Biochemical<br />
Methods, John Wiley & Sons.<br />
6. Wooton, I. D. P., Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry, J&A Churchill.<br />
Course Title: Inorganic Chemistry Paper-1 Code: CHEM- 551<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Non Aqueous Solvents<br />
Classification of solvents, types of reactions in different solvents, effect of physical and<br />
chemical properties of solvents on reactions, detailed study of liquid NH3, liquid H2S,<br />
liquid HF and liquid SO2 as solvents.<br />
Coordination Compounds<br />
Study of coordination compounds regarding their historical back ground, nomenclature,<br />
geometry, theories i.e. Jorgensen theory, Werner's theory, valence bond theory, crystal<br />
field theory and molecular orbital theory. Properties of coordination compound i.e.<br />
10
magnetic properties, stability and stereochemistry. Techniques for studying coordination<br />
compounds and their applications.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. J.E. Huheey., E.A Keiter, and R.L. Keiter. “Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of<br />
Structure and Reactivity”, 4th Ed., Harper and Row, New York, 2001<br />
2. F.A. Cotton., G.Wilkinson, and P. L. Gaus. “Basic Inorganic Chemistry”, 3rd Ed.,<br />
Wiley, New York, 1995.<br />
3. F. Basolo. and R.C Johnson. “Coordination Chemistry” Tallahassee, Florida,<br />
1962.<br />
4. F.A. Cotton, G. Wilkinson, C. A. Murillo and M. Bochmann, “Advanced<br />
Inorganic Chemistry”, 6th Ed., Wiley-Intersceince, New York, 1999.<br />
5. A. K. Holliday, and A.G. Massey, "Inorganic Chemistry in Non-Aqueous<br />
Solvents", Pergamon Press, New York, 1990.<br />
6. E. M Larsen. “Transition Elements”, W. A. Benjamin Inc., 1995<br />
7. J. Bassette., G.H. Denney, and J. Mendham. “Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative<br />
Inorganic Analysis Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis” English<br />
Language Book Society, 4 th Edition, 1981.<br />
8. A. I. Vogel, “A Textbook of Micro and Semi-micro Qualitative Inorganic<br />
Analysis” Longman Green & Co. 1995.<br />
Inorganic Chemistry Practical<br />
Credit Hours: 01 Marks: 50<br />
1. Analysis of salts mixtures for anions and cations<br />
2. Preparation of at least four coordination compounds in a pure state<br />
3. Complexometric titrations<br />
Course Title: Organic Chemistry Paper- I Code: CHEM- 161<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Introduction to Organic Chemistry, chemistry of carbon compounds; organic chemistry, a<br />
historical perspective.<br />
Chemical Bonding and Properties of Organic Molecules<br />
Localized and delocalized chemical bonding; concept of hybridization leading to bond<br />
angles, bond lengths, bond energies and shape of organic molecules; dipole moment;<br />
11
inductive and field effects; resonance; aromaticity; tautomerism; hyperconjugation;<br />
hydrogen bonding; acids and bases; factors affecting the strengths of acids and bases.<br />
Stereochemistry<br />
Introduction to Stereochemistry, stereoisomerism, geometrical isomerism, E/Z notations,<br />
chirality, enantiomers and diasteromers, meso compounds, optical isomerism, optical<br />
activity and specific rotation, absulote configuration and relative configuration, R/S<br />
nomenclature, conformations and conformational analysis ethane, n-butane and cylohexane.<br />
Classes and Nomenclature of Organic Compounds<br />
Classification of organic compounds; development of systematic nomenclature of organic<br />
compounds; IUPAC nomenclature of hydrocarbons and heteroatom functional groups.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Clayden, J., Greeves, N., Warren, S. and Wothers, P., “Organic Chemistry”,<br />
Oxford University Press, New York.<br />
2. Loudon, G. M., “Organic Chemistry”, Oxford University Press, New York<br />
3. Sorrell, T. N., “Organic Chemistry”, Viva Books Private Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
4. Finar, I. L., “Organic Chemistry”, Vol. 1, Pearson Education, Delhi.<br />
5. Carey, F. A., “Organic Chemistry”, McGraw-Hill, New York.<br />
6. Ahluwalia, V. K. and Goyal, M., “A Text Book of Organic Chemistry”, Narosa<br />
Publishing House, New Delhi<br />
7. March, J., “Advanced Organic Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
8. Bansal, R. K., “Organic Reaction Mechanisms”, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing<br />
Company Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
9. Pine, S. H., “Organic Chemistry”, National Book Foundation, Islamabad.<br />
10. Bailey Jr., P. S. and Bailey, C. A., “Organic Chemistry-A Brief Survey of<br />
Concepts and Applications”, Prentice-Hall, New Jersey.<br />
Organic Chemistry Practical Marks: 50<br />
Credit Hours: 01<br />
1. Laboratory Ethics and safety measures<br />
2. Awareness about the toxic nature of chemicals and their handling, cleaning of<br />
glassware, safe laboratory operations<br />
3. Laboratory work illustrating topics covered in the lecture of Organic Chemistry<br />
Paper I<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Clarke, H. T., “A Handbook of Organic Analysis-Qualitative and Quantitative”,<br />
CBS Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi.<br />
2. Mann, F. G. and Saunders, B. C., “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Longman,<br />
London.<br />
3. Vogel, A. I., “Elementary Practical Organic Chemistry Part 3: Quantitative<br />
Organic Analysis”, Longman, London.<br />
12
4. Vishnoi, N. K., “Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry”, Vikas Publishing<br />
House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
5. Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G. and Tatchell, A. R., “Vogel’s<br />
Text Book of Practical Organic Chemistry”, National Book Foundation,<br />
Islamabad.<br />
6. Shriner, R. L., Hermann, C. K. F., Morrill, T. C., Curtin, D. Y. and Fuson, R. C.,<br />
“The Systematic Identification of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons,<br />
New York.<br />
7. Mendham, J., Denney, R. C., Barnes, J. D. and Thomas, M. J. K., “Vogel’s Text<br />
Book of Quantitative Chemical Analysis”, Pearson Education, New Delhi.<br />
8. Beckett, A. H. and Stenlake, J. B., “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, Athlone<br />
Press, London.<br />
Course Title: Physical Chemistry Paper-I Code: CHEM- 171<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Kinetic Theory of Gases<br />
Maxwell’s law of molecular velocities. Calculation of molecular velocities and binary<br />
collisions. Maxwell-Boltzmann’s law of energy distribution. Method for the<br />
determination of the Avogadro number (NA).<br />
Chemical Thermodynamics<br />
Relation of entropy and energy with equilibrium constant, and their dependence on<br />
temperature. Clausius-Clapeyron’s equation. Chemical potential. Partial molar quantities.<br />
Free energy change. Fugacity of gases.<br />
Chemical Kinetics<br />
Integrated rate laws: Third order reactions with same and different initial concentrations<br />
of reactants. Effect of temperature on the reaction rate. Elementary and complex<br />
reactions: opposing, parallel, consecutive bimolecular reactions and chain reactions.<br />
Steady state approximation, Lindemann’s theory of unimolecular reactions. Bimolecular<br />
collision theory, transition state theory.<br />
Physical Chemistry Practical<br />
Credit Hours: 01 Marks: 50<br />
1. Equilibrium constant of the KI � I 2 ���<br />
�KI<br />
3 reaction.<br />
2. Kinetics of saponification of ethyl acetate.<br />
3. Study of the adsorption isotherms of acetic acid-charcoal system.<br />
4. Determination of activation energy for the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of ethyl<br />
acetate.<br />
5. Determination of partial molar volumes.<br />
6. Characterization of the given compound by UV-Vis spectroscopy.<br />
13
Books Recommended<br />
1. Alberty, R. A., Robert J.S. and Moungi G. B. “Physical Chemistry”. 4 th<br />
ed, John<br />
Wiley and Sons (2004).<br />
2. Ball, D W., “Physical Chemistry” 1 st<br />
ed., Brooks/Cole Co. Inc. (2003).<br />
3. Engel, Thomas and .Reid p., “Thermodynamics, Statistical Thermodynamics, and<br />
Kinetics” 1 st<br />
ed., Benjamin Cummings (2006).<br />
4. James K. and Wothers, P., “Why Chemical Reactions Happen”. Oxford<br />
University Press (2003).<br />
5. Smith, E. Brain, “Basic Chemical Thermodynamics” 5 th<br />
ed., Imperial College<br />
Press (2004).<br />
6. Stephen B. R., Rice S. A. and Roses J., “Physical Chemistry”2 nd<br />
ed., Oxford<br />
University Press (2000).<br />
7. Jurg W., “Basic Chemical Thermodynamics” W. A. Banjamin (1969).<br />
8. Chorkendorff, I. and Niemantsverdriet, J.W. “Concept of Modern Catalysis and<br />
Kinetics” 1 st<br />
ed., John Wiley and Sons (2003).<br />
9. Espenson, J. H. “Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanism” 2 nd<br />
ed., McGraw<br />
Hill (2002).<br />
10. Berry R. S., Stuart A.R., and Roses J. “Physical and Chemical Kinetics” 2 nd<br />
ed.,<br />
Oxford University Press (2000).<br />
11. Helpern Arthur M., “Experimental Physical Chemistry: A Laboratory Textbook”<br />
2 nd<br />
ed., Prentice Hall (1997).<br />
12. Bassette J., Denney C., Jeffery G. H. and Mendham J. “Vogel’s Textbook of<br />
Quantitative Inorganic Analysis Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis”<br />
English Language Book Society. 4 th<br />
ed. (1978).<br />
13. Daniel, F., “Experimental Physical Chemistry” McGraw Hill (1962).<br />
14. Shoemaker, D., “Experimental Physical Chemistry” McGraw Hill (1989)<br />
14
M.SC, 1 ST YEAR – SEMESTER- II<br />
Course Title: Analytical Chemistry Paper-II Code: CHEM- 211<br />
Credit Hours: 02 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Electrogravimetry, Voltammetry and Polarography, Solvent Extraction and<br />
Chromatography, Spectrometry, Columetry, Amperometry, Electrophoresis, Basic<br />
concepts of IR, UV-Visible, Mass Spectrometry with applications, Introduction to<br />
Electron Resonance Spectroscopy and X-Rays Analysis.<br />
Analytical Chemistry Practical Credit Hours: 01<br />
1. To verify Beer’s Law and to evaluate molar extinction coefficient.<br />
2. Spectrophotometric determination of Ammonia.<br />
3. To determine Iron by spectroscopic method using phenanthroline.<br />
4. To determine the distribution coefficient of a given solute between an<br />
aqueous/non-aqueous system.<br />
5. To determine Calcium by indirect volumetric method.<br />
6. To determine Zinc by direct titration with EDTA.<br />
7. Colometric determination of Iron(III) with Potassium thiocynate.<br />
8. To separate and quantify Copper in Brass using constant-current electrolysis.<br />
9. To estimate Lead amperometrically through titration with Potassium dichromate.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Gary D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons.<br />
2. Douglas A. Skoog, Donald M. West, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch,<br />
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Reinhote, New York.<br />
3. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Chemical Analysis,<br />
4. I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
5. David Harvey, Modern Analytical Chemistry.<br />
15
Course Title: Inorganic Chemistry Paper-II Code: CHEM- 251<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Acceptor Complexes<br />
Mononuclear and polynuclear metal carbonyls: Calculation of valance electrons, the<br />
eighteen electrons rule as applied to metal carbonyls, rationalization of molecular<br />
structure, evaluation of structures based on spectroscopic evidences, chemistry of metal<br />
carbonyls and their derivatives (nitrosyls, halides and hydrides)<br />
Chemistry of f-Block Elements<br />
Lanthanides: Electronic structure and position in the periodic table, Lanthanide’s<br />
contraction, oxidation states, spectral and magnetic properties, general characteristics,<br />
occurrence, extraction and general principles of separation, complexes and uses.<br />
Actinides: Electronic structure and position in the periodic table, oxidation states,<br />
general characteristics, half life and decay law.<br />
Books recommended<br />
1. J. E. Huheey., E.A. Keiter., and R.L. Keiter,., “Inorganic Chemistry: Principles of<br />
Structure and Reactivity”, 4th Ed., Harper & Row, New York, 2001.<br />
2. F.A. Cotton., G. Wilkinson., C.A.Murillo, and M. Bochmann.,“Advanced<br />
Inorganic Chemistry”, 6th Ed., Wiley-Intersceince, New York, 1999.<br />
3. N.N. Greenwood., and A Earnshaw. “Chemistry of the Elements”, 2nd Ed.,<br />
Pergamon Press, New York, 1992.<br />
4. W. Willium. Porterfield. Inorganic chemistry, Unified approach, Elsevier<br />
Company, Delhi, (2005)<br />
5. K.M. Mackay., R.A., Mackay., and W. Henderson,., “Introduction to Modern<br />
Inorganic Chemistry”, 5th Edition, Stanley Thomas Publisher Ltd. 1996<br />
6. J. Bassette., G.H Denney., and J. Mendham,. “Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative<br />
Inorganic Analysis Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis” English<br />
Language Book Society, 4 th Edition, 1981.<br />
7. A.I. Vogel. “A Textbook of Micro and Semi-micro Qualitative Inorganic<br />
Analysis” Longman Green & Co. 1995.<br />
Inorganic Practical<br />
Credit Hours: 01 Marks: 50<br />
16
1. Separation of cations and anions in a mixture by paper chromatography.<br />
2. Redox Titration<br />
3. Gravimetric estimation of Ba 2+ and Fe 3+ ions<br />
Course Title: Organic Chemistry Paper- II Code: CHEM- 261<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Functional Chemistry: A brief introduction to the chemistry of hydrocarbons, alkyl,<br />
halides, alcohol, phenols, ethers aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids and their<br />
derivatives.<br />
Reaction Mechanism: Introduction to reaction mechanism, methods of determination of<br />
the reaction mechanism and comprehensive study on the mechanism of different types of<br />
substitution addition and elimination reaction with emphasis on their determination.<br />
Introductory organic Spectroscopy: introduction to UV, IR, 1 HNMR and mass<br />
spectrometric methods and their uses for the structure determination of simple organic<br />
compounds.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1 March, J., “Advanced Organic Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New<br />
York.<br />
2 Loudon, G. M., “Organic Chemistry”, Oxford University Press, New<br />
York.<br />
3 Brown, W. H., “Introduction to Organic Chemistry”, Saunders College<br />
Publishing, Tokyo.<br />
4 Sykes, P., “A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”,<br />
Longman, London.<br />
5 Pine, S. H., “Organic Chemistry”, National Book Foundation, Islamabad.<br />
6 McMurry, J., “Organic Chemistry”, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company,<br />
California.<br />
7 Carey, F. A., “Organic Chemistry”, McGraw-Hill, New York.<br />
8 Kalsi, P.S. “Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”, Wiley Eastern Ltd.,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
9 Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M. and Kriz, G. S., “Introduction to<br />
Spectroscopy: A Guide for Students of Organic Chemistry”, Saunders<br />
Golden Sunburst Series, London.<br />
Organic Chemistry Practical<br />
Credit Hours: 01 Marks: 50<br />
Laboratory work illustrating topics covered in the lecture of Organic Chemistry Paper II<br />
17
Recommended Books<br />
1 Clarke, H. T., “A Handbook of Organic Analysis-Qualitative and<br />
Quantitative”, CBS Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi.<br />
2 Mann, F. G. and Saunders, B. C., “Practical Organic Chemistry”,<br />
Longman, London.<br />
3 Vogel, A. I., “Elementary Practical Organic Chemistry Part 3:<br />
Quantitative Organic Analysis”, Longman, London.<br />
4 Vishnoi, N. K., “Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry”, Vikas<br />
Publishing House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
5 Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G. and Tatchell, A. R.,<br />
“Vogel’s Text Book of Practical Organic Chemistry”, National Book<br />
Foundation, Islamabad.<br />
6 Shriner, R. L., Hermann, C. K. F., Morrill, T. C., Curtin, D. Y. and Fuson,<br />
R. C., “The Systematic Identification of Organic Compounds”, John<br />
Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
7 Mendham, J., Denney, R. C., Barnes, J. D. and Thomas, M. J. K.,<br />
“Vogel’s Text Book of Quantitative Chemical Analysis”, Pearson<br />
Education, New Delhi.<br />
8 Beckett, A. H. and Stenlake, J. B., “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry”,<br />
Athlone Press, London.<br />
9 Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M. and Kriz, G. S. “Introduction to<br />
Spectroscopy: A Guide for Students of Organic Chemistry”, Saunders<br />
Golden Sunburst Series, London.<br />
10 Silverstein, R. N., Barrler, G. C. and Morrill, T. C., “Spectrometric<br />
Identification of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
Course Title: Physical Chemistry Paper-II Code: CHEM- 271<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Electrochemistry<br />
An introduction to electrochemistry, Ohm’s law, conductance, molar conductance and<br />
equivalent conductance, chemical reactions and redox potentials, electrochemical cells<br />
and types of electrodes. Ionic activity and Debye Huckle theory, Nernst equation and its<br />
applications.<br />
Solution Chemistry<br />
Solubility and Henry’s law, statistical thermodynamics of ideal solution and non ideal<br />
solutions, colligative properties and lowering of vapour pressure, elevation in boiling<br />
point, depression in freezing point, osmotic pressure and their applications in<br />
determination of molecular masses. Salt hydrolysis and determination of hydrolysis<br />
constant (K).<br />
PRACTICAL<br />
Credit Hours: 01 Marks: 50<br />
18
Spectroscopic determination of Cu % in the given sample. Conductometric determination<br />
of Cu (II)- EDTA mole ratio in the complex. To determine the effectiveness of an<br />
extraction of I 2 solution by using Solvent Extraction method. Determination of molecular<br />
weight of a polymer by viscosity method. Determination of percentage composition of<br />
KMnO 4 / K 2 Cr 2 O 7 in a given solution by spectrophotometry. Evaluation of pK a value of<br />
an indicator by spectrometric method. Conductometric determination of hydrolysis<br />
constant (K h ) of conjugate base of a weak acid.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Albert R.A., Robert J.S. and Moungi G.B. “Physical Chemistry”. 4 th<br />
ed., John<br />
Wiley and Sons (2004).<br />
2. Ball D.W. “Physical Chemistry” 1 st<br />
ed., Brooks/Cole Co. Inc. (2003).<br />
3. Bassetts J., Denney C., Jeffery G.H. and Mendham J. “Vogel’s Textbook of<br />
Quantitative Inorganic Analysis Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis”<br />
English Language Book Society. 4 th<br />
ed. (1978).<br />
4. Hatch R.C. “Experimental Chemistry” van Nostrand Reinhold Company (1972).<br />
5. Halpern, Arthur M. “Experimental Physical Chemistry: A Laboratory Textbook”<br />
2 nd<br />
ed., Prentice Hall (1962).<br />
19
M.SC, 2 ND YEAR – SEMESTER- III<br />
Course Title: Environmental Chemistry Paper-1 Code: CHEM-<br />
Credit Hours: 02+01 Marks: 100<br />
The atmosphere and air pollution:<br />
Structure and properties of the atmosphere, temperature inversion and air pollution,<br />
atmosphere photochemistry, possible depletion of stratospheric ozone, natural vs polluted<br />
air, particulate matter, analysis and control of particulations, sulphur oxides, effects of<br />
sulphur dioxides and particulates, other industrial air pollutants, carbon monoxide, oxides<br />
of nitrogen photochemicals smog, airborne load, control of automobile emissions.<br />
Water and water treatment:<br />
Unique physical and chemical properties of water, criteria of water quality, natural watereutrophiction,<br />
detergents and phosphates, importance of micro organisms in water<br />
purification, primary and secondary treatment of water, advanced waste water treatment,<br />
removal of nitrogen and phosphorus, sources of industrial water pollution, heavy metals<br />
and mercury.<br />
The green revolution:<br />
Pest control, pesticides, toxicity of pesticides, pest management.<br />
Books Recommended:<br />
1. Anil Kumar, Environmental chemistry, Wiley Eastern, New DelhiJ. W. Moore &<br />
E. 2). A. Moore, Environmental chemistry, Academic Press, New York.<br />
2. S. K. Banerji, Environmental chemistry, Prentice Hall, Delhi.<br />
3. S. K. Banerji, Environmental chemistry, Tata Publisher, Delhi.<br />
4. Staneley E. Manahan, Environmental chemistry, Brooks, California<br />
SPECIALIZATION IN ANALYTICAL <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Title of Course: Elementary Analytical Chemistry Paper-I Code: CHEM-311<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
The task of statistics in chemical analysis: Theory of sampling, source of variation and<br />
error, Presentation of results and rounding off the data. Confidence limit for the mean and<br />
standard deviation, comparison of standard deviations, inference from the tests, fitting<br />
lines to data, correlation and regression.<br />
Precipitation<br />
20
Solubility and solubility product. Effects of salt, solvents, hydration, hydrolysis, pH<br />
changes, beginnings surface exchange, adsorption etc, on precipitates. Determination of<br />
error in gravimetric analysis, thermogravimetric methods for testing of thermal stability.<br />
Complexation<br />
Chelate formation; competing reactions in complexation. The computation of stability<br />
constant from various experimental data. The use of complexes in analytical chemistry as<br />
reagents. Masking agents. Indicators and metal ion buffers. Complexometric titrations.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Gary D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons, New York.<br />
2. Douglas A. Skoog, Donald M. West, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch,<br />
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Reinholt, New York.<br />
3. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Chemical Analysis, McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
4. I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
5. J.G. Dick, Analytical Chemistry, McGraw Hill Book Co. New York.<br />
6. David Harvey, Modern Analytical Chemistry.<br />
Title of Course: Chromatographic Techniques Paper-II Code: CHEM-312<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Chromatography<br />
Adsorption and distribution laws applied to chromatography, the displacement, frontal<br />
method of analysis and elution techniques: Column, paper and thin-layer<br />
chromatography, suitable systems for analysis of some simple organic substances,<br />
reversed phase chromatography, high pressure liquid chromatography.<br />
Gas chromatography<br />
GSC and GLC parameters governing gas phase separation, simple instrumentation for<br />
gas chromatography, suitable systems for analysis high temperature programmed<br />
analysis.<br />
Introduction to HPLC<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Gary D. Christian, Analytical Chemistry, John Wiley and Sons.<br />
2. Douglas A. Skoog, Donald M. West, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch,<br />
Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, Reinholt, New York.<br />
3. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Chemical Analysis, McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
21
4. I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
Course Title: Spectroscopy and Advanced Instrumentation Paper-III Code:<br />
CHEM- 313<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Ultraviolet, visible spectroscopy; Molecular absorption of radiation, effect of structure on<br />
absorption, quantitative absorption spectroscopy, application,<br />
Instrumentation<br />
Various sources of light. Types of prime and gratings. Monochromators and their<br />
efficiency. The construction and optics of typical spectrograph. The use of a<br />
spectrophotometer in the analysis of one component or multicomponent systems, source<br />
of error and optimum conditions.<br />
Atomic spectroscopy<br />
Atomic absorption spectrophotometers and atomic fluorescence spectrometer.Flame<br />
photometry. Mass spectrometry, basic principles, instrumentation and applications.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Instrumental Analysis McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
2. Gary D. Christian, James E. O’Reilly, Instrumental Analysis, Allyn and Bacon<br />
Inc. New York.<br />
3. Douglas A. Skoog, Stanley R. Crouch, Instrumental Analysis, Reinholt, New<br />
York.<br />
4. F.W. Fifield and D. Kealy, Principles and Practice of Analytical Chemistry I.T.B,<br />
London.<br />
5. Willard, Meritte and Dean, Instrumental Analysis, D. Van Nostrand, New York.<br />
6. Bernhard Wetz, Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy, Verlay Chemie, New York.<br />
Course Title: Advanced Analytical Chemistry Paper-IV Code: CHEM-314<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
DTA and TGA Basic principles, instrumentation and applications, thermal analysis and<br />
calorimetry. Automation in analytical chemistry: Instrumental parameters for automated<br />
instrument, automated process and instruments in process control and clinical laboratory.<br />
Preparation of sample for the analysis.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Instrumental Analysis McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
22
2. Gary D. Christian, James E. O’Reilly, Instrumental Analysis, John Wiley and<br />
Sons.<br />
3. Douglas A. Skoog, Stanley R. Crouch, Instrumental Analysis, Reinholt, New<br />
York.<br />
4. I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
5. F.W. Fifield and D. Kealy, Principles and Practice of Analytical Chemistry I.T.B,<br />
London.<br />
Advance Analytical Chemistry Lab/Research. Credit Hours: 03<br />
Marks:100<br />
23
SPECIALIZATION IN BIO<strong>CHEMISTRY</strong> BIO-<strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Biochemistry Paper -II Code: CHEM- 331<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Biochemistry-1<br />
Brief introduction to the history and scope of biochemistry.<br />
Physical aspects of biochemistry<br />
Water, ionization of water, pH, Acid-base reactions, Buffers.<br />
Biomolecules-Carbohydrates<br />
General introduction, Nomenclature, Classification, Structural and Dynamic functions,<br />
Physical and Chemical properties. Nomenclature, Classification, and Structural<br />
configuration of monosaccharides. Isomerism, Mutarotation, recemic mixture and inter<br />
conversion of monomers. Ring structure (pyran and furan). Fischer’s formula and<br />
Haworth projection formula. Nomenclature, Classification, and Structural configuration<br />
of oligosaccharides, Glycosidic linkage. Classification and Structural configuration of<br />
polysaccharides.Chemistry and Biomedical Functions of Glycoprotein.<br />
Proteins<br />
Classification and properties of Amino acids. Overview of protein structure: Primary,<br />
Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary structures. Protein denaturation and folding. Proteins<br />
classification, properties, functions and their biological role.<br />
Lipids<br />
Classification, Fatty acids and their properties. Biological significance of glycerides.<br />
Phospholipids, non-phospholipids and steroids.<br />
Nucleic Acids<br />
Introduction to DNA, RNA. Nucleosides and Nucleotides, Purines and Pyrimidines.<br />
Enzymes<br />
Chemical nature, Nomenclature and Classification. Enzyme activity. Effect of different<br />
factors on enzyme activity. How enzymes work? Regulation of enzyme activity.<br />
Metabolism Pathways<br />
Glycolysis, Tricarboxylic acid Cycle, Gluconeogenesis.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Essentials of Carbohydrate Chemistry (1998) by John F. Robyt. Springer verlag<br />
24
2. Text book of Biochemistry (2008) by S.P. Singh. CBS Publishers<br />
3. Text book of Biochemistry (2007) by K. Rambabu.<br />
4. Fundamentals of Biochemistry (2008) 3rd Ed. by D. J. Voet, G.J. Voet and C. W. Pratt.<br />
J. Wiley & Sons Inc.<br />
5. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry (2008) 5th Ed. D. L. Nelson, M. M. Cox. W. H.<br />
Freeman Publishers.<br />
6. Fundamentals of Biochemistry by J. I. Jain. (2008) S. Chand & Co. India<br />
7. Biochemistry. (1999) 3rd Ed. by C. K. Mathews, K. E. Van Holde, & K.G. Ahern.<br />
Prentice Hall.<br />
8. Text book of Biochemistry & Human Biology (2006) 3rd Ed. by G.P. Talwar & L.M.<br />
Srivastava. Prentice Hall India.<br />
9. Text book of Biochemistry 3rd edition (2009) by Satyanarayana.<br />
10. Biochemistry 3rd Ed. (1999) by C. K. Mathews, K. E.van Holde and K.G. Ahern.<br />
Prentice Hall<br />
Course Title: Biochemistry Paper- III Code: CHEM- 332<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Molecular biology<br />
Gene theory, Gene, Allele, Structure of DNA, Chromosome, DNA replication,<br />
Transcription, Translation and post translational modification. DNA repair,<br />
Recombination, Gene expression and regulation, Genotype and Phenotype, Mutation and<br />
Types of mutation, DNA Sequencing.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Molecular Cell Biology (2007) 6th Edition H.Lodish, C.A. Kaiser, M.Krieger. M.P.<br />
Scott, A Bretscher, H Ploegh, & P. Matsudaira, W.H. Freeman<br />
2. Biochemistry 6th edition by J.M. Berg, J.L.Tymoczko & L. Stryer (2007) W.H.<br />
Freeman & Co.<br />
3. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Ed. by D. L. Nelson, M. M. Cox. W. H.<br />
Freeman Publishers<br />
25
4. Modern Genetic Analysis: Integrating Genes and Genomes (2002) 2nd Edition by A.<br />
J. F. Griffiths, J.H.Miller, D.T.Suzuki, R. C. Lewontin and W. M. Gelbart W. H.<br />
Freeman.<br />
Course Title: Biochemistry Paper: IV Code: CHEM- 333<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Physical techniques in Biochemistry<br />
Homogenization, Centrifugation, Ultra centrifugation, Paper and TLC, and Column<br />
chromatography, Gel Chromatography, Gel filtration, Ion exchange chromatography,<br />
Affinity chromatography, HPLC, Electrophoresis, Flame photometry, Atomic absorption<br />
Spectrophotometry, Spectrofluorimetry, UV/visible spectrophotometry. Extraction,<br />
Purification of Macromolecules, Purification based on differential solubility,<br />
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Two Dimensional electrophoresis, Radioactivity<br />
Techniques and its application in Biological System, Biochemical Techniques, Cloning,<br />
RFLP, Sequencing, Northern and Southern Blotting, Hybridisation, PCR, Recombinant<br />
DNA Technology.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Physical Biochemistry: Applications to Biochemistry and Moleculart Biology (1982)<br />
by David Freifelder,W. H. Freeeman<br />
2. Introduction to Modern liquid chromatography (1979) by L.L.Snyder & J.J Kirkland.<br />
John Wiley & Sons<br />
3. Tools of Biochemistry (1977) T. G. Cooper & T. C. Cooper John Wiley & Sons<br />
Centrifugation.<br />
4. A practical approach. (1987) Ed. D. Rickwood, Oxford: IRL press England.<br />
5. Varley’s Pratical Clinical Biochemistry (1991) 5th Edition byA.H. Gowenlock and M<br />
Bell. CBS Publishers & Distributors.<br />
6. Hawk's Physiological chemistry Mc Graw-Hill publishing company<br />
7. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry (1999) by C.A. Burtis, Ashwood & N.W. Tietz<br />
(Eds) W. B. Saunders Co.<br />
8. Principles and Techniques of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 6th Edition. Edited<br />
by K. Wilson & J. Walker.<br />
26
Course Title: Biochemistry Paper- V Code: CHEM- 334<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Molecular genetics<br />
Mendelian and Non-Mendelian genetics, Patterns of Inheritance, Mutational Analysis,<br />
Recombination and Genetic Mapping, Linkage Analysis, Chromatin and Chromosome,<br />
Mitosis and Meiosis, Interaction of genes, Chromosomal basis of heredity, Sex<br />
chromosome and Sex determination, Chromosomal aberrations, Gene mutations, Genetic<br />
code.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Strickberger, M. W. Genetics. The MacMillan Company.<br />
2. Pai, A.C. and H. Marcus-Roberts. 1981. Genetics Its Concepts and Implications.<br />
3. Goodenough, U. 1978. Genetics.<br />
4. Ayala, F.J. and Kiger, Jr. 1980. Modern Genetics.<br />
Advanced Biochemistry laboratory/Research thesis<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
1. Qualitative Analysis of carbohydrates of given unknown samples.<br />
2. Extraction of starch from plant sources & its confirmative tests (Sources: Potato,<br />
Wheat, Rice, Pulses, Barely, Maize etc)<br />
3. Extraction of Glycogen from animal sources & its confirmative tests. (Sources: Liver<br />
& Muscles etc)<br />
4. Extraction of total Lipids from plant seeds (by iodometric flask method).<br />
(Sources: Sunflower seed, Cotton seed, Corn seed, Coconut, Neem Seed, sesame).<br />
5. Extraction of Lipids from animal sources. Sources: Egg yolk & Animal tissues).<br />
6. Qualitative tests of proteins & amino acids:<br />
Biuret Test, Niuhydrin Test, Xanthoproteic Test, Pauly’s Test, Hoplein’s Test,<br />
Ehrich’s Test, Sakaguchi Test, Sodium nitroprusside Test, Sullivan Test, Load sulphate<br />
Test, Phosphate Test, Aldehyde Test<br />
7. Extraction of proteins from plant sources & their confirmative tests<br />
(Sources: Wheat, Rice Barely, Maize, Pulses etc)<br />
27
8. Extraction of proteins from animal sources & their confirmative tests. (Sources: Egg<br />
White, Milk, Liver, Muscles etc)<br />
9. Isolation of DNA from tissues<br />
10. Extraction of plasmid DNA<br />
11. Separation of DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis<br />
12. Determination of melting temperature of DNA<br />
13. Mineral analysis of plant tissues using atomic absorption spectrophotometer.<br />
14. Determination of sodium and potassium content in blood serum by flamephotometer,<br />
Gel chromatography and ion exchange chromatography.<br />
15. Determination of molecular weight of a given protein by gel filtration.<br />
16. Separation of Hb and serum proteins by electrophoresis<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Wilson, A. Practical Biochemistry: Principle and techniques (2000).<br />
2. Swotzer, Experiment Biochemistry theory and exercises in fundamental method<br />
(2000).<br />
3. Dryer, R. L. and G. F. Lata, Experimental Biochemistry, Oxford University Press.<br />
4. Plummer, D. T., Introduction to Practical Biochemistry, , McGraw Hill Book Co.,<br />
New York (1986).<br />
5. Alexander, R. R., J. M Griggiths and M. L. Wikinson, Basic Biochemical<br />
Methods, John Wiley & Sons.<br />
6. Wooton, I. D. P., Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry, J&A Churchill.<br />
28
SPECIALIZATION IN INORGANIC <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Chromatographic Methods of Analysis Paper-III, Code: CHEM- 351<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Paper chromatography, thin layer chromatography, Theory and applications. Gas<br />
chromatography, basic principles, instrumentation and applications. High pressure liquid<br />
chromatography, partition chromatography, adsorption chromatography, liquid solid<br />
chromatography and Ion Exchange chromatography. Basic principles instrumentation and<br />
applications.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Skoog. Holler. Nieman. Principles of instrumental analysis, fifth edition,<br />
Thomson Learning Academic.<br />
2. M.H. Willard, L.L. Merrite, Jr.J.A. Dean, instrumental metods of analysis, Van<br />
Nostrand. New York.<br />
3. H.G. Gsssidy, fundamental chromatography, inters science publications, New<br />
York.<br />
Course Title: Nuclear Chemistry Paper-IV Code: CHEM-352<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Nuclear Reactions<br />
Nature of nuclear reactions, nuclear reaction mechanism, Nuclear cross sections,<br />
excitation functions, types of nuclear reactions, fission and fusion reactions and<br />
photonuclear reactions,<br />
Radioactivity decay, detection and interaction of radiations<br />
Half life and average life of radioactive species, types of radioactive equilibrium, units of<br />
radioactivity. Radioactive decay series, Determination of half lives, radiation detection<br />
and measurements, Geiger mullar counters, scintillation counters. Interaction of radiation<br />
with matter. Determination of alpha and beta particles range.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. G. F. Friellander, J. W. Kennedy, and J. M. Miller, Nuclear and Radiochemistry,<br />
John Wiley and Sons, New York<br />
2. Kaplan Traving, Nuclear Physics, Pak Publishers, Karachi.<br />
3. Glasstone Samuel, Source book on atomic energy, von Nostrand, New York.<br />
4. W. M. Gibbson, Nuclear reactions, Penguin books Inc., New York.<br />
5. J. M. Reid, The atomic nuclear reactions, Penguin books Inc., New York.<br />
6. Chopman and Ryedberg, Nuclear chemistry, Prentice Hall, New York.<br />
29
Course Title: Bio Inorganic Chemistry Paper-V Code: CHEM-353<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Biochemistry of selenium, Bio Chemistry of Organo selenium Compounds, Antioxidant<br />
Activity of Organoselenium Compounds, Toxicology of Organoselenium Compounds;<br />
The biochemistry of iron, Iron storage and transfer in bacteria, ion transport,<br />
haemoglobin and myoglobin, nature of haemo-dioxygen , Model systems, cyto chromes,<br />
P/450 enzymes, iron sulphur protein , ferrodoxins, haemoerthrins, the biochemistry of Zn,<br />
Cu. Co, Mg, F2, I2 and Alkaline earth metals.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. F.A. Cotton, and S.W, Advanced inorganic chemistry, John Wiley and sons, New<br />
York.<br />
2. F. Basolo and R. Johnson, Mechanism of inorganic reactions, John Wiley and<br />
sons, New York.<br />
3. F. Basalo and R. Johnson, Coordination chemistry, W.A. Benjamen , Row<br />
Publishers, New York.<br />
4. J. E. Huheey, Inorganic Harper and Row Publisher, New York.<br />
5. D. Jonson, Mechanism of inorganic reaction in solutions, McGraw-Hill, London.<br />
6. Nicolaou, K. C.; Petasi, N. A. Selenium in Natural Products Synthesis; CIS:<br />
Philadelphia, PA, 1984.<br />
7. Paulmier, C. SeleniumReagents and Intermediates in Organic Synthesis;<br />
Pergamon: Oxford, U.K., 1986.<br />
8. Patai, S.; Rappoport, Z. The Chemistry of Organic Selenium and Tellurium<br />
Compounds;Wiley: New York, 1986; Vol. 1.<br />
Course Title:Spectroscopic Methods of analysis-Paper-VI Code: CHEM- 354<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
General introduction to spectroscopy<br />
Atomic absorption spectroscopy, Origin of spectra, excitation methods spectrographs<br />
and its qualitative and quantitative applications.<br />
UV/ Visible spectroscopy<br />
Basic instrumentation of U.V/visible spectrophotometers, Spectra of transition metal<br />
complexes, applications of the principles related to electronic transition. Structural<br />
evidence from electronic spectra<br />
Emission spectroscopy<br />
Atomic emission spectroscopy, qualitative and quantitative applications in inorganic<br />
chemistry.<br />
30
Books Recommended<br />
1. C.N.Banwale, Fundamentals of molecular spectroscopy, McGraw-Hill, New<br />
York.<br />
2. Skoog. Holler. Nieman. Principles of instrumental analysis, fifth edition,<br />
Thomson Learning Academic.<br />
3. M.H.willard, L.L.Merrite, J.J A.Dean, instrumental methods of analysis, Van<br />
Nostrand, New York.<br />
4. R.D. Braun, introduction to instrumental analysis. Mc. graw-Hill, new york, 1987.<br />
Advance Inorganic chemistry laboratory<br />
Advance inorganic laboratory/research Credit Hours = 03<br />
31
SPECIALIZATION COURSES IN ORGANIC <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Chemistry of Hetrocycles Paper- III Code: CHEM- 351<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks = 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Introduction, significance and applications. Nomenclature of hetrocyclic compounds<br />
according to IUPAC, Hantzsch-Widmann-Pettersen system and SMILES. Geometry and<br />
Stereochemistry of heterocyclic compounds<br />
Saturated, Unsaturated and Aromatic Hetrocycles, aromaticity, Tautomerism in small to<br />
large ring hetrocycles. Chemistry of Furan, Thiophene and pyrrole; synthesis of indole<br />
and isoindoles; chemistry of pyridine, quinoline and isoquinoline; occurrence of<br />
hetrocyclic compounds.<br />
Photochemistry<br />
Woodward and Hofmann rule: Introduction, excitation and the excited state.<br />
Intramolecular reactions of the olefinic bond, carbonyl group, and cycloaddition reaction.<br />
Generalized woodward and Hofmann rules for concerted reactions.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. 1R. K. Bansal, Hetrocyclic Chemistry, 4 th ed., New Age international. Pvt. Ltd.,<br />
India (2005).<br />
2. T. Eicher and s. Hauptmann, The Chemistry of Hetrocycles,George Thieme<br />
Verlag, New York(1995).<br />
3. J. A. Joule, K. Mills, G.F. Smith, Hetrocyclic Chemistry, Stanely Thomes<br />
Publication Ltd.; (1998).<br />
4. R. H. Acheson, An introduction to Chemistry of Hetrocycles, John Wiley, New<br />
York (1987).<br />
5. M. Samisburg, Hetrocyclic Chemistry, Royal Society of Chemistry (2001)<br />
6. H. Charles, Deputy and S. Orville, Chapman, Molecular reaction and<br />
photochemistry. Prentice Hall. New York.<br />
Course Title Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry Paper- IV, Code:<br />
CHEM- 352<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Introduction Fundamental of spectroscopy. UV-Visible Spectroscopy: Introduction,<br />
theory, Instrumentation and sample handling. Infra Red Spectroscopy: Introduction,<br />
theory, Instrumentation and sample handling. Mass Spectroscopy: Introduction, theory,<br />
Instrumentation and sample handling. Applications: Structure elucidation of simple<br />
organic molecules by UV, IR and MS.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
32
1. Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G.M. and Kriz, G.S., Introduction to spectroscopy: a<br />
Guide for Students of Organic Chemistry, Thomson Learning, Australia (2001).<br />
2. Silverstein, R. M. Webster F.X. and Kiemle, D.J. Spectrometeric Identification of<br />
Organic Compounds, John Wiley and Sons Inc., USA (2005).<br />
3. Brown, D.W., Floyed, A.J. and Sainsury, M. Organic spectroscopy, 1. Wiley and<br />
Sons, Chichester (1998).<br />
4. Willians, D. H. and Fleming, I. Spectroscopic methods in organic Chemistry, 4 th<br />
ed., McGraw-Hill Book. Co., Lodon (1987).<br />
5. Younas, M. Organic Spectroscopy, Ilmi Kitab Khana, Lahore (2004).<br />
6. Kalsi, P.S. “Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New<br />
Delhi.<br />
7. Lambert, J. B, Shurvell, H. F., Lightner, D. A. and Cooks, R. G., “Introduction to<br />
Organic Spectroscopy”, Macmillan Publishing Company, New York.<br />
8. Williams D. H. and Fleming, I., “Spectroscopic Methods in Organic Chemistry”,<br />
Athlone Press, London.<br />
9. Atta-ur-Rehman, “Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy”, UGC, Islamabad.<br />
10. Davis, R. and Freason, M., “Mass Spectrometry”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
33
Course Title: Stereochemistry Paper- V Code: CHEM- 353<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Introduction History and Significance. Static Stereochemistry: Structure and Symmetry,<br />
configurations and conformations, methods for determination of relative and absolute<br />
configuration, stereochemical nomenclature. Types of Chirlity: Central, Axial and planar<br />
chiral compounds , atropisomerism, molecular overcrowding and cyclostereisomereism.<br />
Dynamic stereochemistry; steereochemical reactions, stereoselectivity and<br />
stereospeciticity, prostereoisomerism and prochirility. Analytical methods: determination<br />
of enantiomers and distereomers composition using chiroptical, chromatographic and<br />
NMR spectroscopic methods. Resolution: Diasteroisomers formation , Chiral<br />
derivatization agents (CDAs), Chiral resolving agents (CRAs), chromatographic kinetic,<br />
mechanical and enzymetic resolutions, preferential crystallization.<br />
Book Recommended<br />
1. Eliel, E. L.; Wilen, S. H Doyle, M.P. and Michael, P. Basic Organic<br />
Stereochemistry, Willey Inter Science, New York (2003).<br />
2. Kalsi, P. S. Sterochemistry and mechanism through Solved problems, new age<br />
international publishers, New Delhi, India (2001).<br />
3. Mislow, K. Introduction to stereochemistry, W.A. Benjamin, New York (1966).<br />
4. Morris, D.G. Stereochemistry, Royal Society of Chemistry, UK. (2001).<br />
5. M. North. Principles and application of stereochemistry, Stanely Thornes:<br />
Cheltenham, UK (1998).<br />
6. Morrison, R. T. and Boyd, R. N., “Organic Chemistry”, Prentice-Hall of India,<br />
New Delhi.<br />
34
Course Title: Organic synthesis Paper-VI Code: CHEM- 354<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Oxidations/Reduction Reactions, an introduction to carbon-carbon bond synthesis,<br />
Reactive intermediates, Pericyclic reactions.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. March, J. Advanced Organic chemistry: Reaction, Mechanism and Structure, 5 th<br />
ed., John Wiley, New York (2007).<br />
2. Caruthers, W. Some modern methods of organic Synthesis, 3 rd ed., Cambridge<br />
University Press, Cambridge (1986).<br />
3. Aansari, F.L., Quershi R. and Quershi, M.L. Electrocyclic Reactions, John Wiley<br />
and Sons (1999).<br />
4. Norman, R.O.C. Principles of Organic Synthesis, 3 rd ed., Chapman and Hall,<br />
London (1993).<br />
5. Carey, F. A. and Sundberg, R. J., “Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A: Structure<br />
and Mechanisms”, Kluwer Academic /Plenum Publishers, New York.<br />
6. Sykes, P., “A Guide Book to Mechanism in Organic Chemistry”, Longman,<br />
London.<br />
7. McMurry, J., “Organic Chemistry”, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company,<br />
California.<br />
8. Solomons, T. W. G. and Fryhle, C. B., “Organic Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons,<br />
New York.<br />
Advance Organic Chemistry Laboratory/Research Thesis<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Multistep synthesis of different types organic compounds, purification and identification<br />
of synthesized compounds by physical and chemical methods.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Clarke, H. T., “A Handbook of Organic Analysis-Qualitative and Quantitative”,<br />
CBS Publishers & Distributors, New Delhi.<br />
2. Mann, F. G. and Saunders, B. C., “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Longman,<br />
London.<br />
3. Vogel, A. I., “Elementary Practical Organic Chemistry Part 3: Quantitative<br />
Organic Analysis”, Longman, London.<br />
4. Vishnoi, N. K., “Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry”, Vikas Publishing<br />
House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
5. Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G. and Tatchell, A. R., “Vogel’s<br />
Text Book of Practical Organic Chemistry”, National Book Foundation,<br />
Islamabad.<br />
35
6. Shriner, R. L., Hermann, C. K. F., Morrill, T. C., Curtin, D. Y. and Fuson, R. C.,<br />
“The Systematic Identification of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons,<br />
New York.<br />
7. Mendham, J., Denney, R. C., Barnes, J. D. and Thomas, M. J. K., “Vogel’s Text<br />
Book of Quantitative Chemical Analysis”, Pearson Education, New Delhi.<br />
8. Beckett, A. H. and Stenlake, J. B., “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, Athlone<br />
Press, London.<br />
9. Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M. and Kriz, G. S. “Introduction to Spectroscopy: A<br />
Guide for Students of Organic Chemistry”, Saunders Golden Sunburst Series,<br />
London.<br />
10. Silverstein, R. N., Barrler, G. C. and Morrill, T. C., “Spectrometric Identification<br />
of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
11. Kalsi, P.S. “Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New<br />
Delhi.<br />
12. Palleros, D. R., “Experimental Organic Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New<br />
York.<br />
36
SPECIALIZATION IN PHYSICAL <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Statistical Thermodynamics Paper-III Code: CHEM- 371<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Permutation and probability, Partition functions. The relationship of partition function to<br />
the various thermodynamic functions like translational energy, vibrational energy,<br />
rotational energy, entropy, heat, enthalpy, pressure, Gibbs free energy, Entropy of mixing<br />
of gases, heat capacity etc. Transitional, vibrational and rotational partitional functions<br />
and equilibrium constant.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Gasser R.P.H. and Richards W.G. “Entropy and Energy Levels” Oxford<br />
University Press (1974).<br />
2. Wayatt P.A.H. “The Molecular Basis of Entropy and Chemical Equilibrium”<br />
Royal Institute of Chemistry London (1971).<br />
3. Smith E.B. “Basic Chemical Thermodynamics” 4 th<br />
Press(1990).<br />
ed. Oxford University<br />
4. Seddon J.M. and Gale J.D. “Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics” Royal<br />
Soc Chem, UK (2002).<br />
5. Aston J.G. and Fritz J.J. “Thermodynamics and Statistical Thermodynamics”<br />
John-Wiley, New York (1987).<br />
Course Title: Polymer Chemistry Paper-IV Code: CHEM- 372<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Introduction to Polymers. Step-growth Polymerizations. Polymer chain growth. Kinetics<br />
of polymer chain growth. Copolymerization. Emulsion Polymerization. Natural and<br />
Inorganic Polymers. Physical Aspects of polymers. Molecular Weight of Polymers:<br />
Distribution, averages, and methods of determination. Viscosity. Osmometry. Light<br />
scattering method. Diffusion, sedimentation. Optical rotation method. Structure of<br />
Polymer Chain: Introduction to chain isomerism, stereochemistry, configurations, and<br />
conformations. (not in Hiemenz). Amorphous State of Polymers: In depth examination of<br />
polymer conformation, microstructure, and dynamics in the amorphous state. Polymer<br />
viscoelasticity: Stress relaxation, mechanical models of polymer behavior, timetemperature<br />
superposition, perhaps rheology. Crystalline State of Polymers:<br />
crystallization and kinetics, crystalline structures, experimental methods. Polymer<br />
Solutions and Blends:<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Hiemenz P.C. “Polymer Chemistry: The Basic Concepts” Marcel Dekker (1984).<br />
37
2. Stevens M.P. “Polymer Chemistry: An Introduction” Oxford University Press<br />
(1999).<br />
1. Allcock H.R. and Lampe F.W. “Contemporary Polymer Chemistry” Prentice-Hall<br />
(1990).<br />
3. Rudin “The Element of Polymer Science and Engineering” Academic Press<br />
(1990).<br />
4. Sperling L.H. “Introduction to Physical Polymer Science” Wiley Interscience<br />
(1992).<br />
5. Boyd R.H. and Phillips P.J. “The Science of Polymer Molecules” Cambridge<br />
(1993).<br />
6. Malcolm P.S. “Polymer Chemistry” Oxford University Press (2005).<br />
7. Ravue, “Principles of Polymer Chemistry” 2 nd<br />
ed. Plenum Publishers (2000).<br />
Course Title: Quantum Chemistry Paper-V Code: CHEM- 373<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Limitation of classical mechanics, wave and particle nature of matter, de-Broglie’s<br />
equation, Heisenberg’s uncertainity principle, concept of quantization of energy,<br />
Operators and their properties. Types of operators, Hemaltonian operator, Hermition<br />
operator, Angular momentum. Postulates of quantum chemistry, Eigen function and<br />
Eigen values, general wave equation, Schrödinger wave equation (Time dependent +<br />
Time independent). Particle in one dimensional box, three dimensional box, hydrogen<br />
atom and harmonic oscillator, comparision between general wave equation and<br />
Schrödinger wave equation, Central field problem. Approximate methods. Perturbation<br />
methods. Many electron systems. Treatment of simple harmonic oscillator, diatomic rigid<br />
rotor. Valence bond and molecular orbital theories. Pi-electron calculations.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Micheal D.F. “Elements of Quantum Mechanics” Oxford University Press (2005).<br />
2. Griffiths, David J., “Introduction to Quantum Mechanics” 2 nd<br />
ed., Prentice Hall (2004).<br />
3. Hayward, David O., “Quantum Mechanics for Chemists” 1 st<br />
ed., John Wiley (2003).<br />
4. House, James E., “Fundamentals of Quantum Mechanics” 2 nd<br />
ed., Elsevier-Academic<br />
Press (2003).<br />
Course Title: Photochemistry Paper-VI Code: CHEM- 374<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
38
Scope of photochemistry. Energy transfer in photochemical reaction. Quantum yield of<br />
emission process radiation and nonradiation process. Kinetics and Quantum yields of<br />
radiative and nonradiative process (fluorescence, phosphorescence, inter system crossing,<br />
internal conversion , quenching), and Stern-Volmer reactions. Photosensitized reactions.<br />
Photochemical reaction in gas phase and in solutions. Flash photolysis. Advance<br />
approach to kinetics of photochemical reactions. Applied photochemistry. Atmospheric<br />
photochemistry. Photosynthesis, photochemistry of polymers, photomedicines.<br />
Techniques in photochemistry, introduction, light source. Incandescent filament lamps,<br />
discharge lamps, lasers, synchrotron reaction.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Calvert J.G. and Pitts J.N. “Photochemistry” John Wiley, New York (1966).<br />
2. Suppan P. “Principles of Photochemistry”, the Chemical Soc., UK (1973).<br />
3. Albert R.A., Robert J.S. and Moungi G.B. “Physical Chemistry”. 4 th<br />
ed., John Wiley<br />
and Sons (2004).<br />
4. Ball D.W. “Physical Chemistry” 1 st<br />
ed., Brooks/Cole Co. Inc. (2003).<br />
Advanced Physical Laboratory<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Specific experiments may be set making use of the following instruments depending<br />
upon their availability. Special experiments may also be designed for which a specimen<br />
list of instruments is given below. For the innovative designing of experiments the<br />
Journal of Chemical Education may be consulted.<br />
Instruments:<br />
PH-meter , Conductivity meter ,Dipole meters, Electrogravimetric apparatus,UV/Visible<br />
spectrometer<br />
Infrared spectrophotometer, Atomic absorption spectrophotometer,Stopped flow<br />
spectrometers<br />
Gas Chromatography, HPLC ,Light Scattering Instruments<br />
Practical<br />
Determination of partial molar quantities.<br />
Determination of free energy changes, standard free energies.<br />
Verification of Kohlrausch law.<br />
Study of temperature dependence of electrode potentials.<br />
39
Determination of heat of solution, ionic reactions and other experiments from<br />
thermochemistry.<br />
Determination of molecular weight of a polymer by viscosity method.<br />
Precipitation value of electrolytes.<br />
Measurement of IR spectra of simple compound and their interpretation.<br />
Measurement of cyclic voltammogram of an organic compound and its interpretation.<br />
Determination of dipole moment of an organic liquid.<br />
Determination of percentage composition of KMnO 4 -K 2 Cr 2 O 7 in given solution by<br />
spectrometry.<br />
Evaluation of pKa value an indicator by spectrometric method.<br />
Synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and their characterization using IR and XRD<br />
techniques.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Braun R.D. and Walters F. “Application of Chemical Analysis” (1982).<br />
2. David P. “Experiments in Physical Chemistry” 5 th<br />
ed. (1989).<br />
3. James A.M. and Prichard F.E. “Practical Physical Chemistry” 3 rd<br />
ed. Longman (1974).<br />
4). Shoemaker D.P., Garland C.W. and Nibler J.W. “Experiments in Physical Chemistry”<br />
McGraw Hills, New York (1989).<br />
40
M.SC, 2 ND YEAR, SEMESTER-IV (FINAL SEMESTER)<br />
Course Title: Environmental Chemistry Paper-I1 Code: CHEM-<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Fossil fuels and energy sources<br />
Origin and development of coal: Origin and reserves of petroleum and natural gas,<br />
composition and classification of petroleum, refining, and environmental problems<br />
associated with petroleum, nuclear fission reactors, solar energy, power synthesis, tidal<br />
and geothermal energy, synthetic chemical fuels, the H economy, electrochemical energy<br />
conversion, conservation of free energy, the energy balance of the earth.<br />
Soils and mineral resources<br />
Estimating reserves of mineral resources of earth, extraction of metal-general principles,<br />
iron, steel, aluminium, copper and other metals, sulphur and nitrogen. Organic matter in<br />
soil, soil nutrients, ion exchange in soils, solid pH and nutrients availability.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Anil Kumar, Environmental chemistry, Wiley Eastern, New Delhi J. W. Moore &<br />
E. 2). A. Moore, Environmental chemistry, Academic Press, New York.<br />
2. S. K. Banerji, Environmental chemistry, Prentice Hall, Delhi.<br />
3. S. K. Banerji, Environmental chemistry, Tata Publisher, Delhi.<br />
4. Staneley E. Manahan, Environmental chemistry, Brooks, California.<br />
41
SPECIALIZATION ANALYTICAL <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong> SEMESTER- IV<br />
Course Title: Advanced Analytical Chemistry Paper-VI Code: CHEM- 411<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
1. DTA and TGA: Basic principles, instrumentation and applications, thermal<br />
analysis and calorimetry.<br />
2. Automation in analytical chemistry: Instrumental parameters for automated<br />
instrument, automated process and instruments in process control and clinical<br />
laboratory.<br />
3. Preparation of sample for the analysis.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Instrumental Analysis McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
2. Gary D. Christian, James E. O’Reilly, Instrumental Analysis, John Wiley and<br />
Sons.<br />
3. Douglas A. Skoog, Stanley R. Crouch, Instrumental Analysis, Reinholt, New<br />
York.<br />
4. I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
5. F.W. Fifield and D. Kealy, Principles and Practice of Analytical Chemistry I.T.B,<br />
London.<br />
Course Title: Electro-Analytical Techniques Paper-VII Code: CHEM-412<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
1. Electrode Phenomenon: The electrochemical cell. Oxidation and reductions<br />
potentiometric methods, various types of electrodes and their use, over potentials<br />
membrane potentials, some well known redox reactions of analytical importance,<br />
ion selective electrodes, direct potentiometric measurement, potentiometric<br />
titration.<br />
2. Voltammetry: Principal of voltammetry, Instrumentation, different modes of<br />
polarography. Application of the inorganic and organic analysis, Principles of<br />
stripling voltammetry, types of stripling voltammetry and application analysis of<br />
cation and anions.<br />
3. Introduction to Coulometry and Amperometry.<br />
4. Electrophoresis; Basic theory, instrumentation and applications<br />
5. Radiochemical methods: Neutron activation analysis, isotopic dilution method,<br />
radiometric methods, application<br />
Books Recommended<br />
� Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Instrumental Analysis McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
� Gary D. Christian, James E. O’Reilly, Instrumental Analysis, John Wiley and<br />
Sons.<br />
� Douglas A. Skoog, Stanley R. Crouch, Instrumental Analysis, Reinholt, New<br />
York.<br />
42
� I.M. Kolthoff, Sandell, Text Book of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Macmillan<br />
and Co. New York.<br />
Course Title: Spectroscopy and Advanced Instrumentation Paper-VIII<br />
,Code:CHEM-413<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents:<br />
Principles of molecular fluorescence, instrumentation, analytical parameters and<br />
analytical applications. Principles of flame photometry, instrumentation, application of<br />
flame photometry and interferences. Principles of atomic fluorescence, instrumentation,<br />
analytical parameters and analytical application. NMR Spectroscopy, principles and<br />
interpretation of spectra. Introduction to X-Rays spectroscopy<br />
Books Recommended<br />
� Robert D. Braun, Introduction to Instrumental Analysis McGraw Hill Book Co.<br />
New York.<br />
� Gary D. Christian, James E. O’Reilly, Instrumental Analysis, John Wiley and<br />
Sons.<br />
� Douglas A. Skoog, Stanley R. Crouch, Instrumental Analysis, Reinholt, New<br />
York.<br />
� F.W. Fifield and D. Kealy, Principles and Practice of Analytical Chemistry I.T.B,<br />
London.<br />
� Willard, Meritte and Dean, Instrumental Analysis, D. Van Nostrand, New York.<br />
Advanced Instrumental Chemistry Practical/Research Project Credit Hours: 03<br />
Marks: 100<br />
43
SPECIALIZATION IN BIO<strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Cell Biology Paper-VI Code:CHEM- 431<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Content<br />
Cell theory; Structure and chemical composition of cell, Introduction to Prokaryotes and<br />
Eukaryotes,<br />
Cell organelles<br />
Lysosome, Micro-bodies, Mitochondrial structure and the conservation of chemical<br />
energy, Chloroplast structure, Plasma membrane, Cell wall, Mechanism of<br />
photosynthesis, Separation of cell organelles, Functions of cell organelles.<br />
Membrane transport<br />
The concept of the unit membrane, Fluid mosaic model, Surface receptors and membrane<br />
mediated control.. Active and Passive transport, Actin filaments, Microtubules,<br />
Intermediate filaments.<br />
Cell movements<br />
Structure and function of cytoskeleton, Centriole, Cilia and Flagella, Mitotic apparatus.<br />
Cell surface and cell communication,<br />
Cell adhesion and junctions, Signal transduction and receptor functions, Cell membrane<br />
receptors.<br />
Cell division<br />
Eukaryotic cell cycle, Mitosis and meiosis. Apoptosis and Necrosis.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Molecular Biology of the Cell, (2008) 5th Editon .B. Alberts, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M.<br />
Raff, K. Roberts & P. Walter Garland Sciences.<br />
2. Molecular Cell Biology (2000) 4th Edition. H. Lodish, A. Berk, L. Zipursky, P.<br />
Matsudaira, D. Baltimore & J. Darnell. W.H. Freeman.<br />
3. Cell and Molecular Biology: Concepts and Experiments (2008) by G. Karp John Wiley<br />
& Sons.<br />
Course Title: Immunology Paper-VII Code: CHEM- 432<br />
44
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Introduction<br />
Historical background, general concepts of the immune system. Innate and adaptive<br />
immunity; Inflammation - general properties.Structure, properties and functions of the<br />
immune cells & organs Hematopoeisis, T and B-lymphocytes, NK cells; Monocytes and<br />
macrophages; Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.Mast cells and dendritic cells.<br />
Thymus and Bone marrow; Lymph nodes, spleen, MALT, GALT and CALT.<br />
Antigens and haptens<br />
Properties (foreignness, molecular size, heterogeneity). B and T cell epitopes. T-<br />
dependent and T- independent antigens.<br />
Antibodies<br />
Structure, function and properties of the antibodies; Different classes and biological<br />
activities of antibodies; Antibody as B cell receptor, antigenic determinants on<br />
antibodies (isotype, allotype and idiotype). Genesis of antibody variability (definitions of<br />
combinatorial joining, junctional flexibility, somatic hypermutation, class switching,<br />
allelic exclusion, immunoglobulin superfamily). Hybridoma technology, monoclonal<br />
antibodies and abzymes, Introduction to antibody engineering (definitions of chimeric<br />
and hybrid monoclonal antibodies).Major histocompatibility gene complex<br />
Organization of MHC. Structure and cellular distribution of HLA antigens.<br />
Complement system<br />
Components of the complement activation - classical, alternative and lectin pathways.<br />
Biological consequence of complement activation and names of complement<br />
deficiencies.An overview of maturation and activation of B and T cells B-cell maturation<br />
in bone marrow, humoral immune response, primary and secondary immune response,<br />
generation of plasma and memory B cells. T cell maturation in thymus, thymic selection,<br />
self MHC restriction of T cells, T cell receptor complex, T cell activation, co-stimulatory<br />
signals, clonal expansion, generation of effector and memory T cells. Antigen presenting<br />
cells, antigen processing and presentation pathway (cytosolic and endocytic).<br />
Cell mediated immunity<br />
Cell types (CTLs, NK cells, macrophages and TDTH cells), effector mechanisms and<br />
effector molecules of cell mediated reactions. Assessment of cell-mediated<br />
cytotoxicity. Cytokine properties and functions of IL-1 to IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, IFN- γ.<br />
Regulation and modulation of immune response A general account. Adjuvants, tolerance,<br />
immunopotentiation and immunosuppression Immunological principles of various<br />
reactions and techniques. Affinity and avidity, cross reactivity, precipitation,<br />
agglutination, immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, ELISA (indirect, sandwich,<br />
45
competitive, chemiluminescence, ELISPOT assay), western blotting,<br />
immunofluorescence, flow cytometry and fluorescence, and immunoelectron microscopy.<br />
Hypersensitivity<br />
Types and mechanism of hypersensitive reactions.<br />
Autoimmunity<br />
Mechanisms of induction of organ specific (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, autoimmune<br />
anemias, Goodpasture’s syndrome, IDDM), and systemic (SLE, multiple sclerosis and<br />
rheumatoid arthritis) autoimmune diseases. Therapeutic approach<br />
Transplantation immunology<br />
Types of grafts, immunologic basis of graft rejection, properties and types of<br />
rejection, tissue typing, immunosuppressive therapy and transplants to<br />
immunologically privileged sites.<br />
Immunity and tumors<br />
Types of tumors, tumor antigens (TSTA and TAA), immune response to tumors.<br />
Tumor evasion of the immune system. Immunotherapy for tumors.<br />
Immunodeficiency disorders<br />
Animal models of primary immunodeficiency (nude mouse and SCID mouse).<br />
Specific impaired functions in lymphoid lineage (SCID, Waldanstorm<br />
agamaglobulinemia, DiGeorge syndrome, common variable immunodeficiency),<br />
myeloid lineage (CGD, congenital neutropenia, Chediak-Higashi Syndrome and<br />
leucocyte adhesion deficiency).<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Medical Immunology 10th Editon by T.G. Parslow, D.P.Stites, A.I. Terr &<br />
J.B.Imboden.Lange.<br />
2. Immunology,6th Editon. by I. Riott, J. Brostoff, & D. Male. Publisher: C. V. Mosby.<br />
3. Kuby Immunology,(2006) 6th Edition by T. J. Kindt, B. Osborne & R.A.Goldsby,<br />
W.H.Freeman<br />
4. Principles of Microbiolgy,(1995) by R.M. Atlas<br />
46
5. Advance Molecular Biology (1999) by W.Wisden & R. M. Twyman.<br />
Course Title: Enzymology Paper- VIII Code: CHEM- 433<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Nomenclature, Effect of various factors on rate of reaction, Riboenzyme, General<br />
characteristics of enzymes.<br />
Classification of enzymes<br />
Oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, ligases<br />
Enzyme catalysis<br />
Covalent catalysis, Acid base catalysis, Substrate specificity, Isozymes, Coenzymes,<br />
Cofactors, Enzyme activity, Regulation of enzyme activity, Proximity and orientation.<br />
Enzyme kinetics<br />
Lineweaver-Burk Plots, Michaelis-Menten equation, Multienzyme system, Bisubstrate<br />
reactions, Catalytic mechanisms, Regulatory enzymes, Immobilised enzyme, Enzyme<br />
activity.<br />
Enzyme Inhibition<br />
Enzyme inhibitors, Types of inhibition, Feedback inhibition, Allosteric inhibition<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Biochemistry (2007) 6th edition by J.M. Berg, J.L. Tymoczko & L. Stryer W.H.<br />
Freeman & Co.<br />
2. Fundamentals of Biochemistry (2008) 3rd Ed. by D. J. Voet, G.J. Voet and C. W.<br />
Pratt. J. Wiley & Sons Inc.<br />
3. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Ed. by D. L. Nelson, M. M. Cox. W. H.<br />
Freeman Publishers<br />
4. Biochemistry. (1999) 3rd Ed. by C. K. Mathews, K. E. Van Holde, & K.G. Ahern.<br />
Prentice Hall.<br />
5. Harper’s Illustrated Biochemistry, 27th Ed. By R.K. Murray, D.K. Grannar, V.W.<br />
Rodwell. McGraw Hill.<br />
6. Modern Experimental Biochemistry (1993) by R.F. Boyer. Benjamin-Cummings pub.<br />
47
Co.<br />
7. Varley’s Pratical Clinical Biochemistry (1991) 5th Edition byA.H. Gowenlock and M.<br />
Bell. CBS Publishers & Distributors.<br />
8. Text Book of Biochemistry (1971) by B. Harrow and A. Mazur W.B.Saunders<br />
Company.<br />
Course Title: Molecular Evolution Paper- IX Code: CHEM- 434<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Introduction to Evolution, Systematics, Patterns of Evolution, Macroevolution: Fossils<br />
Microevolution: Natural Selection, Species and Speciation, Conflict and Cooperation<br />
Evolution and Society<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Ayala, F.J. and Kiger, Jr. 1980. Modern Genetics.<br />
2. Page, R. and E. Holmes. 1998. Molecular evolution: a phylogenetic approach.<br />
Blackwell, London.<br />
3. Yang Z.2006. Computational Molecular Evolution. Oxford University Press,<br />
Oxford, England.<br />
4. Graur, D. and W. H. Li 2000.Fundamentals of molecular evolution. 2 nd Edition,<br />
Sinauer Associates, Massachussetts.<br />
5. Li, W. H. 1997. Molecular Evolution. Sinauer Associates, Massachusetts.<br />
6. Nei, M and S. Kumar.2000. Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford:<br />
Oxford University Press.<br />
7. Gillespie, J. H. 1998. Population genetics:a concise guide.John Hopkins<br />
University Press, Baltimore.<br />
Course Title: Advanced Biochemistry Lab/Research Project<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
1. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).<br />
2. Study of cell structure using compound microscope and elucidation of ultra-structure<br />
from electron microphotographs.<br />
3. Cell structure in the staminal hair of Tradescantia.<br />
48
4. Cellular reproduction, mitosis: smear/squash preparation of onion roots/cheek cells.<br />
5. Extraction and estimation of enzymes from plant source. Acid and enzymatic<br />
hydrolysis of glycogen and starch<br />
6. Biosynthesis of enzymes by fungi and bacteria.<br />
7. Effect of Temperature, Substrate concentration and Enzyme concentration on enzyme<br />
activity.<br />
8. Analysis of normal and abnormal constituents in urine<br />
9. Analysis of organic and inorganic constituents of blood<br />
10. Estimation of different vitamins<br />
11. Separation of subcellular fractions in cells<br />
12. Enzymes: Purification and kinetic studies of invertase,lactic dehydrogenase, and<br />
peroxidase<br />
13. Electrophoresis of plasma proteins, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Agarose<br />
electrophoresis of DNA.<br />
14. Cultivation of microorganisms in laboratory using solid and liquid culture media, test<br />
tube, Petri plates<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Wilson, A. Practical Biochemistry: Principle and techniques (2000).<br />
2. Swotzer, Experiment Biochemistry theory and exercises in fundamental method<br />
(2000).<br />
3. Dryer, R. L. and G. F. Lata, Experimental Biochemistry, Oxford University Press.<br />
4. Plummer, D. T., Introduction to Practical Biochemistry, McGraw Hill Book Co.,<br />
New York (1986).<br />
5. Alexander, R. R., J. M Griggiths and M. L. Wikinson, Basic Biochemical<br />
Methods, John Wiley & Sons.<br />
6. Wooton, I. D. P., Microanalysis in Medical Biochemistry, J&A Churchill.<br />
7. Gowenlock, A. H., Varley’s Practical Clinical Biochemistry, 6 th ed., Heinemann<br />
Professional Publishing, Oxford (1988).<br />
8. T. N. Pattabiraman. Laboratory Manual in biochemistry. India Publishers (1988).<br />
49
9. Gosling, J. P. Immunoassay: laboratory Analysis and Clinical application (1994).<br />
10. Sauhney, Introductory Practical Biochemistry (1998).<br />
50
SPECIALIZATION IN INORGANIC <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Advanced Spectroscopic Methods of analysis-Paper- VII Code:<br />
CHEM- 451<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Infra red spectroscopy: Basic instrumentation and Applications to the<br />
determination of structure of inorganic compounds.<br />
Raman spectroscopy: Basic instrumentation and Applications.<br />
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: Basic principles and instrumentation<br />
and applications to structure determination.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. C. N. Banwale, Fundamentals of molecular spectroscopy, McGraw-Hill, New<br />
York.<br />
2. Skoog. Holler. Nieman. Principles of instrumental analysis, fifth edition,<br />
Thomson Learning Academic.<br />
3. M. H. willard, L. L. Merrite, J.J A.Dean, instrumental methods of analysis, Van<br />
Nostrand, New York.<br />
Course Title: Inorganic Reaction mechanism Paper- VIII,Code: CHEM-45<br />
Course contents<br />
Credit Hours : 03 Marks: 100<br />
Ligand replacement reactions<br />
D, ID, Ia and A mechanisms, activation parameter, order and rates of reaction, formation<br />
of complexes from equations, acid and base hydrolysis, displacement reaction in square<br />
complexes , trans effect, substitution reactions and mechanism of substitution in<br />
tetrahedral complexes.<br />
Electron transfer processes<br />
“Outer sphere” reactions, ligand bridge (inner sphere) reactions, two electron transfer and<br />
redox reactions.<br />
Theories of Acid-Base<br />
Acid-Base and Donor-Acceptor Chemistry: Acid and Base Strength; Hard and Soft.<br />
Acids and Bases;<br />
Books Recommended<br />
51
1. F.A. Cotton, and S.W, Advanced inorganic chemistry, John Wiley and sons, New<br />
York.<br />
2. F.Basolo and R. Johnson, Mechanism of inorganic reactions, John Wiley and<br />
sons, New York.<br />
3. F.Basalo and R. Johnson, Coordination chemistry, W.A. Benjamen , Row<br />
Publishers, New York.<br />
4. J.E. Huheey, Inorganic Harper and Row Publisher, New York.<br />
5. D.Jonson, Mechanism of inorganic reaction in solutions, McGraw-Hill, London.<br />
Course Title: Elementary group theory Paper- IX Code: CHEM-453<br />
Course contents<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Symmetry elements and symmetry operations, point groups, properties of groups,<br />
matrices, transformation of matrices, character tables and their applications in<br />
hybridization, IR and Raman spectroscopy.<br />
Books recommended<br />
1. Cotton F.A. “Chemical Applications of Groups Theory” Interscience Publishers<br />
(1963).<br />
2. Lowell Hall H. “Group Theory and Symmetry in Chemistry” McGraw Hill Book<br />
Company (1969).<br />
3. Vincent A. “Molecular symmetry and Group Theory”, John Wiley &sons,<br />
London, (1977)<br />
Course Title: Organometallics and Catalysis Paper- X Code: CHEM-454<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Definition and classification of organometallic compounds, sigma bonded organometallic<br />
compounds (Metal alkyls and Grignard reagents). Synthesis, properties and nature of<br />
bonding in pi complexes such as η 2 -η 7 . Catalysis, Types of catalysis, Organic synthesis<br />
via transition metal complexes (Hydroformylation, olefin hydrogenation, polymerization<br />
of ethene and oxidation of ethene to acetaldehyde).<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. M. Bochmann. Organometallic-1. Oxford University press (1994).<br />
2. M. Bochmann. Organometallic-2. Oxford University press (1994).<br />
3. A. Yamamoto. Organotransition metal chemistry. John wiley & sons, USA<br />
(1986).<br />
4. P. Pawell. Principles of organometallic chemistry. 2 nd edition, Chapman and Hall,<br />
New York (1988).<br />
52
Advance Inorganic Laboratory/ Research Project<br />
Credit Hours = 03 Marks : 100<br />
SPECIALIZATION COURSES IN ORGANIC <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Organic Chemistry Semester- IV<br />
Course Title: Natural Product Chemistry Paper -VII Code: CHEM- 461<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course contents<br />
Introduction to Natural Product: Primary and Secondary Metabolite and drug discoveries<br />
from Natural Products,<br />
Alkaloids<br />
Introduction; classification; isolation; general methods for structure elucidation;<br />
discussion with particular reference to structure and synthesis of ephedrine, nicotine<br />
quinine, and morphine.<br />
Terpenoids<br />
Introduction; classification; isolation; general methods for structure elucidation;<br />
discussion with particular reference to structure and synthesis of citral, α-terpineol, αpinene<br />
and camphor.<br />
Steroids<br />
Introduction; nomenclature and stereochemistry of steroids; structure determination of<br />
cholesterol and bile acids; introduction to steroidal hormones with particular reference to<br />
adrenal cortical hormones.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1 Clayden, J., Greeves, N. Warren, S. and Worthers, P. Organic Chemistry, Oxford<br />
University (2001).<br />
2 Mann, J., Davidson, R.S., Hobbs, J.B., Banthrope, D.V. and. Harborne, J.B,<br />
Natural Products, Longman Group Ltd., U.K.(1994).<br />
3 Nakanishi, K. ,Goto, T., Ioto, S. Natori, S. Nozone, S. et.al., Natural Products,<br />
Vol. 1, Academic Press Inc, New York (1974).<br />
4 Finar, I. L., Organic Chemistry, Stereochemistry and the Chemistry of Natural<br />
Products, Vol. 2, Pearson Education, Delhi (1975).<br />
5 Shoppee, C. W., “Chemistry of the Steroids”, Butterworths, London.<br />
6 Hesse, M., “Alkaloid Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
53
7 Fieser, L. F. and Fieser, M., “Steroids”, Asia Publishing House, London.<br />
Course Title: Retro Chemistry Paper -VIII Code: CHEM- 462<br />
Course Contents<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Introduction to retrosynthesis: concepts of synthons and retrosynthetic approach synthesis<br />
and uses: alkyl halides, alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, ethers, aromatic compounds, carbonyl<br />
and nitrogen compounds. Bond formations; C-C, C-N, and C-O bond formation.<br />
Difuctionalised compounds, 1,2; 1,3; 1,4; and 1,6 cyclizations, simple intramolecular<br />
reactions such as aldol, claisen condensation an robinson annulations reaction leading to<br />
cyclic structures. Application of the concepts to target molecules.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Waren, S., “Organic Synthesis-The Disconnection Approach”, John Wiley &<br />
Sons, New York (1992).<br />
2. Norman, R.O.C. and. Coxon, J.M Principles of organic synthesis, Blackie<br />
Academic and Professional, London (1993).<br />
3. Clayden, J. Greeves, N. Warren S. and Worthers, P. Organic Chemistry, Oxford<br />
University (2001).<br />
4. Willis, C. and Willis, M., Organic Synthesis, Oxford Science press (1995).<br />
5. Smith, M. B., “Organic Synthesis”, McGraw-Hill, New York.<br />
6. Waren, S., “Workbook for Organic Synthesis-The Disconnection Approach”,<br />
John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
7. Loudon, G. M., “Organic Chemistry”, Oxford University Press, New York.<br />
Course Title: Name Organic Reactions Paper IX Code: CHEM- 463<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Name Organic Reactions: Recent developments, mechanistic, stereochemical aspects and<br />
synthetic applications of various Name reactions: Aldol Condensation, Diels-alder<br />
reaction, Michael Addition, Robinson annulations, Knoevenagal Condensation, Clasien<br />
Condensation, Dickmann Condensation, Mannich Reaction, Wittig reaction, Peterson<br />
reaction, Heck Reaction, Friedal-Craft reaction, Favorski rearrangement, Husdiecker<br />
reaction and fischer indole synthesis, pinacole Rearrangement, Birgmann,s<br />
cyclisation,Birch reduction,<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Mundy, B.P. Ellerd, M.G. Favalozo F.G. and Favalozo, Jr. Name Reactions and<br />
Reagents in Organic Synthesis, john Wiley, New York (2005).<br />
54
2. Smith, M. B. and Marks, Advanced Organic Chemistry, Reactions, Mechanism<br />
and Structure, 5 th ed., John Wiley, New York (2001).<br />
3. R.O.S. Norman, Principles of organic synthesis, 3 rd ed., Chapman-Hall, London<br />
(1993).<br />
4. Gilchrist, T.L. and Rees, C. W., “Carbenes, Nitrenes and Arynes’ Nelson,<br />
London.<br />
5. Clayden, J., Greeves, N., Warren, S. and Wothers, P., “Organic Chemistry”,<br />
Oxford University press New York.<br />
6. Sykes, P.,“A guide book to Mechanism in organic Chemistry” longmann,<br />
London.<br />
7. Carry, F. A. and Sundberg, R.J., “ Advanced Organic Chemistry” Part A:”<br />
Structure and Mechanisms” oxford university press.<br />
8. Bruchner, R., Advance Organic Chemistry-Reaction Mechanism” Harcourt<br />
Science and Technology company, New York.<br />
Course Title: Interpretive Spectroscopy Paper- X Code: CHEM- 464<br />
Course Contents<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance: introduction, theory, instrumentation and sample handling.<br />
Chemical shifts in H-and C-NMR, factors affecting chemical shifts, chemical shifts<br />
equivalence and magnetic equivalence. Spin coupling: spin couplings and factors<br />
affecting spin couplings, first order spin systems. Double resonance experiments:<br />
selective spin decoupling. NOE difference spectra, H BB decoupled and DEPT spectra.<br />
Applications: shift reagents, dynamic NMR, structure elucidation of organic compounds<br />
by joint applications of UV, IR, NMR and MS.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Hesse, M. Meier H. and Zeeh, B. Spectroscopic methods in organic Chemistry,<br />
Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, Germany (1997).<br />
2. Pavia, D.L. Lampan G. M. and Kirz, G.S., Introduction to spectroscopy,<br />
Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning, USAS (2001).<br />
3. Silverstein, R.M. Webster, F.X. and Kiemle, Spectroscopic identification of<br />
organic compounds, John Wiley and Sons Inc., USA (2005).<br />
4. Harwood, L.M. and. Claridge, T.D.W introduction to Organic spectroscopy,<br />
Oxford University Press Inc., New York (1997).<br />
5. Friebolin, H., Basic one and two dimensional NMR spectroscopy, 4 th ed., Wiley<br />
VCH, New York (2005).<br />
6. Macomber, R.S., NMR Spectroscopy: Basic Principles and Applications,<br />
Harcourt Brace Jovanovich Publishers, San Diego (1998).<br />
7. Younas, M., Organic Spectroscopy,Ilmi kitab Khana, Lahore (2001).<br />
8. Breitmaier, E., Structure Elucidation by NMR in Organic chemistry: a Practical<br />
Guide, John Wiley, West Suessex (2002).<br />
55
Course Title: Advance Organic Chemistry Laboratory/ Research Project<br />
Course Code: Practical/ Research<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Synthesis and characterization of some commercially important polymers, isolation,<br />
purification and identification of natural products, synthesis of some pharmaceutically<br />
important hetrocyclic compounds.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Clarke, H. T., “A Handbook of Organic Analysis-Qualitative and Quantitative”,<br />
CBS Publishers & Distributors , New Delhi.<br />
2. Mann, F. G. and Saunders, B. C., “Practical Organic Chemistry”, Longman,<br />
London.<br />
3. Vogel, A. I., “Elementary Practical Organic Chemistry Part 3: Quantitative<br />
Organic Analysis”, Longman, London.<br />
4. Vishnoi, N. K., “Advanced Practical Organic Chemistry”, Vikas Publishing<br />
House Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
5. Furniss, B. S., Hannaford, A. J., Smith, P. W. G. and Tatchell, A. R., “Vogel’s<br />
Text Book of Practical Organic Chemistry”, National Book Foundation,<br />
Islamabad.<br />
6. Shriner, R. L., Hermann, C. K. F., Morrill, T. C., Curtin, D. Y. and Fuson, R. C.,<br />
“The Systematic Identification of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons,<br />
New York.<br />
7. Mendham, J., Denney, R. C., Barnes, J. D. and Thomas, M. J. K., “Vogel’s Text<br />
Book of Quantitative Chemical Analysis”, Pearson Education, New Delhi.<br />
8. Beckett, A. H. and Stenlake, J. B., “Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry”, Athlone<br />
Press, London.<br />
9. Pavia, D. L., Lampman, G. M. and Kriz, G. S. “Introduction to Spectroscopy: A<br />
Guide for Students of Organic Chemistry”, Saunders Golden Sunburst Series,<br />
London.<br />
10. Silverstein, R. N., Barrler, G. C. and Morrill, T. C., “Spectrometric Identification<br />
of Organic Compounds”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
11. Kalsi, P.S. “Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds”, Wiley Eastern Ltd., New<br />
Delhi.<br />
12. Palleros, D. R., “Experimental Organic Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New<br />
York.<br />
13. Keese, R, Muller, R. K. and Toube, T. P., “Fundamentals of Preparative Organic<br />
Chemistry”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
14. Gurtu, J. N. and Kapoor, R., “Advanced Experimental Chemistry”, S. Chand &<br />
Company Ltd., New Delhi.<br />
15. Newman, M. S., “An Advanced Organic Laboratory Course”, Macmillan, New<br />
York.<br />
56
16. Zubrick, J. W., “The Organic Chem Lab Survival Manual: A Student’s Guide to<br />
Techniques”, John Wiley & Sons, New York.<br />
SPECIALIZATION IN PHYSICAL <strong>CHEMISTRY</strong><br />
Course Title: Chemical Kinetics Paper-VII, Code: CHEM- 471<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Derivation of the rate equations. Theory of absolute reaction rate. Reversible reactions,<br />
parallel reactions and consecutive reactions. Correlation between physical properties and<br />
concentration. Comparison of collision and absolute reaction theories. Advanced theories<br />
of unimolecular reactions. Potential energy surfaces. Thermodynamic formulation of<br />
reaction rates. Calculation of entropy and enthalpy changes. Thermal decomposition of<br />
nitrogen pentaoxide.<br />
Recommended Books<br />
1. Albery J., Electrode Kinetics, Clarendon, Oxford (1975).<br />
1. Espenson, J. H. Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanism 2 nd<br />
ed., McGraw Hill<br />
London (2002).<br />
2. Espenson J.H. “Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanisms” 2 nd<br />
ed. McGraw<br />
Hill, New York (1995).<br />
3. Frost A.A. and Pearson R.G. “Kinetic and Mechanism” 2 nd<br />
ed. John Wiley and<br />
Sons Inc, New York (1961).<br />
4. Laidler K.J. “Chemical Kinetics” 3 rd<br />
ed. Pearson Education Company, New York<br />
(1987).<br />
5. Laidler L.J. “Reaction Kinetic VII, II Reaction in Solution” Pergamon Press, New<br />
York (1963).<br />
Course Title: Molecular Spectroscopy Paper-VIII , Code: CHEM- 472<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter. Symmetry properties of molecules.<br />
Microwave and infrared spectroscopy. Rotational, vibrational and rotational-vibrational<br />
spectra of diatomic and polyatomic molecules. Electronic spectra of simple molecules.<br />
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Raman spectroscopy.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Whiffen D. H. “Spectroscopy” Longmans Green and Co.: London, (1966).<br />
2. Barrow G. “Molecular Spectroscopy” McGraw Hill (1962).<br />
57
1. Becker E. D. “High Resolution NMR; Theory & Chemical Application”, New<br />
York, Academic Press (1980).<br />
3. Graybal J.D. “Molecular Spectroscopy”, New York, McGraw-Hill (1988).<br />
Course Title: Surface Chemistry and Catalysis Paper - IX , Code: CHEM- 473<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Adsorption, types of adsorption, adsorption isotherm, Langmuir, Freundlich, B.E.T<br />
adsorption isotherm, application of B.E.T adsorption isotherm,Gas adsorption isotherm or<br />
Henry equation, Surface active and surface inactive substances, Solid surfaces. Gas solid<br />
interface. Thermodynamics of adsorption. Heterogeneous catalysis. Kinetic and<br />
mechanisms of catalyzed reactions. Adsorption at liquid surfaces. Enzymatic catalysis.<br />
Organized molecular assemblies. Colloidal solutions. Catalyst preparation methods.<br />
Industrial catalysts.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Segal H. “Enzyme Kinetics” John Wiley New York (1975).<br />
2. Schlutz A.R. “Enzyme Kinetics” (1964) Cambridge University Press England.<br />
Course Title: Nuclear Chemistry Paper-X Code: CHEM- 474<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
Course Contents<br />
Radioactivity, elemental particles, isotopes, isobars, isotones,<br />
transmutation and artificial radioactivity, Bohar,s theory of nuclear reaction,<br />
classification of nuclear reactions, nuclear reactions vs chemicals reactions, mass defect<br />
and binding energy, nuclear fusion and nuclear fission, Q.value of nuclear reaction.<br />
Atomic nucleus, nuclides, nuclear stability, nuclear energetic, nuclear models (shell +<br />
liquid drop model), non-spontaneous nuclear processes, nuclear reactors, beta decay<br />
systematic, nuclear spins. Atomic bomb, hydrogen bomb, uses of radioisotopes in<br />
reaction mechanism, in diagnosis of diseases, in industry, in agriculture. Determination of<br />
the age of the earth by rock dating method, determination of the age of recent objects by<br />
radioactive carbon dating method.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Albert R.A., Robert J.S. and Moungi G.B. “Physical Chemistry”. 4 th<br />
ed., John<br />
Wiley and Sons (2004).<br />
2. Ball D.W. “Physical Chemistry” 1 st<br />
ed., Brooks/Cole Co. Inc. (2003).<br />
58
3. Vertes A. “Basics of Nuclear Science” Kluwer Academic Publisher London<br />
(2003).<br />
4. Friedlander G. and Kennedy J.W. “Nuclear and Radiochemistry” 3 rd<br />
ed., Wiley,<br />
New York (1981).<br />
Advanced Physical Lab/Research Project<br />
Credit Hours: 03 Marks: 100<br />
� Study of multistep reactions.<br />
� Sugar analysis and inversion studies by polarimetry.<br />
� Study of isotherms and experiments of surface chemistry.<br />
� Kinetics of fading of phenolphthalein in alkaline solution.<br />
� Study of the effect of pH on the rate constant of the reaction between iodide and<br />
persulphate ions.<br />
� Study of the salt effect on the rate constant of the reaction between similar<br />
charges of ions.<br />
� Kinetics of autocatalytic reaction between permanganate and oxalate ions.<br />
� Determination of energy of activation of the reaction between similar chargers of<br />
ions.<br />
� Kinetics of the reaction between methyl orange and peroxodisulphate ions in<br />
presence of bromide ions.<br />
� Stoichiometry of a complex in solution by Job’s method.<br />
Books Recommended<br />
1. Braun R.D. and Walters F. “Application of Chemical Analysis” (1982).<br />
2. David P. “Experiments in Physical Chemistry” 5 th<br />
ed. (1989).<br />
1. 3). Shoemaker C.W., Nibler G.J.W. and Christian G.D. “Analytical Chemistry”<br />
6 th<br />
ed. (2004).<br />
3. James A.M. and Prichard F.E. “Practical Physical Chemistry” 3 rd<br />
ed. Longman<br />
(1974).<br />
4. Mowry S. and Ogren P.J., J. Chemical Education, 76(7) (1999).<br />
2. 6). Shoemaker D.P., Garland C.W. and Nibler J.W. “Experiments in Physical<br />
Chemistry” McGraw Hills, New York (1989).<br />
59