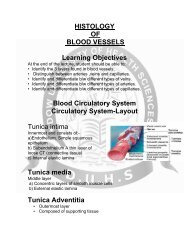
morphological changes of reversible injury
morphological changes of reversible injury
morphological changes of reversible injury
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
FATES OF NECROTIC CELL<br />
• May persists for sometimes<br />
• Digested by enzymes<br />
• Replaced by myelin figures<br />
• Phagocytosed by other cells<br />
• Further degraded in to fatty acids<br />
• Calcified<br />
NECROSIS: TYPES<br />
Macroscopic<br />
• Coagulative necrosis,<br />
• Caseous necrosis<br />
• Liquefactive necrosis<br />
• Fat necrosis<br />
Microscopic<br />
• Fibrinoid necrosis<br />
COAGULATIVE NECROSIS<br />
“Underlying tissue architecture is preserved for several<br />
days”<br />
can be observed by light microscopy<br />
Is typically seen in hypoxic (low-oxygen) environments<br />
Examples<br />
Infarcts <strong>of</strong> solid organs such as Heart, spleen, kidney (except<br />
brain).