Menadione Nicotinamide Bisulfite Is a Bîoactîve Source of ...
Menadione Nicotinamide Bisulfite Is a Bîoactîve Source of ...
Menadione Nicotinamide Bisulfite Is a Bîoactîve Source of ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
niacin bioactivity <strong>of</strong> MNB when compared with<br />
nicotinamide (U.S. Biochemicals, Cleveland, OH). On<br />
d 8 posthatching, quadruplicate groups <strong>of</strong> four male<br />
chicks were assigned to the following dietary treat<br />
ments: 0, 2.5, 5.0 and 30 mg/kg nicotinamide (the<br />
latter a positive control) or 0, 2.5 and 5.0 mg/kg<br />
nicotinamide from MNB. The NRC (1984) estimate <strong>of</strong><br />
the dietary nicotinic acid requirement <strong>of</strong> young<br />
chicks is 27 mg/kg. On d 22 posthatching, chicks and<br />
feed were weighed, and chick weight gain, feed intake<br />
and feed efficiency were determined. Chicks that had<br />
been fed 0 and 5.0 mg/kg nicotinamide (from both<br />
MNB and nicotinamide) were killed by cervical dislo<br />
cation at d 22 posthatching, and portions (0.25 g) <strong>of</strong><br />
liver tissue were removed and pooled by replicate.<br />
Liver samples were homogenized and heated in a<br />
boiling water bath for 5 min. Hepatic pyridine nucleotides<br />
(NAD + NADH) were then determined by the<br />
enzyme-cycling<br />
(1969).<br />
procedure <strong>of</strong> Nisselbaum and Green<br />
Toxicity assays. Assay 3 was conducted to de<br />
termine the toxic effects <strong>of</strong> an acute oral (crop intu<br />
bation) dose <strong>of</strong> menadione from MPB (as a standard)<br />
or MNB. Preliminary work in our laboratory had es<br />
tablished that doses <strong>of</strong> MNB or MPB providing mena<br />
dione at 500 mg/kg body weight or less caused neither<br />
mortality nor morbidity. Assay 3 was therefore<br />
designed to provide logarithmic doses <strong>of</strong> menadione,<br />
starting at 100 mg/kg and working up to 1600 mg/kg<br />
body weight. Following dosing at d 8 posthatching,<br />
triplicate groups <strong>of</strong> four chicks at each dose level were<br />
fed a 23% protein corn soybean meal starter diet5 for<br />
a 14-d observation period.<br />
Assay 4 was a 14-d chronic toxicity study involving<br />
triplicate groups <strong>of</strong> four chicks at each menadione<br />
dose level (0, 30, 300, 3000 and 6000 mg/kg diet) from<br />
MPB or MNB. Additions were made to the cornsoybean<br />
meal starter diet. At termination <strong>of</strong> the assay<br />
on d 22 posthatching, blood was obtained by heart<br />
puncture after which 1-mL portions from each chick<br />
in a pen were pooled, resulting in three pooled<br />
samples for each <strong>of</strong> the nine treatments. Blood hemo<br />
globin was determined by the method <strong>of</strong> Crosby et al.<br />
(1954).<br />
Statistical analyses. Common-intercept multiple<br />
linear regression was conducted for data in Assays 1<br />
and 2 using the General Linear Model procedure <strong>of</strong><br />
SAS (1985). Data were first fitted to simple linear<br />
regression equations to establish that Y-intercepts<br />
were not different (P > 0.05) after which the multiplelinear<br />
regression model was fitted<br />
menadione biopotency assessment<br />
to the data. For<br />
in Assay 1, prothrombin<br />
time (s) was regressed on supplemental<br />
menadione intake (/¿g); for nicotinamide biopotency,<br />
weight gain (g) was regressed on supplemental<br />
nicotinamide intake (mg). The ratio <strong>of</strong> slopes (MNB:<br />
MPB) gave estimates <strong>of</strong> menadione or nicotinamide<br />
potency for MNB relative to MPB.<br />
MENADIONE NICOTINAMIDE BISULFITE 739<br />
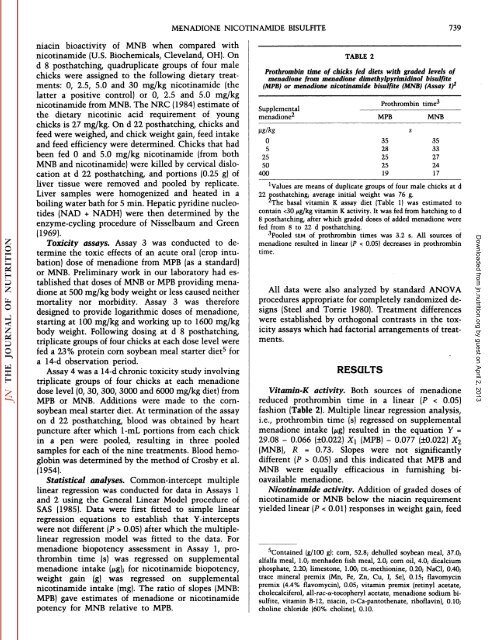
TABLE 2<br />
Prothrombin time <strong>of</strong> chicks fed diets with graded levels <strong>of</strong><br />
menadione from menadione dimethylpyrimidinol bisulfite<br />
(MPB) or menadione nicotinamide bisulfite (MNB) (Assay I)1<br />
menadioneUS/kg052550400ProthrombinMPBs3528252519time3MNB3533272417<br />
'Values are means <strong>of</strong> duplicate groups <strong>of</strong> four male chicks at d<br />
22 posthatching; average initial weight was 76 g.<br />
The basal vitamin K assay diet (Table 1) was estimated to<br />
contain 0.05) and this indicated that MPB and<br />
MNB were equally efficacious in furnishing bioavailable<br />
menadione.<br />
<strong>Nicotinamide</strong> activity. Addition <strong>of</strong> graded doses <strong>of</strong><br />
nicotinamide or MNB below the niacin requirement<br />
yielded linear (P < 0.01) responses in weight gain, feed<br />
5Contained (g/100 g): corn, 52.8; dehulled soybean meal, 37.0;<br />
alfalfa meal, 1.0; menhaden fish meal, 2.0; corn oil, 4.0; dicalcium<br />
phosphate, 2.20; limestone, 1.00; DL-methionine, 0.20; NaCl, 0.40;<br />
trace mineral premix (Mn, Fé,Zn, Cu, I, Se), 0.15; flavomycin<br />
premix (4.4% flavomycin), 0.05; vitamin premix (retinyl acetate,<br />
cholecalciferol, all-rac-a-tocopheryl acetate, menadione sodium bi<br />
sulfite, vitamin B-12, niacin, D-Ca-pantothenate, rib<strong>of</strong>lavin), 0.10;<br />
choline chloride (60% choline), 0.10.<br />
Downloaded from<br />
jn.nutrition.org<br />
by guest on April 2, 2013