A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
16 A Guide to Carotenoid Analysis in Foods<br />
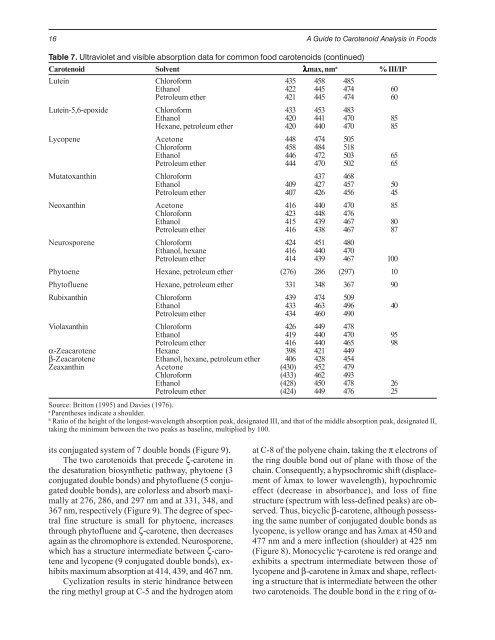
Table 7. Ultraviolet and visible absorption data for common food carotenoids (continued)<br />
Carotenoid Solvent λmax, nm a % III/II b<br />
Lutein Chloroform<br />
Ethanol<br />
435<br />
422<br />
458<br />
445<br />
485<br />
474 60<br />
Petroleum ether 421 445 474 60<br />
Lutein-5,6-epoxide Chloroform<br />
Ethanol<br />
433<br />
420<br />
453<br />
441<br />
483<br />
470 85<br />
Hexane, petroleum ether 420 440 470 85<br />
Lycopene Acetone<br />
Chloroform<br />
448<br />
458<br />
474<br />
484<br />
505<br />
518<br />
Ethanol 446 472 503 65<br />
Petroleum ether 444 470 502 65<br />
Mutatoxanthin Chloroform 437 468<br />
Ethanol 409 427 457 50<br />
Petroleum ether 407 426 456 45<br />
Neoxanthin Acetone 416 440 470 85<br />
Chloroform 423 448 476<br />
Ethanol<br />
Petroleum ether<br />
415<br />
416<br />
439<br />
438<br />
467<br />
467<br />
80<br />
87<br />
Neurosporene Chloroform 424 451 480<br />
Ethanol, hexane<br />
Petroleum ether<br />
416<br />
414<br />
440<br />
439<br />
470<br />
467 100<br />
Phytoene Hexane, petroleum ether (276) 286 (297) 10<br />
Phytofluene Hexane, petroleum ether 331 348 367 90<br />
Rubixanthin Chloroform 439 474 509<br />
Ethanol 433 463 496 40<br />
Petroleum ether 434 460 490<br />
Violaxanthin Chloroform 426 449 478<br />
Ethanol 419 440 470 95<br />
α-Zeacarotene<br />
Petroleum ether<br />
Hexane<br />
416<br />
398<br />
440<br />
421<br />
465<br />
449<br />
98<br />
β-Zeacarotene Ethanol, hexane, petroleum ether 406 428 454<br />
Zeaxanthin Acetone<br />
Chloroform<br />
(430)<br />
(433)<br />
452<br />
462<br />
479<br />
493<br />
Ethanol (428) 450 478 26<br />
Petroleum ether (424) 449 476 25<br />
Source: Britton (1995) and Davies (1976).<br />
a Parentheses indicate a shoulder.<br />
b Ratio of the height of the longest-wavelength absorption peak, designated III, and that of the middle absorption peak, designated II,<br />
taking the minimum between the two peaks as baseline, multiplied by 100.<br />
its conjugated system of 7 double bonds (Figure 9).<br />
The two carotenoids that precede ζ-carotene in<br />
the desaturation biosynthetic pathway, phytoene (3<br />
conjugated double bonds) and phytofluene (5 conjugated<br />
double bonds), are colorless and absorb maximally<br />
at 276, 286, and 297 nm and at 331, 348, and<br />
367 nm, respectively (Figure 9). The degree of spectral<br />
fine structure is small for phytoene, increases<br />
through phytofluene and ζ-carotene, then decreases<br />
again as the chromophore is extended. Neurosporene,<br />
which has a structure intermediate between ζ-carotene<br />
and lycopene (9 conjugated double bonds), exhibits<br />
maximum absorption at 414, 439, and 467 nm.<br />
Cyclization results in steric hindrance between<br />
the ring methyl group at C-5 and the hydrogen atom<br />
at C-8 of the polyene chain, taking the π electrons of<br />
the ring double bond out of plane with those of the<br />
chain. Consequently, a hypsochromic shift (displacement<br />
of λmax to lower wavelength), hypochromic<br />
effect (decrease in absorbance), and loss of fine<br />
structure (spectrum with less-defined peaks) are observed.<br />
Thus, bicyclic β-carotene, although possessing<br />
the same number of conjugated double bonds as<br />
lycopene, is yellow orange and has λmax at 450 and<br />
477 nm and a mere inflection (shoulder) at 425 nm<br />
(Figure 8). Monocyclic γ-carotene is red orange and<br />
exhibits a spectrum intermediate between those of<br />
lycopene and β-carotene in λmax and shape, reflecting<br />
a structure that is intermediate between the other<br />
two carotenoids. The double bond in the ε ring of α-