A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
A GUIDE TO CAROTENOID ANALYSIS IN FOODS
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
22 A Guide to Carotenoid Analysis in Foods<br />
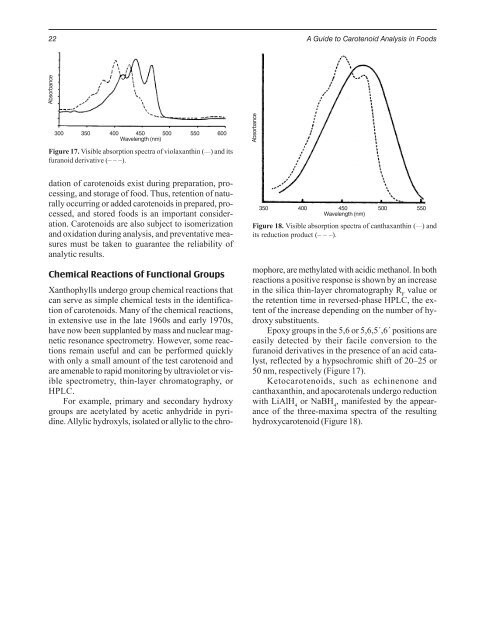
Absorbance<br />
300 350 400 450 500 550 600<br />
Wavelength (nm)<br />
Figure 17. Visible absorption spectra of violaxanthin ( ___ ) and its<br />
furanoid derivative (– – –).<br />
dation of carotenoids exist during preparation, processing,<br />
and storage of food. Thus, retention of naturally<br />
occurring or added carotenoids in prepared, processed,<br />
and stored foods is an important consideration.<br />
Carotenoids are also subject to isomerization<br />
and oxidation during analysis, and preventative measures<br />
must be taken to guarantee the reliability of<br />
analytic results.<br />
Chemical Reactions of Functional Groups<br />
Xanthophylls undergo group chemical reactions that<br />
can serve as simple chemical tests in the identification<br />
of carotenoids. Many of the chemical reactions,<br />
in extensive use in the late 1960s and early 1970s,<br />
have now been supplanted by mass and nuclear magnetic<br />
resonance spectrometry. However, some reactions<br />
remain useful and can be performed quickly<br />
with only a small amount of the test carotenoid and<br />
are amenable to rapid monitoring by ultraviolet or visible<br />
spectrometry, thin-layer chromatography, or<br />
HPLC.<br />
For example, primary and secondary hydroxy<br />
groups are acetylated by acetic anhydride in pyridine.<br />
Allylic hydroxyls, isolated or allylic to the chro-<br />
Absorbance<br />
350 400 450 500 550<br />
Wavelength (nm)<br />
Figure 18. Visible absorption spectra of canthaxanthin ( ___ ) and<br />
its reduction product (– – –).<br />
mophore, are methylated with acidic methanol. In both<br />
reactions a positive response is shown by an increase<br />
in the silica thin-layer chromatography R F value or<br />
the retention time in reversed-phase HPLC, the extent<br />
of the increase depending on the number of hydroxy<br />
substituents.<br />
Epoxy groups in the 5,6 or 5,6,5´,6´ positions are<br />
easily detected by their facile conversion to the<br />
furanoid derivatives in the presence of an acid catalyst,<br />
reflected by a hypsochromic shift of 20–25 or<br />
50 nm, respectively (Figure 17).<br />
Ketocarotenoids, such as echinenone and<br />
canthaxanthin, and apocarotenals undergo reduction<br />
with LiAlH 4 or NaBH 4 , manifested by the appearance<br />
of the three-maxima spectra of the resulting<br />
hydroxycarotenoid (Figure 18).