Chapter 9 - University of Dayton Academic Webserver
Chapter 9 - University of Dayton Academic Webserver
Chapter 9 - University of Dayton Academic Webserver
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
324<br />
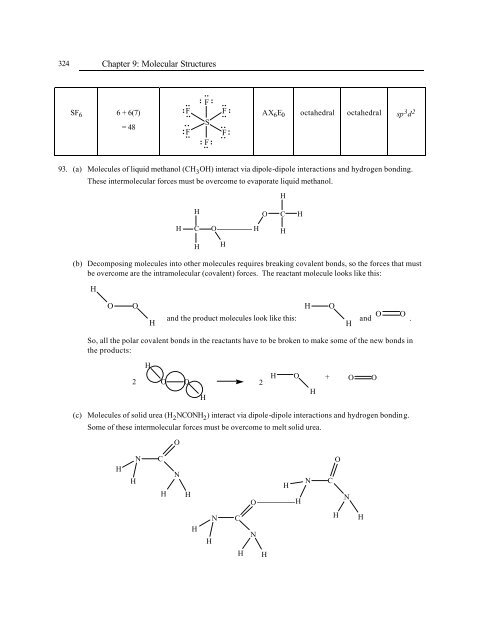
SF 6<br />
<strong>Chapter</strong> 9: Molecular Structures<br />
6 + 6(7)<br />
= 48<br />
. . .<br />
..<br />
. ..<br />
..<br />
. .<br />
F<br />
F. F<br />
S<br />
F<br />
.. F<br />
. .<br />
. F.<br />
.<br />
. .<br />
.. .<br />
.<br />
AX 6E 0<br />
octahedral<br />
octahedral<br />
93. (a) Molecules <strong>of</strong> liquid methanol (CH 3 OH) interact via dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.<br />
These intermolecular forces must be overcome to evaporate liquid methanol.<br />
H<br />
H C<br />
H<br />
O<br />
H<br />
H<br />
O<br />
H<br />
C<br />
H<br />
H<br />
sp 3 d 2<br />
(b) Decomposing molecules into other molecules requires breaking covalent bonds, so the forces that must<br />
be overcome are the intramolecular (covalent) forces. The reactant molecule looks like this:<br />
H<br />
O O<br />
H<br />
and the product molecules look like this:<br />
H O<br />
H and O O .<br />
So, all the polar covalent bonds in the reactants have to be broken to make some <strong>of</strong> the new bonds in<br />
the products:<br />
H<br />
2 O O<br />
2<br />
H<br />
H O<br />
H<br />
+<br />
O O<br />
(c) Molecules <strong>of</strong> solid urea (H 2 NCONH 2 ) interact via dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.<br />
Some <strong>of</strong> these intermolecular forces must be overcome to melt solid urea.<br />
H<br />
H<br />
N C<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
N C<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
N C<br />
O<br />
N<br />
H H