chapter 1 - Bentham Science
chapter 1 - Bentham Science
chapter 1 - Bentham Science
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
64 HPFP: Recent Advances in Insects and Other Arthropods Vol. 1 Goto and Kurata<br />
residues) at the C-terminal that has sequence similarity to N-acetyl-muramyl-alanine amidases, such as<br />
bacteriophage lysozymes. This homology also implies that PGRPs and prokaryotic N-acetyl-muramylalanine<br />
amidases evolved from a common ancestor gene [19-20].<br />
Epithelial immune<br />
responses<br />
JAK/STAT<br />
?<br />
?<br />
?<br />
DAMPs<br />
Imd<br />
Danger<br />
signals<br />
AMPs and effector<br />
genes expression<br />
Stress<br />
Host recognition<br />
?<br />
Humoral immune<br />
responses<br />
Serine proteases<br />
cascades<br />
spz/Toll<br />
Serpins<br />
?<br />
?<br />
Coagulation proPO<br />
cascades activation<br />
? ?<br />
Pathogens PAMPs<br />
(LPS, β-glucan, PGN etc..)<br />
Clot Melanization<br />
PRRs<br />
(PGRPs,GNBPs, lectins etc..)<br />
Cellular immune<br />
responses<br />
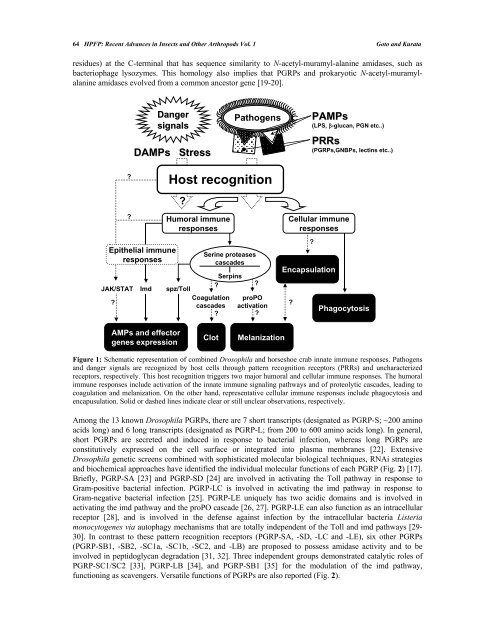
Figure 1: Schematic representation of combined Drosophila and horseshoe crab innate immune responses. Pathogens<br />
and danger signals are recognized by host cells through pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) and uncharacterized<br />
receptors, respectively. This host recognition triggers two major humoral and cellular immune responses. The humoral<br />
immune responses include activation of the innate immune signaling pathways and of proteolytic cascades, leading to<br />
coagulation and melanization. On the other hand, representative cellular immune responses include phagocytosis and<br />
encapusulation. Solid or dashed lines indicate clear or still unclear observations, respectively.<br />
Among the 13 known Drosophila PGRPs, there are 7 short transcripts (designated as PGRP-S; ~200 amino<br />
acids long) and 6 long transcripts (designated as PGRP-L; from 200 to 600 amino acids long). In general,<br />
short PGRPs are secreted and induced in response to bacterial infection, whereas long PGRPs are<br />
constitutively expressed on the cell surface or integrated into plasma membranes [22]. Extensive<br />
Drosophila genetic screens combined with sophisticated molecular biological techniques, RNAi strategies<br />
and biochemical approaches have identified the individual molecular functions of each PGRP (Fig. 2) [17].<br />
Briefly, PGRP-SA [23] and PGRP-SD [24] are involved in activating the Toll pathway in response to<br />
Gram-positive bacterial infection. PGRP-LC is involved in activating the imd pathway in response to<br />
Gram-negative bacterial infection [25]. PGRP-LE uniquely has two acidic domains and is involved in<br />
activating the imd pathway and the proPO cascade [26, 27]. PGRP-LE can also function as an intracellular<br />
receptor [28], and is involved in the defense against infection by the intracellular bacteria Listeria<br />
monocytogenes via autophagy mechanisms that are totally independent of the Toll and imd pathways [29-<br />
30]. In contrast to these pattern recognition receptors (PGRP-SA, -SD, -LC and -LE), six other PGRPs<br />
(PGRP-SB1, -SB2, -SC1a, -SC1b, -SC2, and -LB) are proposed to possess amidase activity and to be<br />
involved in peptidoglycan degradation [31, 32]. Three independent groups demonstrated catalytic roles of<br />
PGRP-SC1/SC2 [33], PGRP-LB [34], and PGRP-SB1 [35] for the modulation of the imd pathway,<br />
functioning as scavengers. Versatile functions of PGRPs are also reported (Fig. 2).<br />
?<br />
Encapsulation<br />
?<br />
Phagocytosis