chapter 1 - Bentham Science
chapter 1 - Bentham Science
chapter 1 - Bentham Science
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
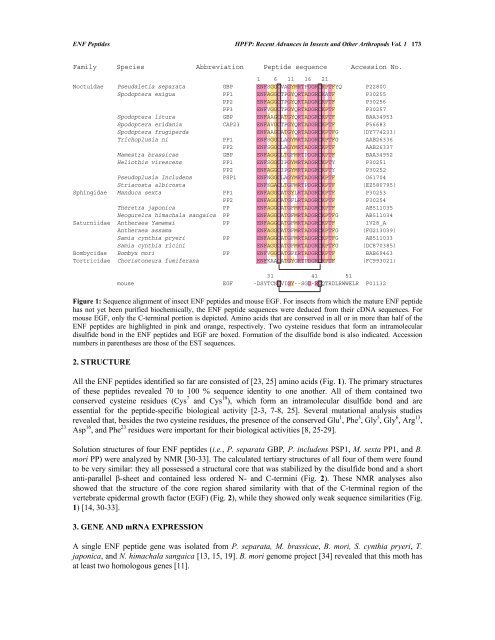
ENF Peptides HPFP: Recent Advances in Insects and Other Arthropods Vol. 1 173<br />
Family Species Abbreviation Peptide sequence Accession No.<br />
1 6 11 16 21<br />
Noctuidae Pseudaletia separata GBP ENFSGGCVAGYMRTPDGRCKPTFYQ P22800<br />
Spodoptera exigua PP1 ENFAGGCTPGYQRTADGRCKATF P30255<br />
PP2 ENFAGGCTPGYQRTADGRCKPTF P30256<br />
PP3 ENFVGGCTPGYQRTADGRCKPTF P30257<br />
Spodoptera litura GBP ENFAAGCATGYQRTADGRCKPTF BAA34953<br />
Spodoptera eridania CAP23 ENFAVGCTPGYQRTADGRCKPTF P56683<br />
Spodoptera frugiperda ENFAAGCATGYQRTADGRCKPTFG (DY774233)<br />
Trichoplusia ni PP1 ENFSGGCLAGYMRTADGRCKPTFG AAB26336<br />
PP2 ENFSGGCLAGYMRTADGRCKPTF AAB26337<br />
Mamestra brassicae GBP ENFAGGCLTGFMRTPDGRCKPTF BAA34952<br />
Heliothis virescens PP1 ENFSGGCIPGYMRTADGRCKPTY P30251<br />
PP2 ENFAGGCIPGYMRTADGRCKPTY P30252<br />
Pseudoplusia Includens PSP1 ENFNGGCLAGYMRTADGRCKPTF O61704<br />
Striacosta albicosta ENFKGACLTGFMRTPDGRCKPTF (EZ580795)<br />
Sphingidae Manduca sexta PP1 ENFAGGCATGYLRTADGRCKPTF P30253<br />
PP2 ENFAGGCATGFLRTADGRCKPTF P30254<br />
Theretra japonica PP ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTF AB511035<br />
Neogurelca himachala sangaica PP ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTFG AB511034<br />
Saturniidae Antheraea Yamamai PP ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTF 1V28_A<br />
Antheraea assama ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTFG (FG213039)<br />
Samia cynthia pryeri PP ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTFG AB511033<br />
Samia cynthia ricini ENFAGGCATGFMRTADGRCKPTFG (DC870385)<br />
Bombycidae Bombyx mori PP ENFVGGCATGFKRTADGRCKPTF BAB69463<br />
Tortricidae Choristoneura fumiferana ENFKAACATGYGRTPDGRCKPTF (FC993021)<br />
Figure 1: Sequence alignment of insect ENF peptides and mouse EGF. For insects from which the mature ENF peptide<br />
has not yet been purified biochemically, the ENF peptide sequences were deduced from their cDNA sequences. For<br />
mouse EGF, only the C-terminal portion is depicted. Amino acids that are conserved in all or in more than half of the<br />
ENF peptides are highlighted in pink and orange, respectively. Two cysteine residues that form an intramolecular<br />
disulfide bond in the ENF peptides and EGF are boxed. Formation of the disulfide bond is also indicated. Accession<br />
numbers in parentheses are those of the EST sequences.<br />
2. STRUCTURE<br />
31 41 51<br />
mouse EGF -DSYTCNCVIGY--SGD-RCQTRDLRWWELR P01132<br />
All the ENF peptides identified so far are consisted of [23, 25] amino acids (Fig. 1). The primary structures<br />
of these peptides revealed 70 to 100 % sequence identity to one another. All of them contained two<br />
conserved cysteine residues (Cys 7 and Cys 19 ), which form an intramolecular disulfide bond and are<br />
essential for the peptide-specific biological activity [2-3, 7-8, 25]. Several mutational analysis studies<br />
revealed that, besides the two cysteine residues, the presence of the conserved Glu 1 , Phe 3 , Gly 5 , Gly 6 , Arg 13 ,<br />
Asp 16 , and Phe 23 residues were important for their biological activities [8, 25-29].<br />
Solution structures of four ENF peptides (i.e., P. separata GBP, P. includens PSP1, M. sexta PP1, and B.<br />
mori PP) were analyzed by NMR [30-33]. The calculated tertiary structures of all four of them were found<br />
to be very similar: they all possessed a structural core that was stabilized by the disulfide bond and a short<br />
anti-parallel -sheet and contained less ordered N- and C-termini (Fig. 2). These NMR analyses also<br />
showed that the structure of the core region shared similarity with that of the C-terminal region of the<br />
vertebrate epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Fig. 2), while they showed only weak sequence similarities (Fig.<br />
1) [14, 30-33].<br />
3. GENE AND mRNA EXPRESSION<br />
A single ENF peptide gene was isolated from P. separata, M. brassicae, B. mori, S. cynthia pryeri, T.<br />
japonica, and N. himachala sangaica [13, 15, 19]. B. mori genome project [34] revealed that this moth has<br />
at least two homologous genes [11].