chapter 2 - Bentham Science
chapter 2 - Bentham Science
chapter 2 - Bentham Science
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Monovalent and Multivalent Glycoconjugates as High Affinity Synthesis and Biological Applications of Glycoconjugates 93<br />
additional chimera type [9, 14, 15]. Galectins are soluble cytosolic proteins and their quaternary structure depends<br />
on their concentration and environment [15]. Below a concentration of 10 µM, galectins are usually present as noncovalent<br />
symmetric dimers while some members may occur as trimers and tetramers (Fig. 1) [15, 16].<br />
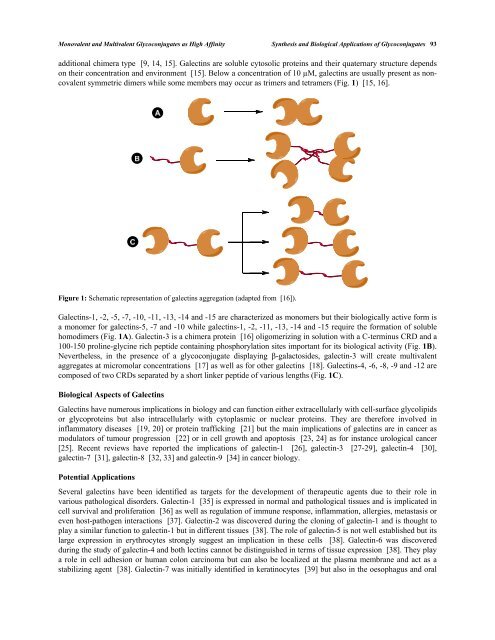
Figure 1: Schematic representation of galectins aggregation (adapted from [16]).<br />
Galectins-1, -2, -5, -7, -10, -11, -13, -14 and -15 are characterized as monomers but their biologically active form is<br />
a monomer for galectins-5, -7 and -10 while galectins-1, -2, -11, -13, -14 and -15 require the formation of soluble<br />
homodimers (Fig. 1A). Galectin-3 is a chimera protein [16] oligomerizing in solution with a C-terminus CRD and a<br />
100-150 proline-glycine rich peptide containing phosphorylation sites important for its biological activity (Fig. 1B).<br />
Nevertheless, in the presence of a glycoconjugate displaying -galactosides, galectin-3 will create multivalent<br />
aggregates at micromolar concentrations [17] as well as for other galectins [18]. Galectins-4, -6, -8, -9 and -12 are<br />
composed of two CRDs separated by a short linker peptide of various lengths (Fig. 1C).<br />
Biological Aspects of Galectins<br />
Galectins have numerous implications in biology and can function either extracellularly with cell-surface glycolipids<br />
or glycoproteins but also intracellularly with cytoplasmic or nuclear proteins. They are therefore involved in<br />
inflammatory diseases [19, 20] or protein trafficking [21] but the main implications of galectins are in cancer as<br />
modulators of tumour progression [22] or in cell growth and apoptosis [23, 24] as for instance urological cancer<br />
[25]. Recent reviews have reported the implications of galectin-1 [26], galectin-3 [27-29], galectin-4 [30],<br />
galectin-7 [31], galectin-8 [32, 33] and galectin-9 [34] in cancer biology.<br />
Potential Applications<br />
Several galectins have been identified as targets for the development of therapeutic agents due to their role in<br />
various pathological disorders. Galectin-1 [35] is expressed in normal and pathological tissues and is implicated in<br />
cell survival and proliferation [36] as well as regulation of immune response, inflammation, allergies, metastasis or<br />
even host-pathogen interactions [37]. Galectin-2 was discovered during the cloning of galectin-1 and is thought to<br />
play a similar function to galectin-1 but in different tissues [38]. The role of galectin-5 is not well established but its<br />
large expression in erythrocytes strongly suggest an implication in these cells [38]. Galectin-6 was discovered<br />
during the study of galectin-4 and both lectins cannot be distinguished in terms of tissue expression [38]. They play<br />
a role in cell adhesion or human colon carcinoma but can also be localized at the plasma membrane and act as a<br />
stabilizing agent [38]. Galectin-7 was initially identified in keratinocytes [39] but also in the oesophagus and oral