Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics
Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics
Introduction to Relativistic Hydrodynamics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
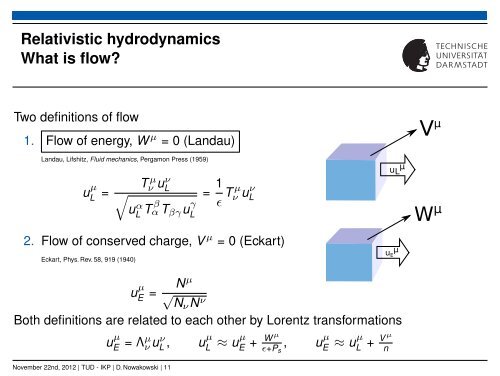
<strong>Relativistic</strong> hydrodynamics<br />
What is flow?<br />
Two definitions of flow<br />
1. Flow of energy, W µ = 0 (Landau)<br />
Landau, Lifshitz, Fluid mechanics, Pergamon Press (1959)<br />
u µ<br />
L =<br />
T µ ν uν L<br />
<br />
u α L T β α Tβγu γ<br />
L<br />
= 1<br />
ɛ T µ ν uν L<br />
2. Flow of conserved charge, V µ = 0 (Eckart)<br />
Eckart, Phys. Rev. 58, 919 (1940)<br />
u µ<br />
E =<br />
N µ<br />
√<br />
NνN ν<br />
Both definitions are related <strong>to</strong> each other by Lorentz transformations<br />
November 22nd, 2012 | TUD - IKP | D. Nowakowski | 11<br />
u µ<br />
E = Λµ ν uν µ<br />
µ<br />
W V<br />
L , uµ<br />
L ≈ uµ<br />
E + , uµ<br />
ɛ+Ps E ≈ uµ<br />
L + n<br />
uL μ<br />
u E μ<br />
V μ<br />
W μ