Urology & Kidney Disease News Fall 2009 - Cleveland Clinic
Urology & Kidney Disease News Fall 2009 - Cleveland Clinic
Urology & Kidney Disease News Fall 2009 - Cleveland Clinic
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
18 <strong>Urology</strong> & <strong>Kidney</strong> <strong>Disease</strong> <strong>News</strong><br />
Prostate Cancer<br />
A Nomogram for Predicting Upgrading in Patients with Low and Intermediate Grade<br />
Prostate Cancer in the Era of Extending Prostate Sampling<br />
Ayman S. Moussa, MD, Michael W.<br />
Kattan, PhD, Changhong Yu, and J.<br />
Stephen Jones, MD, FACS<br />
The Gleason score (GS) is considered<br />
the most important factor in characterizing<br />
the biological potential of<br />
a prostate cancer and plays a major<br />
role in treatment decision making.<br />
However, the GS assigned at biopsy<br />
exhibits a limited correlation with the<br />
GS assigned following radical prostatectomy<br />
(RP). In previous studies, we<br />
found that 50% of patients with GS<br />
6 and 26.2 % of patients with GS > 7<br />
experienced postoperative upgrading.<br />
For men with biopsy GS 6 and/or 7<br />
(3+4), it is important not to underestimate<br />
the disease risk and to assess<br />
the accuracy of biopsy GS in predict-<br />
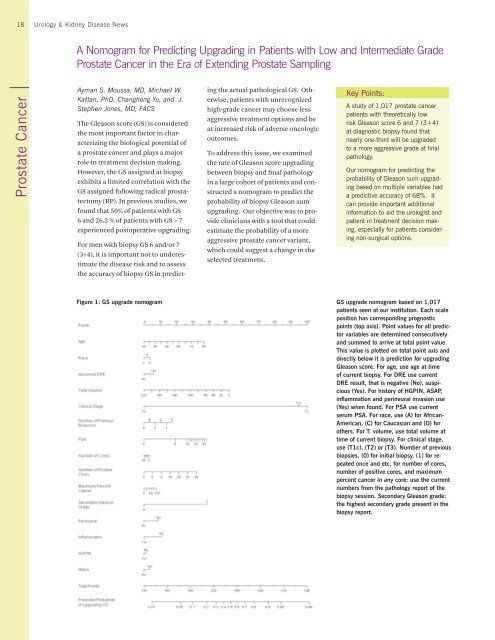
Figure 1: GS upgrade nomogram<br />
ing the actual pathological GS. Otherwise,<br />
patients with unrecognized<br />
high-grade cancer may choose less<br />
aggressive treatment options and be<br />
at increased risk of adverse oncologic<br />
outcomes.<br />
To address this issue, we examined<br />
the rate of Gleason score upgrading<br />
between biopsy and final pathology<br />
in a large cohort of patients and constructed<br />
a nomogram to predict the<br />
probability of biopsy Gleason sum<br />
upgrading. Our objective was to provide<br />
clinicians with a tool that could<br />
estimate the probability of a more<br />
aggressive prostate cancer variant,<br />
which could suggest a change in the<br />
selected treatment.<br />
Key Points:<br />
A study of 1,017 prostate cancer<br />
patients with theoretically low<br />
<br />
at diagnostic biopsy found that<br />
nearly one-third will be upgraded<br />
<br />
pathology.<br />
Our nomogram for predicting the<br />
probability of Gleason sum upgrading<br />
based on multiple variables had<br />
a predictive accuracy of 68%. It<br />
can provide important additional<br />
information to aid the urologist and<br />
ing,<br />
especially for patients considering<br />
non-surgical options.<br />
<br />
patients seen at our institution. Each scale<br />
position has corresponding prognostic<br />
-<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
Gleason score. For age, use age at time<br />
<br />
-<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
American, (C) for Caucasian and (O) for<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
-<br />
<br />
<br />
percent cancer in any core: use the current<br />
<br />
<br />
the highest secondary grade present in the