t - VTU e-Learning Centre
t - VTU e-Learning Centre
t - VTU e-Learning Centre
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
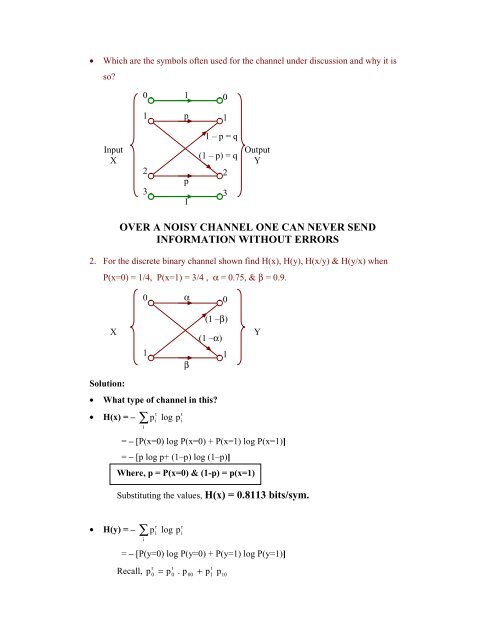
Which are the symbols often used for the channel under discussion and why it is<br />
so?<br />
Input<br />
X<br />
OVER A NOISY CHANNEL ONE CAN NEVER SEND<br />
INFORMATION WITHOUT ERRORS<br />
2. For the discrete binary channel shown find H(x), H(y), H(x/y) & H(y/x) when<br />
P(x=0) = 1/4, P(x=1) = 3/4 , = 0.75, & = 0.9.<br />
Solution:<br />
What type of channel in this?<br />
H(x) = – i<br />
p<br />
t<br />
i<br />
log p<br />
t<br />
i<br />
= – [P(x=0) log P(x=0) + P(x=1) log P(x=1)]<br />
= – [p log p+ (1–p) log (1–p)]<br />
Where, p = P(x=0) & (1-p) = p(x=1)<br />
Substituting the values, H(x) = 0.8113 bits/sym.<br />
H(y) = – i<br />
0<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
0<br />
X<br />
(1 –)<br />
(1 –)<br />
Y<br />
1<br />
p<br />
r<br />
i<br />
log p<br />
r<br />
i<br />
<br />
= – [P(y=0) log P(y=0) + P(y=1) log P(y=1)]<br />
r t<br />
t<br />
Recall, p 0 p 0 . p 00 p1<br />
p10<br />
1<br />
p<br />
p<br />
1<br />
<br />
0<br />
1<br />
1 – p = q<br />
(1 – p) = q<br />
2<br />
3<br />
0<br />
1<br />
Output<br />
Y