Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
23<br />
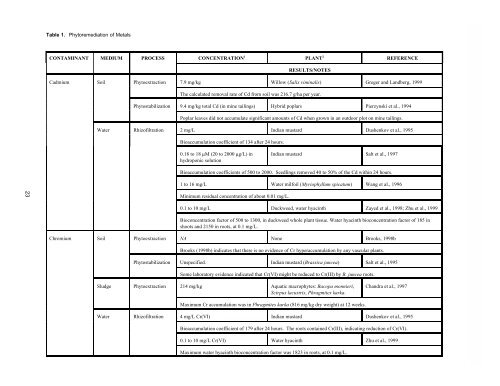
Table 1. <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> <strong>of</strong> Metals<br />
CONTAM<strong>IN</strong>ANT MEDIUM PROCESS CONCENTRATION 1<br />
PLANT 2<br />
RESULTS/NOTES<br />
REFERENCE<br />
Cadmium Soil Phytoextraction 7.9 mg/kg Willow (Salix viminalis) Greger and Landberg, 1999<br />
The calculated removal rate <strong>of</strong> Cd from soil was 216.7 g/ha per year.<br />
Phytostabilization 9.4 mg/kg total Cd (in mine tailings) Hybrid poplars Pierzynski et al., 1994<br />
Poplar leaves did not accumulate significant amounts <strong>of</strong> Cd when grown in an outdoor plot on mine tailings.<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 2 mg/L Indian mustard Dushenkov et al., 1995<br />
Bioaccumulation coefficient <strong>of</strong> 134 after 24 hours.<br />
0.18 to 18 M (20 to 2000 g/L) in<br />
hydroponic solution<br />
Indian mustard Salt et al., 1997<br />
Bioaccumulation coefficients <strong>of</strong> 500 to 2000. Seedlings removed 40 to 50% <strong>of</strong> the Cd within 24 hours.<br />
1 to 16 mg/L <strong>Water</strong> milfoil (Myriophyllum spicatum) Wang et al., 1996<br />
Minimum residual concentration <strong>of</strong> about 0.01 mg/L.<br />
0.1 to 10 mg/L Duckweed, water hyacinth Zayed et al., 1998; Zhu et al., 1999<br />
Bioconcentration factor <strong>of</strong> 500 to 1300, in duckweed whole plant tissue. <strong>Water</strong> hyacinth bioconcentration factor <strong>of</strong> 185 in<br />
shoots and 2150 in roots, at 0.1 mg/L.<br />
Chromium Soil Phytoextraction NA None Brooks, 1998b<br />
Brooks (1998b) indicates that there is no evidence <strong>of</strong> Cr hyperaccumulation by any vascular plants.<br />
Phytostabilization Unspecified. Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) Salt et al., 1995<br />
Some laboratory evidence indicated that Cr(VI) might be reduced to Cr(III) by B. juncea roots.<br />
Sludge Phytoextraction 214 mg/kg Aquatic macrophytes: Bacopa monnieri,<br />
Scirpus lacustris, Phragmites karka.<br />
Maximum Cr accumulation was in Phragmites karka (816 mg/kg dry weight) at 12 weeks.<br />
Chandra et al., 1997<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 4 mg/L Cr(VI) Indian mustard Dushenkov et al., 1995<br />
Bioaccumulation coefficient <strong>of</strong> 179 after 24 hours. The roots contained Cr(III), indicating reduction <strong>of</strong> Cr(VI).<br />
0.1 to 10 mg/L Cr(VI) <strong>Water</strong> hyacinth Zhu et al., 1999<br />
Maximum water hyacinth bioconcentration factor was 1823 in roots, at 0.1 mg/L.