Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
25<br />
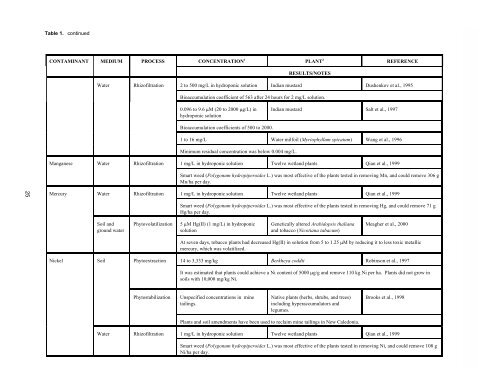
Table 1. continued<br />
CONTAM<strong>IN</strong>ANT MEDIUM PROCESS CONCENTRATION 1<br />
PLANT 2<br />
RESULTS/NOTES<br />
REFERENCE<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 2 to 500 mg/L in hydroponic solution Indian mustard Dushenkov et al., 1995<br />
Bioaccumulation coefficient <strong>of</strong> 563 after 24 hours for 2 mg/L solution.<br />
0.096 to 9.6 M (20 to 2000 g/L) in<br />
hydroponic solution<br />
Bioaccumulation coefficients <strong>of</strong> 500 to 2000.<br />
Indian mustard Salt et al., 1997<br />
1 to 16 mg/L <strong>Water</strong> milfoil (Myriophyllum spicatum) Wang et al., 1996<br />
Minimum residual concentration was below 0.004 mg/L.<br />
Manganese <strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 1 mg/L in hydroponic solution Twelve wetland plants Qian et al., 1999<br />
Smart weed (Polygonum hydropiperoides L.) was most effective <strong>of</strong> the plants tested in removing Mn, and could remove 306 g<br />
Mn/ha per day.<br />
Mercury <strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 1 mg/L in hydroponic solution Twelve wetland plants Qian et al., 1999<br />
Soil and<br />
ground water<br />
Smart weed (Polygonum hydropiperoides L.) was most effective <strong>of</strong> the plants tested in removing Hg, and could remove 71 g<br />
Hg/ha per day.<br />
Phytovolatilization 5 M Hg(II) (1 mg/L) in hydroponic<br />
solution<br />
Genetically altered Arabidopsis thaliana<br />
and tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum)<br />
Meagher et al., 2000<br />
At seven days, tobacco plants had decreased Hg(II) in solution from 5 to 1.25 M by reducing it to less toxic metallic<br />
mercury, which was volatilized.<br />
Nickel Soil Phytoextraction 14 to 3,333 mg/kg Berkheya coddii Robinson et al., 1997<br />
It was estimated that plants could achieve a Ni content <strong>of</strong> 5000 g/g and remove 110 kg Ni per ha. Plants did not grow in<br />
soils with 10,000 mg/kg Ni.<br />
Phytostabilization Unspecified concentrations in mine<br />
tailings.<br />
Native plants (herbs, shrubs, and trees)<br />
including hyperaccumulators and<br />
legumes.<br />
Plants and soil amendments have been used to reclaim mine tailings in New Caledonia.<br />
Brooks et al., 1998<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 1 mg/L in hydroponic solution Twelve wetland plants Qian et al., 1999<br />
Smart weed (Polygonum hydropiperoides L.) was most effective <strong>of</strong> the plants tested in removing Ni, and could remove 108 g<br />
Ni/ha per day.