Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
29<br />
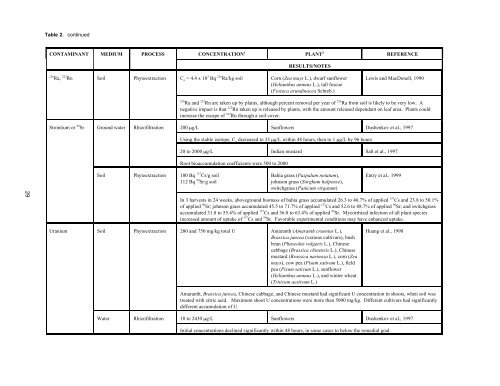
Table 2. continued<br />
CONTAM<strong>IN</strong>ANT MEDIUM PROCESS CONCENTRATION 1<br />
PLANT 2<br />
RESULTS/NOTES<br />
226 Ra, 222 Rn Soil Phytoextraction Co = 4.4 x 10 3 Bq 226 Ra/kg soil Corn (Zea mays L.), dwarf sunflower<br />
(Helianthus annuus L.), tall fescue<br />
(Festuca arundinacea Schreb.)<br />
REFERENCE<br />
Lewis and MacDonell, 1990<br />
226 Ra and 222 Rn are taken up by plants, although percent removal per year <strong>of</strong> 226 Ra from soil is likely to be very low. A<br />
negative impact is that 222 Rn taken up is released by plants, with the amount released dependant on leaf area. Plants could<br />
increase the escape <strong>of</strong> 222 Rn through a soil cover.<br />
Strontium or 90 Sr <strong>Ground</strong> water Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 200 g/L Sunflowers Dushenkov et al., 1997<br />
Soil Phytoextraction 100 Bq 137 Cs/g soil<br />
112 Bq 90 Sr/g soil<br />
Using the stable isotope, C o decreased to 35 g/L within 48 hours, then to 1 g/L by 96 hours<br />
20 to 2000 g/L Indian mustard Salt et al., 1997<br />
Root bioaccumulation coefficients were 500 to 2000<br />
Bahia grass (Paspalum notatum),<br />
johnson grass (Sorghum halpense),<br />
switchgrass (Panicum virgatum)<br />
Entry et al., 1999<br />
In 3 harvests in 24 weeks, aboveground biomass <strong>of</strong> bahia grass accumulated 26.3 to 46.7% <strong>of</strong> applied 137 Cs and 23.8 to 50.1%<br />
<strong>of</strong> applied 90 Sr; johnson grass accumulated 45.5 to 71.7% <strong>of</strong> applied 137 Cs and 52.6 to 88.7% <strong>of</strong> applied 90 Sr; and switchgrass<br />
accumulated 31.8 to 55.4% <strong>of</strong> applied 137 Cs and 36.8 to 63.4% <strong>of</strong> applied 90 Sr. Mycorrhizal infection <strong>of</strong> all plant species<br />
increased amount <strong>of</strong> uptake <strong>of</strong> 137 Cs and 90 Sr. Favorable experimental conditions may have enhanced uptake.<br />
Uranium Soil Phytoextraction 280 and 750 mg/kg total U Amaranth (Amaranth cruentus L.),<br />
Brassica juncea (various cultivars), bush<br />
bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.), Chinese<br />
cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.), Chinese<br />
mustard (Brassica narinosa L.), corn (Zea<br />
mays), cow pea (Pisum sativum L.), field<br />
pea (Pisum sativum L.), sunflower<br />
(Helianthus annuus L.), and winter wheat<br />
(Triticum aestivum L.)<br />
Huang et al., 1998<br />
Amaranth, Brassica juncea, Chinese cabbage, and Chinese mustard had significant U concentration in shoots, when soil was<br />
treated with citric acid. Maximum shoot U concentrations were more than 5000 mg/kg. Different cultivars had significantly<br />
different accumulation <strong>of</strong> U.<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 10 to 2430 g/L Sunflowers Dushenkov et al., 1997<br />
Initial concentrations declined significantly within 48 hours, in some cases to below the remedial goal.