Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
27<br />
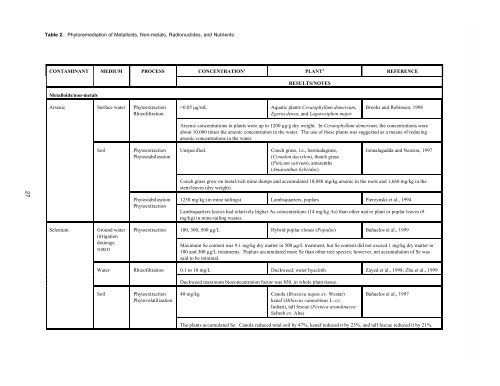
Table 2. <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> <strong>of</strong> Metalloids, Non-metals, Radionuclides, and Nutrients<br />
CONTAM<strong>IN</strong>ANT MEDIUM PROCESS CONCENTRATION 1<br />
Metalloids/non-metals<br />
Arsenic Surface water Phytoextraction<br />
Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration<br />
Selenium <strong>Ground</strong> water<br />
(irrigation<br />
drainage<br />
water)<br />
Soil Phytoextraction<br />
Phytostabilization<br />
Phytostabilization<br />
Phytoextraction<br />
PLANT 2<br />
RESULTS/NOTES<br />
>0.05 g/mL Aquatic plants Ceratophyllum demersum,<br />
Egeria densa, and Lagarosiphon major<br />
REFERENCE<br />
Brooks and Robinson, 1998<br />
Arsenic concentrations in plants were up to 1200 g/g dry weight. In Ceratophyllum demersum, the concentrations were<br />
about 10,000 times the arsenic concentration in the water. The use <strong>of</strong> these plants was suggested as a means <strong>of</strong> reducing<br />
arsenic concentrations in the water.<br />
Unspecified. Couch grass, i.e., bermudagrass,<br />
(Cynodon dactylon), thatch grass<br />
(Pinicum sativum), amaranths<br />
(Amaranthus hybridus)<br />
Jonnalagadda and Nenzou, 1997<br />
Couch grass grew on metal-rich mine dumps and accumulated 10,880 mg/kg arsenic in the roots and 1,660 mg/kg in the<br />
stem/leaves (dry weight).<br />
1250 mg/kg (in mine tailings) Lambsquarters, poplars Pierzynski et al., 1994<br />
Lambsquarters leaves had relatively higher As concentrations (14 mg/kg As) than other native plant or poplar leaves (8<br />
mg/kg) in mine-tailing wastes.<br />
Phytoextraction 100, 300, 500 g/L Hybrid poplar clones (Populus) Bañuelos et al., 1999<br />
Maximum Se content was 9.1 mg/kg dry matter in 500 g/L treatment, but Se content did not exceed 1 mg/kg dry matter in<br />
100 and 300 g/L treatments. Poplars accumulated more Se than other tree species; however, net accumulation <strong>of</strong> Se was<br />
said to be minimal.<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Rhiz<strong>of</strong>iltration 0.1 to 10 mg/L Duckweed, water hyacinth Zayed et al., 1998; Zhu et al., 1999<br />
Soil Phytoextraction<br />
Phytovolatilization<br />
Duckweed maximum bioconcentration factor was 850, in whole plant tissue.<br />
40 mg/kg Canola (Brassica napus cv. Westar)<br />
kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L. cv.<br />
Indian), tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea<br />
Schreb cv. Alta)<br />
Bañuelos et al., 1997<br />
The plants accumulated Se. Canola reduced total soil by 47%, kenaf reduced it by 23%, and tall fescue reduced it by 21%.