Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
Ground Water Issue Phytoremediation of Contaminated ... - CLU-IN
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
31<br />
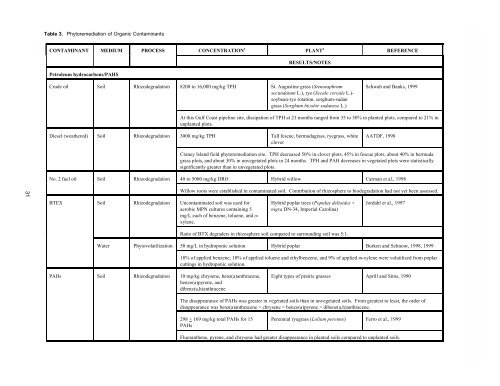
Table 3. <strong>Phytoremediation</strong> <strong>of</strong> Organic Contaminants<br />
CONTAM<strong>IN</strong>ANT MEDIUM PROCESS CONCENTRATION 1<br />
Petroleum hydrocarbons/PAHS<br />
PLANT 2<br />
RESULTS/NOTES<br />
Crude oil Soil Rhizodegradation 8200 to 16,000 mg/kg TPH St. Augustine grass (Stenotaphrum<br />
secundatum L.), rye (Secale cereale L.)soybean-rye<br />
rotation, sorghum-sudan<br />
grass (Sorghum bicolor sudanese L.)<br />
REFERENCE<br />
Schwab and Banks, 1999<br />
At this Gulf Coast pipeline site, dissipation <strong>of</strong> TPH at 21 months ranged from 35 to 50% in planted plots, compared to 21% in<br />
unplanted plots.<br />
Diesel (weathered) Soil Rhizodegradation 3000 mg/kg TPH Tall fescue, bermudagrass, ryegrass, white<br />
clover<br />
AATDF, 1998<br />
Craney Island field phytoremediation site. TPH decreased 50% in clover plots, 45% in fescue plots, about 40% in bermuda<br />
grass plots, and about 30% in unvegetated plots in 24 months. TPH and PAH decreases in vegetated plots were statistically<br />
significantly greater than in unvegetated plots.<br />
No. 2 fuel oil Soil Rhizodegradation 40 to 5000 mg/kg DRO Hybrid willow Carman et al., 1998<br />
BTEX Soil Rhizodegradation Uncontaminated soil was used for<br />
aerobic MPN cultures containing 5<br />
mg/L each <strong>of</strong> benzene, toluene, and oxylene.<br />
Willow roots were established in contaminated soil. Contribution <strong>of</strong> rhizosphere to biodegradation had not yet been assessed.<br />
Hybrid poplar trees (Populus deltoides ×<br />
nigra DN-34, Imperial Carolina)<br />
Ratio <strong>of</strong> BTX degraders in rhizosphere soil compared to surrounding soil was 5:1.<br />
Jordahl et al., 1997<br />
<strong>Water</strong> Phytovolatilization 50 mg/L in hydroponic solution Hybrid poplar Burken and Schnoor, 1998, 1999<br />
PAHs Soil Rhizodegradation 10 mg/kg chrysene, benz(a)anthracene,<br />
benzo(a)pyrene, and<br />
dibenz(a,h)anthracene<br />
18% <strong>of</strong> applied benzene, 10% <strong>of</strong> applied toluene and ethylbenzene, and 9% <strong>of</strong> applied m-xylene were volatilized from poplar<br />
cuttings in hydroponic solution.<br />
Eight types <strong>of</strong> prairie grasses Aprill and Sims, 1990<br />
The disappearance <strong>of</strong> PAHs was greater in vegetated soils than in unvegetated soils. From greatest to least, the order <strong>of</strong><br />
disappearance was benz(a)anthracene > chrysene > benzo(a)pyrene > dibenz(a,h)anthracene.<br />
298 + 169 mg/kg total PAHs for 15<br />
PAHs<br />
Perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) Ferro et al., 1999<br />
Fluoranthene, pyrene, and chrysene had greater disappearance in planted soils compared to unplanted soils.