Value of the ventilation / perfusion scan in acute pulmonary ...
Value of the ventilation / perfusion scan in acute pulmonary ...
Value of the ventilation / perfusion scan in acute pulmonary ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
.<br />
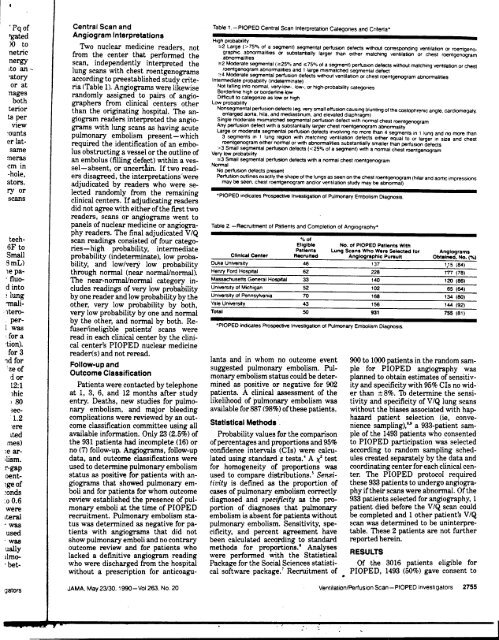
'Pq <strong>of</strong> Central Scan and Table 1-PIOPED Central Scan Interpretation Categories and Criteria'<br />
'gated<br />
)() ~o<br />
Angiogram Interpretations<br />
Two nuclear medic<strong>in</strong>e readers, not<br />
c,,-~ ---~-~,,~ -<br />
High probability<br />
;,,2 Large (> 750/0 <strong>of</strong> a segment) segmental perf1JSIOn defects WIthout correspond<strong>in</strong>g ~ntilation or roenlgenonetric<br />
from <strong>the</strong> center that performed <strong>the</strong> graphIC abnom1alitles or substantially larger than eI<strong>the</strong>r match<strong>in</strong>g ventIlation or chest roentgenogram<br />
nergy<br />
Ito an ~<br />
-atory<br />
or at<br />
llages<br />
..abnom181ltles<br />
<strong>scan</strong>, mdepe?dently Interpreted <strong>the</strong><br />
lung <strong>scan</strong>s WIth chest roentgenograms<br />
accordl 'ng to preestabl ' h d t d .t<br />
IS e S u y cn e-<br />
ria (Table 1). Angiograms were likewise<br />
d I . d ..Bordertlne<br />
ran om y asslgne. .w pairs <strong>of</strong> angIo-<br />
;,,2 Moderate segmental (;,,25% and ~75% <strong>of</strong> a segment) perf1JsK)n defects without match<strong>in</strong>g ~ntilation or chest<br />
roentgenogram abnOm1alitles and 1 large mIsmatched segmental defect<br />
;,,4 Moderate segmental perf1JsK)n defects without <strong>ventilation</strong> or chest roentgenogram abnom1alities<br />
IntermedIate probabIlity (Indetem1<strong>in</strong>ate)<br />
Not lall<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>to nom1al. ve~low-. low-, or high-probability categories<br />
high or borderlIne low<br />
DIfficult to categonze as low or high<br />
both<br />
terior<br />
ts<br />
per<br />
VIeW<br />
~ounts<br />
er latsame<br />
graphers from clInical centers o<strong>the</strong>r<br />
than <strong>the</strong> ori .nnat<strong>in</strong> g hos p ital The an-<br />
.e' .'.<br />
gIogram readers Interpreted <strong>the</strong> angIograms<br />
with lung <strong>scan</strong>s as hav<strong>in</strong>g <strong>acute</strong><br />
uI b I ..Large<br />
p m.onary e~ 0 I.sm present-which<br />
required <strong>the</strong> IdentIfication <strong>of</strong> an embo-<br />
I b t t . I th tl ' f<br />
US 0 S ruc mg a vesse or e ou me 0<br />
Low probability<br />
Nonsegmental perf1Jsion defects (~, ~ry small effusion caus<strong>in</strong>g blunt<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> costophrenic angle. cardiomegaly.<br />
enlarged aorta. hIla. and medIastInum, and elevated dIaphragm)<br />
S<strong>in</strong>gle moderate mIsmatched segmental perfuSK)n defect with nom1al chest roentgenogram<br />
Any perf1JSlon defect with a substantially larger chest roentgenogram abnOm1ality<br />
or moderate segmental perf1JSIOn defects InvolvIng no more than 4 segments <strong>in</strong> 1 lung and no more than<br />
3 segments In 1 lung regIOn with match<strong>in</strong>g ~ntilation defects ei<strong>the</strong>r equal to or larger In size and chest<br />
roentgenogram eI<strong>the</strong>r nom1al or with abnom1alltles substantially smaller than perf1JSIOn defects<br />
>3 Small segmental perf1JsK)n defects «25% <strong>of</strong> a segment) with a nom1al chest roentgen.v.ram<br />
Very low probability .._"<br />
me~<br />
cm m<br />
an embolus (fill<strong>in</strong>g deti ct) with<strong>in</strong> a vesse<br />
I -a b sent, or uncert . m. If two read-<br />
~3 Small segmental perf1Jsion defects with a nom1al chest roentgenogram<br />
Nom1al No perf1Jsion defects present<br />
l<br />
-hole, ers disagreed, <strong>the</strong> <strong>in</strong>terpretations'were Perf1J$ion outl<strong>in</strong>es exactly <strong>the</strong> shape <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> lungs as seen on <strong>the</strong> chest roentgenogram (hilar and aortic impressions<br />
ators. adjudicated by readers who were se- may be si3en. chest roentgenogram and/or <strong>ventilation</strong> study may be abnom1al)<br />
ry or le~t~d randomly fro~ .<strong>the</strong>. rema<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g 'PIOPED <strong>in</strong>dicates Prospectiw Investigation <strong>of</strong> Pulmonary Embolism Dia nosis<br />
<strong>scan</strong>s clInical centers. If adJudIcatIng readers g<br />
did not agree with ei<strong>the</strong>r <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> first two<br />
readers, <strong>scan</strong>s or angiograms went to<br />
panels <strong>of</strong> nuclear medic<strong>in</strong>e or angiogra- Table 2 -Recruitment <strong>of</strong> Patients and Completion <strong>of</strong> Angiography'<br />
phy readers. The f<strong>in</strong>al adjudicated V IQ<br />
tech- <strong>scan</strong> read<strong>in</strong>gs consisted <strong>of</strong> four catego- 0/. <strong>of</strong><br />
6F to . h. h b b ' l ' . d .Eligible No. <strong>of</strong> PfOPEO P.tlent. With<br />
nes- Ig pro a Ilty, mterme late Patient. Lung Scan. Who Were Seiec1ed for Angiogram.<br />
Small probability (<strong>in</strong>determ<strong>in</strong>ate), low proba- Cl<strong>in</strong>ical Center Recruited Anglographlc Pu..ult Obta<strong>in</strong>ed. No. ("!o}<br />
8mL) bility, and low/very low probability ~ukeU~n~~ity 46 --137 1,15-'84)'-'<br />
le pa- through normal (near normal/normal). Henry ~ord Hos~it81 62 228 177 (78)<br />
.~uo- The near-normal/normal category <strong>in</strong>- ~assachus~~ ~eneral Hospjtal 33 140 120 (86)<br />
d Into cludes read<strong>in</strong>gs <strong>of</strong> very low probability University <strong>of</strong> Michigan 52 102 65 (64)<br />
~ lun~ by one reader and low probability by <strong>the</strong> University 01 Pennsylvania 70 168 134 (80)<br />
~all- o<strong>the</strong>r, very low probability by both, ~aleuniversity 43 156 144 (92)<br />
1tero- very low probability by one and normal Total 50 931 755 (81)<br />
per- by <strong>the</strong> o<strong>the</strong>r, and normal by both. Re- ,<br />
1 was fu I. I.. bl t ' ts' PIOPED Indicates Prospective Investigation <strong>of</strong> Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis<br />
ser me IgI e pa Ien <strong>scan</strong>s were .<br />
~or a read <strong>in</strong> each cl<strong>in</strong>ical center by <strong>the</strong> cl<strong>in</strong>i-<br />
'tlon). cal center's PIOPED nuclear medic<strong>in</strong>e<br />
for 3 reader(s) and not reread.<br />
1d for F II d lants and <strong>in</strong> whom no outcome event 900 to 1000 patients <strong>in</strong> <strong>the</strong> random sam-<br />
:ze <strong>of</strong> 0 ow-up an ..suggested <strong>pulmonary</strong> embolism. Pul- pie for PIOPED angiography was<br />
d or Outcome ClassIfication monary embolism status could be deter- planned to obta<strong>in</strong> estimates <strong>of</strong> sensitiv-<br />
12:1 Patients were contacted by telephone m<strong>in</strong>ed as positive or negative for 902 ityand specificity with 95% CIs no wid-<br />
1hic at I, 3, 6, and 12 months after study patients. A cl<strong>in</strong>ical assessment <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> er than == 8%. To determ<strong>in</strong>e <strong>the</strong> sensi-<br />
; 80 entry. Deaths, new studies for pulmo- likelihood <strong>of</strong> <strong>pulmonary</strong> embolism was tivity and specificity <strong>of</strong> V IQ lung <strong>scan</strong>s<br />
,ec- nary embolism, and major bleed<strong>in</strong>g available for 887 (98%) <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se patients. without <strong>the</strong> biases associated with hap-<br />
1.2 complications were reviewed by an out- hazard patierlt selection (ie, conveere<br />
come classification committee us<strong>in</strong>g all Statistical Methods nience sampl<strong>in</strong>g).8.t a 933-patient sam-<br />
lted available <strong>in</strong>formation. Only 23 (2.5%) <strong>of</strong> Probability values for <strong>the</strong> comparison pie <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 1493 patients who consented<br />
mes) <strong>the</strong> 931 patients had <strong>in</strong>complete (16) or <strong>of</strong> percentages and proportions and 95% to PIOPED participation was selected<br />
\e ar- no (7) follow-up. Angiograms, follow-up confidence <strong>in</strong>tervals (CIs) were calcu- accord<strong>in</strong>g to random sampl<strong>in</strong>g sched-<br />
\lism, data, and outcome classifications were lated us<strong>in</strong>g standard: tests.' A ~ test ules created separately by <strong>the</strong> data and<br />
r-gap used to determ<strong>in</strong>e <strong>pulmonary</strong> embolism for homogeneity <strong>of</strong> proportions was coord<strong>in</strong>at<strong>in</strong>g center for each cl<strong>in</strong>ical cenoent-<br />
status as positive for patients with an- used to compare distributions.' Sensi- ter, The PIOPED protocol required<br />
1ge <strong>of</strong> giograms that showed <strong>pulmonary</strong> em- tivity is def<strong>in</strong>ed as <strong>the</strong> proportion <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong>se 933 patients to undergo angiogra-<br />
:onds boli and for patients for whom outcome cases <strong>of</strong> <strong>pulmonary</strong> embolism correctly phy if <strong>the</strong>ir <strong>scan</strong>s were abnormal, Of <strong>the</strong><br />
:00.6 review established <strong>the</strong> presence <strong>of</strong> pul- diagnosed and specificity as <strong>the</strong> pro- 933 patients selected for angiography, 1<br />
were monary emboli at <strong>the</strong> time <strong>of</strong> PIOPED portion <strong>of</strong> diagnoses that <strong>pulmonary</strong> patient died before <strong>the</strong> V/Q <strong>scan</strong> could<br />
lteral recruitment. Pulmonary embolism sta- embolism is absent for patients without be completed and 1 o<strong>the</strong>r patient's V/Q<br />
.was tus was determ<strong>in</strong>ed as negative for pa- <strong>pulmonary</strong> embolism. Sensitivity, spe- <strong>scan</strong> was determ<strong>in</strong>ed to be un<strong>in</strong>terpreused<br />
tients with angiograms that did not cificity, and percent agreement have table. These 2 patients are not fur<strong>the</strong>r<br />
.was show <strong>pulmonary</strong> emboli and no contrary been calculated accord<strong>in</strong>g to standard reported here<strong>in</strong>.<br />
ually outcome review and for patients who methods for proportion8,' Analyses<br />
.lImo- lacked a def<strong>in</strong>itive angiogram read<strong>in</strong>g were performed with <strong>the</strong> Statistical RESULTS<br />
.bet- who were discharged from <strong>the</strong> hospital Package for <strong>the</strong> Social Sciences statisti- Of <strong>the</strong> 3016 patients eligible for<br />
without a prescription for anticoagu- cal s<strong>of</strong>tware package.' Recruitment <strong>of</strong> PIOPED, 1493 (50%) gave consent to<br />
gators JAMA. May 23/30. 1990-VoI263, No 20 Ventilation/Perfusion Scan-PIOPED Investigators 2755<br />
~~- "';::: -I<br />
.