- Page 1: System i Programming i5/OS globaliz
- Page 4 and 5: Note Before using this information
- Page 6 and 7: Testing process . . . . . . . . . .
- Page 8 and 9: Turkish IBM Enhanced Keyboard. . .
- Page 10 and 11: Downloading Adobe Reader You need A
- Page 12 and 13: v Slovenian v Spanish v Swedish v T
- Page 14 and 15: CDRA uses a tag field to hold a CCS
- Page 16 and 17: Locales are made up of categories t
- Page 18 and 19: IBM-supplied subsystem descriptions
- Page 20 and 21: For example: STRSBS USERLIB/ABC Rel
- Page 22 and 23: The following list shows the cultur
- Page 24 and 25: You can change the coded character
- Page 26 and 27: Related concepts: “Century (QCENT
- Page 28 and 29: If QIGC is set to 0, no DBCS nation
- Page 30 and 31: Related concepts: “Country or reg
- Page 34 and 35: The libraries in the system part of
- Page 36 and 37: - As using the *CHRIDCTL system val
- Page 38 and 39: Related concepts: “National langu
- Page 40 and 41: Globalization checklist: Part 1 Bef
- Page 42 and 43: Changing the keyboard configuration
- Page 44 and 45: v System i Access printer to emulat
- Page 46 and 47: Related information: Local Device C
- Page 48 and 49: Related concepts: “Setting up i5/
- Page 50 and 51: You must ensure that secondary lang
- Page 52 and 53: Related concepts: “Working with C
- Page 54 and 55: SETJOBATR The parameter value that
- Page 56 and 57: The following example shows the SQL
- Page 58 and 59: If the user wants to display this d
- Page 60 and 61: Market research process In the mark
- Page 62 and 63: Translation process Translating the
- Page 64 and 65: Related concepts: “Subsystems”
- Page 66 and 67: Globalization and localization Nati
- Page 68 and 69: Program module separation: You can
- Page 70 and 71: Textual data v Display files v Prin
- Page 72 and 73: |...+....1....+....2....+....3....+
- Page 74 and 75: Complies Not applicable Rule Specia
- Page 76 and 77: Textual data code design: You can u
- Page 78 and 79: Display files only Constants such a
- Page 80 and 81: Text can be stored externally from
- Page 82 and 83:
For each ISCH tag, there can be sev
- Page 84 and 85:
v Use predefined message descriptio
- Page 86 and 87:
Menu translation To allow for easy
- Page 88 and 89:
Related concepts: “Coded characte
- Page 90 and 91:
v Currency symbol v Date format v D
- Page 92 and 93:
Note: Some operating system functio
- Page 94 and 95:
The time format for presentation sh
- Page 96 and 97:
Designing for running with differen
- Page 98 and 99:
Related concepts: “Cultural-depen
- Page 100 and 101:
For example: A field-name length ty
- Page 102 and 103:
v Use the MSGCON keyword to access
- Page 104 and 105:
French display job CCSID 00297 Germ
- Page 106 and 107:
Coding globalized applications with
- Page 108 and 109:
C FLD1 IFEQ ’ ’ C ... C* Move c
- Page 110 and 111:
The alternative collating sequence
- Page 112 and 113:
exception to this is that the value
- Page 114 and 115:
v RANGE predicate v MAX function v
- Page 116 and 117:
The special bidirectional tags have
- Page 118 and 119:
Using multiple source files You can
- Page 120 and 121:
eference manuals for non-IBM hardwa
- Page 122 and 123:
UTF-8: UTF-8 converts Unicode data
- Page 124 and 125:
Related concepts: “UTF-16” on p
- Page 126 and 127:
Unicode provides a single character
- Page 128 and 129:
Assume that the Greek user wants to
- Page 130 and 131:
When you create Unicode database ap
- Page 132 and 133:
Related concepts: “Object-level c
- Page 134 and 135:
Unicode data is not supported on di
- Page 136 and 137:
v Avoid using characters that are n
- Page 138 and 139:
Function Description of support DDM
- Page 140 and 141:
Related concepts: Changing the CCSI
- Page 142 and 143:
Work management support initializes
- Page 144 and 145:
Related concepts: “Character iden
- Page 146 and 147:
Printer file CHRID is And the panel
- Page 148 and 149:
Object-level coded character set id
- Page 150 and 151:
00037. The number sign (#), X'7B' o
- Page 152 and 153:
For example, message file MYMSGF ha
- Page 154 and 155:
If you set CCSID processing on, sys
- Page 156 and 157:
Messages sent to a message queue th
- Page 158 and 159:
Example 2: Using return fields and
- Page 160 and 161:
3 The replacement data was converte
- Page 162 and 163:
Two different conversions must occu
- Page 164 and 165:
Can I correct the CCSID of a messag
- Page 166 and 167:
Related concepts: “Display files
- Page 168 and 169:
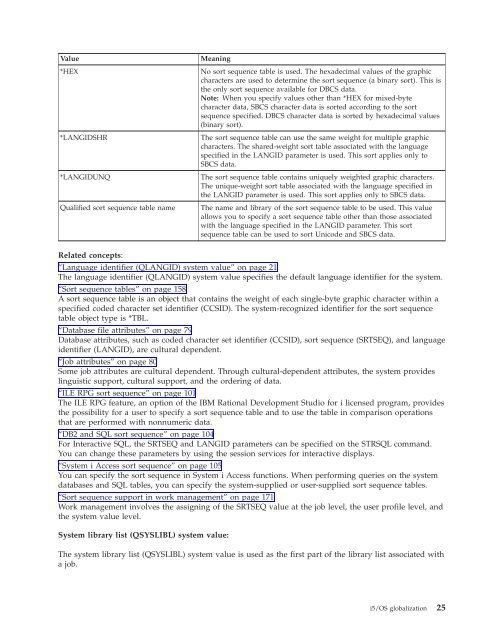
How to build sort sequence tables T
- Page 170 and 171:
GCGID Character Shared weight Uniqu
- Page 172 and 173:
GCGID Character Shared weight Uniqu
- Page 174 and 175:
GCGID Character Shared weight Uniqu
- Page 176 and 177:
GCGID Character Shared weight Uniqu
- Page 178 and 179:
GCGID Character Shared weight Uniqu
- Page 180 and 181:
The LANGID and SRTSEQ parameters de
- Page 182 and 183:
The following table shows an exampl
- Page 184 and 185:
en_us ICU locale sort sequence usin
- Page 186 and 187:
Related reference: DDS concepts Rel
- Page 188 and 189:
Related concepts: DDS concepts Rela
- Page 190 and 191:
v Remember to use the graphic data
- Page 192 and 193:
This table summarizes the changes o
- Page 194 and 195:
Inserting shift-control characters
- Page 196 and 197:
Copying spooled files Copy spooled
- Page 198 and 199:
Limit the length of a double-byte c
- Page 200 and 201:
You might call the dictionary by an
- Page 202 and 203:
The basic symbols of keywords and o
- Page 204 and 205:
If the string contains mixed data,
- Page 206 and 207:
QIGC3232 A Japanese DBCS font table
- Page 208 and 209:
controller as those devices, and th
- Page 210 and 211:
If the table does not exist, the sy
- Page 212 and 213:
v SS:MM:HH Creating locales Locales
- Page 214 and 215:
A string is a sequence of character
- Page 216 and 217:
where directive is one of the direc
- Page 218 and 219:
LC_COLLATE CPYSYSCOL "//QSYS.LIB//Q
- Page 220 and 221:
punct ;;;\ ;;;;\ ;;;\ ;;;;;\ ;;;;\
- Page 222 and 223:
The LC_MONETARY category of a local
- Page 224 and 225:
Example 4 Indicates that the positi
- Page 226 and 227:
values consist of seven semicolon-s
- Page 228 and 229:
the era extends forward to the end
- Page 230 and 231:
2. The values specified in the LC_T
- Page 232 and 233:
v The second through fifth characte
- Page 234 and 235:
This value is specified when the LO
- Page 236 and 237:
This is because the user profile SE
- Page 238 and 239:
COLUMNS ...: 1 71 EDIT localelib/lo
- Page 240 and 241:
characters available, unpredictable
- Page 242 and 243:
v Create user profiles for users na
- Page 244 and 245:
Create Subsystem Description (CRTSB
- Page 246 and 247:
(,);(,);(,);(,);(,);/ (,);(,);(,);(
- Page 248 and 249:
UNDEFINED order_end END
- Page 250 and 251:
Note: By using the code example, yo
- Page 252 and 253:
;;;;/ ;;; / ;;;/ ;/ ;;/ ;;/ ;;/ ;;;
- Page 254 and 255:
- Page 256 and 257:
- Page 258 and 259:
d_t_fmt "%a %b %e %H:%M:%S %Z %Y" d
- Page 260 and 261:
Related concepts: “National langu
- Page 262 and 263:
Country and region name Country and
- Page 264 and 265:
Country and region name Country and
- Page 266 and 267:
Country and region name Country and
- Page 268 and 269:
QDATFMT QTIMSEP QCCSID QCNTRYID QLO
- Page 270 and 271:
QDATFMT QTIMSEP QCCSID QCNTRYID QLO
- Page 272 and 273:
QDATFMT QTIMSEP QCCSID 1 QCNTRYID Q
- Page 274 and 275:
Greek (Feature 2957) The table show
- Page 276 and 277:
Korean (Feature 2986) The table sho
- Page 278 and 279:
Portuguese MNCS (Feature 2996) The
- Page 280 and 281:
Spanish (Feature 2931) The table sh
- Page 282 and 283:
QDATFMT QTIMSEP QCCSID QCNTRYID QLA
- Page 284 and 285:
The sum of the computational factor
- Page 286 and 287:
Language Netherlands Dutch Netherla
- Page 288 and 289:
v Italian v Italian MNCS v Norwegia
- Page 290 and 291:
Related concepts: “Determining th
- Page 292 and 293:
Accent Key Valid characters Example
- Page 294 and 295:
Farsi IBM Enhanced Keyboard: The fi
- Page 296 and 297:
Hungarian IBM Enhanced Keyboard: Th
- Page 298 and 299:
Polish IBM Enhanced Keyboard: The f
- Page 300 and 301:
Slovenian IBM Enhanced Keyboard: Th
- Page 302 and 303:
Turkish IBM Enhanced Keyboard: The
- Page 304 and 305:
v 38F5835 v 38F5843 v 38F5845 v 56F
- Page 306 and 307:
Language KBDTYPE parameter 1A (122-
- Page 308 and 309:
Language KBDTYPE parameter 1A (122-
- Page 310 and 311:
Language KBDTYPE parameter 1A (122-
- Page 312 and 313:
Language KBDTYPE parameter German (
- Page 314 and 315:
The special characters on the enhan
- Page 316 and 317:
Language KBDTYPE EBCDIC character s
- Page 318 and 319:
Language KBDTYPE EBCDIC character s
- Page 320 and 321:
Country extended character set 0069
- Page 322 and 323:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 324 and 325:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 326 and 327:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 328 and 329:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 330 and 331:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 332 and 333:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 334 and 335:
Table name From From text To To tex
- Page 336 and 337:
Related tasks: “Job default coded
- Page 338 and 339:
GCGID Description Graphic character
- Page 340 and 341:
Code page Table object for monocase
- Page 342 and 343:
T.61 Character Set 01252 This figur
- Page 344 and 345:
Table name From description From va
- Page 346 and 347:
CCSID Encoding Description 00424 11
- Page 348 and 349:
CCSID Encoding Description 00959 54
- Page 350 and 351:
CCSID Encoding Description 01363 23
- Page 352 and 353:
From CCSID To CCSID 00037 00256, 00
- Page 354 and 355:
From CCSID To CCSID 00819 00037, 00
- Page 356 and 357:
From CCSID To CCSID 00905 00037, 00
- Page 358 and 359:
From CCSID To CCSID 01026 00037, 00
- Page 360 and 361:
From CCSID To CCSID 01160 00037, 00
- Page 362 and 363:
From CCSID To CCSID 05026 00037, 00
- Page 364 and 365:
From CCSID To CCSID 62222 00424, 62
- Page 366 and 367:
Input CCSID 1100 1200 1301 2100 220
- Page 368 and 369:
Input CCSID 1100 1200 1301 2100 220
- Page 370 and 371:
Encoding scheme identifier (ESID) h
- Page 372 and 373:
Related concepts: “Recommendation
- Page 374 and 375:
Description Member CCSID How shippe
- Page 376 and 377:
Description Member CCSID How shippe
- Page 378 and 379:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 380 and 381:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 382 and 383:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 384 and 385:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 386 and 387:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 388 and 389:
Symbolic name Unicode (ISO 10646) c
- Page 390 and 391:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 392 and 393:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 394 and 395:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 396 and 397:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 398 and 399:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 400 and 401:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 402 and 403:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 404 and 405:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 406 and 407:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 408 and 409:
Uppercase code point Lowercase code
- Page 410 and 411:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 412 and 413:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 414 and 415:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 416 and 417:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 418 and 419:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 420 and 421:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 422 and 423:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 424 and 425:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 426 and 427:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 428 and 429:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 430 and 431:
Lowercase code point Uppercase code
- Page 432 and 433:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 434 and 435:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 436 and 437:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 438 and 439:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 440 and 441:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 442 and 443:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 444 and 445:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 446 and 447:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 448 and 449:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 450 and 451:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 452 and 453:
GCGID Description Token type Token
- Page 454 and 455:
Table 1. Default conversion that ca
- Page 456 and 457:
Checklist Where you can go to read
- Page 458 and 459:
450 System i: Programming i5/OS glo
- Page 460 and 461:
Software Interoperability Coordinat
- Page 462:
IBM reserves the right to withdraw