UNIT-4: PARALLEL COMPUTER MODELS STRUCTURE - Csbdu.in
UNIT-4: PARALLEL COMPUTER MODELS STRUCTURE - Csbdu.in
UNIT-4: PARALLEL COMPUTER MODELS STRUCTURE - Csbdu.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
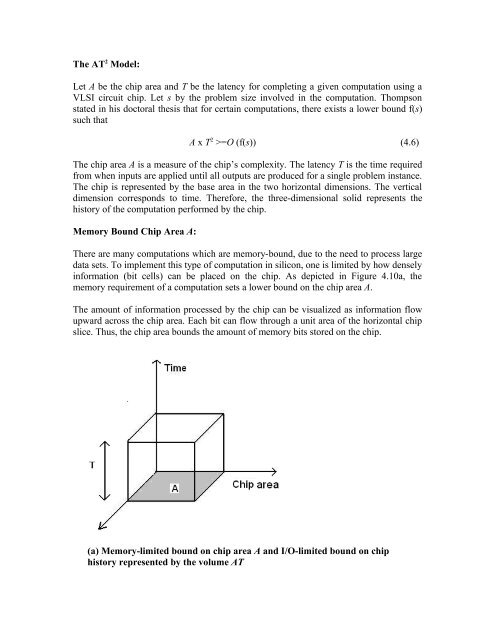
The AT 2 Model:<br />
Let A be the chip area and T be the latency for complet<strong>in</strong>g a given computation us<strong>in</strong>g a<br />
VLSI circuit chip. Let s by the problem size <strong>in</strong>volved <strong>in</strong> the computation. Thompson<br />
stated <strong>in</strong> his doctoral thesis that for certa<strong>in</strong> computations, there exists a lower bound f(s)<br />
such that<br />
A x T 2 >=O (f(s)) (4.6)<br />
The chip area A is a measure of the chip’s complexity. The latency T is the time required<br />
from when <strong>in</strong>puts are applied until all outputs are produced for a s<strong>in</strong>gle problem <strong>in</strong>stance.<br />
The chip is represented by the base area <strong>in</strong> the two horizontal dimensions. The vertical<br />
dimension corresponds to time. Therefore, the three-dimensional solid represents the<br />
history of the computation performed by the chip.<br />
Memory Bound Chip Area A:<br />
There are many computations which are memory-bound, due to the need to process large<br />
data sets. To implement this type of computation <strong>in</strong> silicon, one is limited by how densely<br />
<strong>in</strong>formation (bit cells) can be placed on the chip. As depicted <strong>in</strong> Figure 4.10a, the<br />
memory requirement of a computation sets a lower bound on the chip area A.<br />
The amount of <strong>in</strong>formation processed by the chip can be visualized as <strong>in</strong>formation flow<br />
upward across the chip area. Each bit can flow through a unit area of the horizontal chip<br />
slice. Thus, the chip area bounds the amount of memory bits stored on the chip.<br />
(a) Memory-limited bound on chip area A and I/O-limited bound on chip<br />
history represented by the volume AT