Gait disorder in older adults: Is it NPH? - ResearchGate
Gait disorder in older adults: Is it NPH? - ResearchGate
Gait disorder in older adults: Is it NPH? - ResearchGate
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Ga<strong>it</strong></strong> <strong>disorder</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>older</strong> <strong>adults</strong>: <strong>Is</strong> <strong>it</strong> <strong>NPH</strong>?<br />
evaluation. It is a late sign <strong>in</strong> <strong>NPH</strong><br />
patients and patients will <strong>in</strong><strong>it</strong>ially<br />
relate that they experience ur<strong>in</strong>ary<br />
urgency, frequency, and nocturia.<br />
Other underly<strong>in</strong>g medical<br />
issues and/medications need to<br />
be ruled out before attribut<strong>in</strong>g<br />
<strong>in</strong>cont<strong>in</strong>ence to <strong>NPH</strong>. 2,7,13<br />
■ Diagnostic tests<br />
Standardized neuropsychologic<br />
tests are useful for identify<strong>in</strong>g<br />
cogn<strong>it</strong>ive impairment and to dist<strong>in</strong>quish<br />
subcortical from cortical<br />
dementias. 6 There are several<br />
screen<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>struments useful to<br />
determ<strong>in</strong>e cogn<strong>it</strong>ive defic<strong>it</strong>s <strong>in</strong><br />
those w<strong>it</strong>h <strong>NPH</strong>. The M<strong>in</strong>i-Cog<br />
and Short Portable Mental Status<br />
Questionnaire are useful to<br />
identify cogn<strong>it</strong>ive impairment,<br />
and the Folste<strong>in</strong> M<strong>in</strong>i-Mental<br />
State Exam<strong>in</strong>ation can identify<br />
the sever<strong>it</strong>y of cogn<strong>it</strong>ive impairment.<br />
Visuospatial skills and executive<br />
function are assessed w<strong>it</strong>h<br />
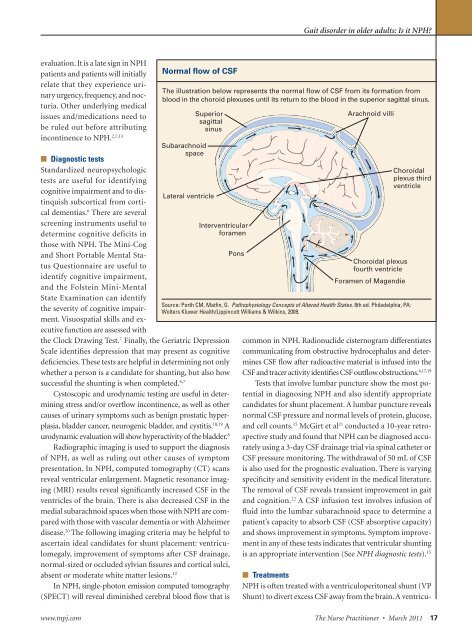
Normal flow of CSF<br />
the Clock Draw<strong>in</strong>g Test. 7 F<strong>in</strong>ally, the Geriatric Depression<br />
Scale identifies depression that may present as cogn<strong>it</strong>ive<br />
deficiencies. These tests are helpful <strong>in</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g not only<br />
whether a person is a candidate for shunt<strong>in</strong>g, but also how<br />
successful the shunt<strong>in</strong>g is when completed. 6,7<br />
Cystoscopic and urodynamic test<strong>in</strong>g are useful <strong>in</strong> determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
stress and/or overflow <strong>in</strong>cont<strong>in</strong>ence, as well as other<br />
causes of ur<strong>in</strong>ary symptoms such as benign prostatic hyperplasia,<br />
bladder cancer, neurogenic bladder, and cyst<strong>it</strong>is. 18,19 A<br />
urodynamic evaluation will show hyperactiv<strong>it</strong>y of the bladder. 8<br />
Radiographic imag<strong>in</strong>g is used to support the diagnosis<br />
of <strong>NPH</strong>, as well as rul<strong>in</strong>g out other causes of symptom<br />
presentation. In <strong>NPH</strong>, computed tomography (CT) scans<br />
reveal ventricular enlargement. Magnetic resonance imag<strong>in</strong>g<br />
(MRI) results reveal significantly <strong>in</strong>creased CSF <strong>in</strong> the<br />
ventricles of the bra<strong>in</strong>. There is also decreased CSF <strong>in</strong> the<br />
medial subarachnoid spaces when those w<strong>it</strong>h <strong>NPH</strong> are compared<br />
w<strong>it</strong>h those w<strong>it</strong>h vascular dementia or w<strong>it</strong>h Alzheimer<br />
disease. 20 The follow<strong>in</strong>g imag<strong>in</strong>g cr<strong>it</strong>eria may be helpful to<br />
ascerta<strong>in</strong> ideal candidates for shunt placement: ventriculomegaly,<br />
improvement of symptoms after CSF dra<strong>in</strong>age,<br />
normal-sized or occluded sylvian fissures and cortical sulci,<br />
absent or moderate wh<strong>it</strong>e matter lesions. 12<br />
In <strong>NPH</strong>, s<strong>in</strong>gle-photon emission computed tomography<br />
(SPECT) will reveal dim<strong>in</strong>ished cerebral blood flow that is<br />
The illustration below represents the normal flow of CSF from <strong>it</strong>s formation from<br />
blood <strong>in</strong> the choroid plexuses until <strong>it</strong>s return to the blood <strong>in</strong> the superior sag<strong>it</strong>tal s<strong>in</strong>us.<br />
Subarachnoid<br />
space<br />
Superior<br />
sag<strong>it</strong>tal<br />
s<strong>in</strong>us<br />
Lateral ventricle<br />
Interventricular<br />
foramen<br />
Pons<br />
Arachnoid villi<br />
Choroidal plexus<br />
fourth ventricle<br />
Foramen of Magendie<br />
Source: Porth CM, Matf<strong>in</strong>, G. Pathophysiology Concepts of Altered Health States. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA:<br />
Wolters Kluwer Health/Lipp<strong>in</strong>cott Williams & Wilk<strong>in</strong>s, 2009.<br />
Choroidal<br />
plexus third<br />
ventricle<br />
common <strong>in</strong> <strong>NPH</strong>. Radionuclide cisternogram differentiates<br />
communicat<strong>in</strong>g from obstructive hydrocephalus and determ<strong>in</strong>es<br />
CSF flow after radioactive material is <strong>in</strong>fused <strong>in</strong>to the<br />
CSF and tracer activ<strong>it</strong>y identifies CSF outflow obstructions. 6,17,19<br />
Tests that <strong>in</strong>volve lumbar puncture show the most potential<br />
<strong>in</strong> diagnos<strong>in</strong>g <strong>NPH</strong> and also identify appropriate<br />
candidates for shunt placement. A lumbar puncture reveals<br />
normal CSF pressure and normal levels of prote<strong>in</strong>, glucose,<br />
and cell counts. 15 McGirt et al 21 conducted a 10-year retrospective<br />
study and found that <strong>NPH</strong> can be diagnosed accurately<br />
us<strong>in</strong>g a 3-day CSF dra<strong>in</strong>age trial via sp<strong>in</strong>al catheter or<br />
CSF pressure mon<strong>it</strong>or<strong>in</strong>g. The w<strong>it</strong>hdrawal of 50 mL of CSF<br />
is also used for the prognostic evaluation. There is vary<strong>in</strong>g<br />
specific<strong>it</strong>y and sens<strong>it</strong>iv<strong>it</strong>y evident <strong>in</strong> the medical l<strong>it</strong>erature.<br />
The removal of CSF reveals transient improvement <strong>in</strong> ga<strong>it</strong><br />
and cogn<strong>it</strong>ion. 22 A CSF <strong>in</strong>fusion test <strong>in</strong>volves <strong>in</strong>fusion of<br />
fluid <strong>in</strong>to the lumbar subarachnoid space to determ<strong>in</strong>e a<br />
patient’s capac<strong>it</strong>y to absorb CSF (CSF absorptive capac<strong>it</strong>y)<br />
and shows improvement <strong>in</strong> symptoms. Symptom improvement<br />
<strong>in</strong> any of these tests <strong>in</strong>dicates that ventricular shunt<strong>in</strong>g<br />
is an appropriate <strong>in</strong>tervention (See <strong>NPH</strong> diagnostic tests). 15<br />
■ Treatments<br />
<strong>NPH</strong> is often treated w<strong>it</strong>h a ventriculoper<strong>it</strong>oneal shunt (VP<br />
Shunt) to divert excess CSF away from the bra<strong>in</strong>. A ventricu-<br />
www.tnpj.com The Nurse Pract<strong>it</strong>ioner • March 2011 17<br />
Copyright © 2011 Lipp<strong>in</strong>cott Williams & Wilk<strong>in</strong>s. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohib<strong>it</strong>ed.