Introduction to Color - Brown University
Introduction to Color - Brown University
Introduction to Color - Brown University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
CS123 | INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS<br />
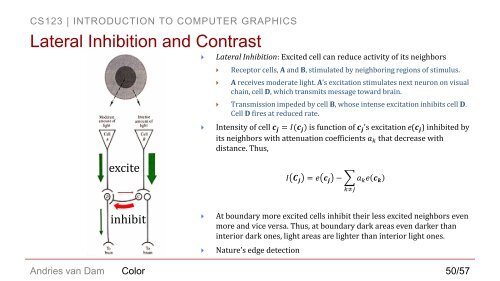
Lateral Inhibition and Contrast<br />
excite<br />
<br />
<br />
Lateral Inhibition: Excited cell can reduce activity of its neighbors<br />
<br />
<br />
Recep<strong>to</strong>r cells, A and B, stimulated by neighboring regions of stimulus.<br />
A receives moderate light. A’s excitation stimulates next neuron on visual<br />
chain, cell D, which transmits message <strong>to</strong>ward brain.<br />
Transmission impeded by cell B, whose intense excitation inhibits cell D.<br />
Cell D fires at reduced rate.<br />
Intensity of cell c j = I(c j ) is function of c j ’s excitation e(c j ) inhibited by<br />
its neighbors with attenuation coefficients a k that decrease with<br />
distance. Thus,<br />
I C j = e c j − a k e c k<br />
k≠j<br />
inhibit<br />
<br />
<br />
At boundary more excited cells inhibit their less excited neighbors even<br />
more and vice versa. Thus, at boundary dark areas even darker than<br />
interior dark ones, light areas are lighter than interior light ones.<br />
Nature’s edge detection<br />
Andries van Dam <strong>Color</strong> 50/57