Slides
Slides
Slides
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
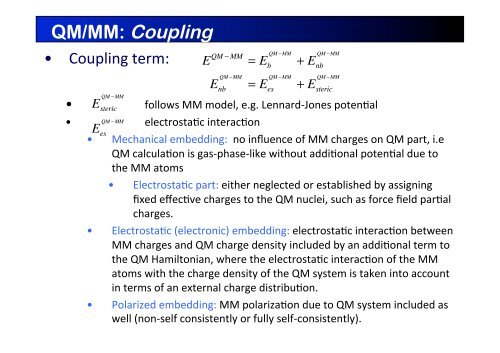
QM/MM: Coupling<br />
• Coupling term: <br />
•<br />
QM −MM<br />
E steric follows MM model, e.g. Lennard-‐Jones poten4al <br />
• electrosta4c interac4on <br />
E es<br />
QM −MM<br />
E QM − MM = E b<br />
QM −MM<br />
QM −MM<br />
E nb<br />
= E es<br />
QM −MM<br />
QM −MM<br />
+ E nb<br />
QM −MM<br />
+ E steric<br />
• Mechanical embedding: no influence of MM charges on QM part, i.e <br />
QM calcula4on is gas-‐phase-‐like without addi4onal poten4al due to <br />
the MM atoms <br />
• Electrosta4c part: either neglected or established by assigning <br />
fixed effec4ve charges to the QM nuclei, such as force field par4al <br />
charges. <br />
• Electrosta4c (electronic) embedding: electrosta4c interac4on between <br />
MM charges and QM charge density included by an addi4onal term to <br />
the QM Hamiltonian, where the electrosta4c interac4on of the MM <br />
atoms with the charge density of the QM system is taken into account <br />
in terms of an external charge distribu4on. <br />
• Polarized embedding: MM polariza4on due to QM system included as <br />
well (non-‐self consistently or fully self-‐consistently).