Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
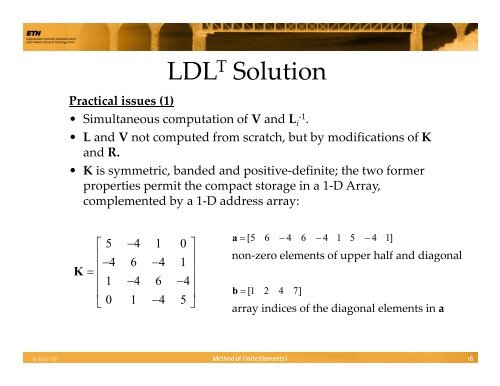
Practical issues (1)<br />
LDL T <strong>Solution</strong><br />
• Simultaneous computation <strong>of</strong> V and L ‐1<br />
i .<br />
• L and V not computed from scratch, but by modifications <strong>of</strong> K<br />
and R.<br />
• K is symmetric, banded and dpositive‐def<strong>in</strong>ite; ite the two <strong>of</strong>ormer<br />
properties permit the compact storage <strong>in</strong> a 1‐D Array,<br />
complemented by a 1‐D address array:<br />
K<br />
⎡ 5 −4 1 0 ⎤<br />
⎢<br />
−<br />
−<br />
⎥<br />
4 6 4 1<br />
= ⎢<br />
⎥<br />
⎢ 1 − 4 6 − 4 ⎥<br />
⎢<br />
⎥<br />
⎣ 0 1 −4 5 ⎦<br />
a = [ 5 6 − 4 6 − 4 1 5 − 4 1]<br />
non‐zero elements <strong>of</strong> upper half and diagonal<br />
b = [1 2 4 7]<br />
array <strong>in</strong>dices <strong>of</strong> the diagonal elements <strong>in</strong> a<br />
15-Jun-07<br />
Method <strong>of</strong> F<strong>in</strong>ite Elements I<br />
16