Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
Solution of Equilibrium Equations in Static Analysis: LDLT Solution ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
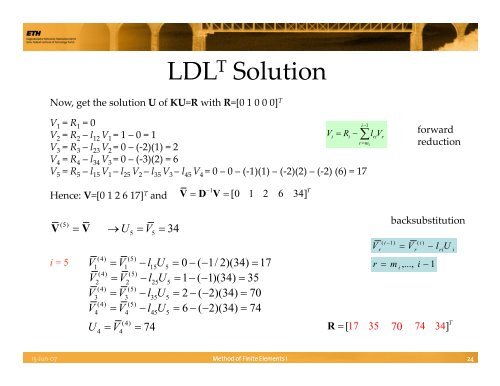
LDL T <strong>Solution</strong><br />
Now, get the solution U <strong>of</strong> KU=R with R=[0 1 0 0 0] T<br />
V 1 = R 1 = 0<br />
i<br />
V 2 = R 2 – l 12 V 1 = 1 –0 = 1<br />
∑ − 1<br />
Vi<br />
= Ri<br />
− l<br />
r=<br />
mi<br />
V 3 = R 3 – l 23 V 2 = 0 –(‐2)(1) = 2<br />
V 4 = R 4 – l 34 V 3 = 0 –(‐3)(2) = 6<br />
V 5 = R 5 – l 15 V 1 – l 25 V 2 – l 35 V 3 – l 45 V 4 = 0 – 0 – (‐1)(1) – (‐2)(2) – (‐2) (6) = 17<br />
ri<br />
V<br />
r<br />
forward<br />
reduction<br />
Hence: V=[0 1 2 6 17] T and<br />
V<br />
− 1<br />
= D V =<br />
[0 1 2 6 34] T<br />
V<br />
(5) =<br />
i = 5<br />
V<br />
→ U = =<br />
5<br />
V5 34<br />
V V l U<br />
V2 = V2 − l25U5 = 1 −( − 1)(34) = 35<br />
(4) (5)<br />
V3 = V3 − l35U5 = 2 −( − 2)(34) = 70<br />
(4) (5)<br />
V 4<br />
= V 4<br />
− l 45U<br />
5<br />
= 6 −( − 2)(34) = 74<br />
U<br />
(4) (5)<br />
1<br />
=<br />
1 −<br />
15 5 = 0 − ( − 1/ 2)(34) =<br />
17<br />
(4) (5)<br />
(4)<br />
4<br />
V4 74<br />
backsubstitution<br />
b i<br />
V = V − l U<br />
r<br />
( i−1) ( i)<br />
r r ri i<br />
= m ,..., i − 1<br />
= = R = [ 17 35 292 70 74 4]<br />
i<br />
3 T<br />
15-Jun-07<br />
Method <strong>of</strong> F<strong>in</strong>ite Elements I<br />
24