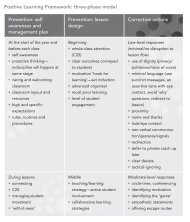
2 Chapter 6 ⢠organising elements Organising elements
2 Chapter 6 ⢠organising elements Organising elements
2 Chapter 6 ⢠organising elements Organising elements
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
It is said that Mendeleev wrote the<br />
names and properties of each element<br />
on a small card that he then arranged<br />
in order of atomic weight. The cards<br />
were then rearranged, maintaining<br />
their order, into groups with similar<br />
properties.<br />
With this organisation complete,<br />
Mendeleev proposed the periodic law:<br />
‘Elements have properties that<br />
recur or repeat according to<br />
their atomic weight.’<br />
More importantly, Mendeleev’s organisation<br />
of cards identified ‘holes’ that he<br />
attributed to <strong>elements</strong> that had yet to<br />
be discovered. The properties of these<br />
undiscovered <strong>elements</strong> could be<br />
predicted from this first periodic<br />
table.<br />
One of Mendeleev’s predictions<br />
was for the element below silicon,<br />
which he called ‘ekasilicon’ (‘eka’<br />
is a Greek word meaning ‘first’,<br />
‘beyond’ or ‘after’; see Table 6.2).<br />
In all, Mendeleev predicted<br />
the properties of 21 unknown or<br />
undiscovered <strong>elements</strong>. His predictions<br />
started searches for the missing <strong>elements</strong>.<br />
When these <strong>elements</strong> were discovered, their<br />
Table 6.2<br />
Predicted properties of ekasilicon compared with the actual properties of germanium<br />
Ekasilicon (symbol Es)<br />
Germanium (symbol Ge)<br />
As predicted in 1871: As discovered in 1886:<br />
Atomic mass 72 Atomic mass 72.6<br />
Density 5.50 g/mL<br />
Colour: grey metal<br />
Forms oxide EsO 2<br />
: density 4.70 g/mL,<br />
slightly basic<br />
Forms chloride EsCl 4<br />
: boiling point 100°C,<br />
density 1.90 g/mL<br />
Density 5.36 g/ml<br />
Colour: grey metal<br />
Forms oxide GeO 2<br />
: density 4.70 g/mL,<br />
slightly basic<br />
Forms chloride GeCl 4<br />
boiling point 86°C,<br />
density 1.88 g/mL<br />
Fig 6.5 The German chemist Lothar Meyer compiled a<br />
periodic table of 56 <strong>elements</strong> a few months after Mendeleev.<br />
Meyer graphed properties of the <strong>elements</strong> against atomic<br />
weight, and noted the repeating properties.<br />
properties were very close to the<br />
properties that had been predicted<br />
by Mendeleev. This convinced many<br />
chemists of the accuracy and value<br />
of Mendeleev’s periodic table.<br />
Mendeleev is given sole credit for<br />
the development of the periodic<br />
table. This is because of the evidence<br />
he provided to support his table and<br />
because he assumed that there were<br />
missing <strong>elements</strong> and he accurately<br />
predicted the properties of these <strong>elements</strong>.<br />
UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS<br />
Unit 7.1 • How do we use the products of chemical reactions?<br />
7<br />
CAS_SB10_TXT_06_1pp.indd 7<br />
11/11/11 4:58 PM