PHONETICS MANUAL.indd - HumBox
PHONETICS MANUAL.indd - HumBox
PHONETICS MANUAL.indd - HumBox
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Consonants like these are known either as STOPS (this term relates to the blockage<br />
of the airflow in stage 1) or as PLOSIVES (this relates to the explosive release of air<br />
in stage 3). But both terms refer to the same category of consonant: nowadays, stop<br />
is used more often than plosive.<br />
4.05 Fricatives<br />
[s] and [z] don’t involve a complete obstruction of the airstream. The blade of the<br />
tongue is held against the teethridge as for [t, d], but sufficiently loosely for the air to<br />
be able to force its way through. Nonetheless, there is enough resistance at the point<br />
of constriction for turbulence to be caused and a sound wave generated. So [s] and [z]<br />
are examples of consonants with partial obstruction of the air-stream, and are known<br />
as FRICATIVES (this term refers to the friction caused by the air as it passes through<br />
the narrow gap).<br />
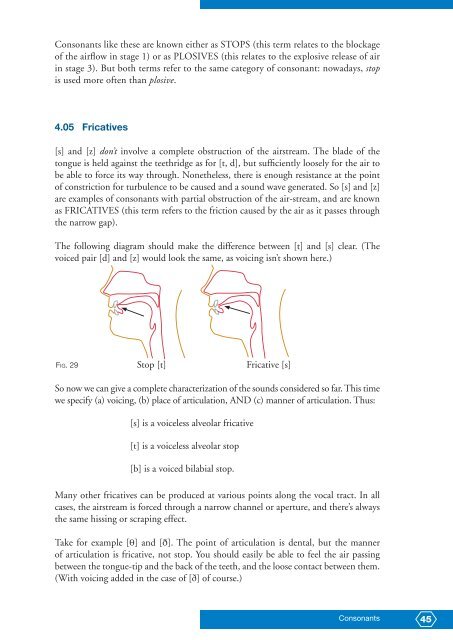
The following diagram should make the difference between [t] and [s] clear. (The<br />
voiced pair [d] and [z] would look the same, as voicing isn’t shown here.)<br />
FIG. 29<br />
Stop [t]<br />
Fricative [s]<br />
So now we can give a complete characterization of the sounds considered so far. This time<br />
we specify (a) voicing, (b) place of articulation, AND (c) manner of articulation. Thus:<br />
[s] is a voiceless alveolar fricative<br />
[t] is a voiceless alveolar stop<br />
[b] is a voiced bilabial stop.<br />
Many other fricatives can be produced at various points along the vocal tract. In all<br />
cases, the airstream is forced through a narrow channel or aperture, and there’s always<br />
the same hissing or scraping effect.<br />
Take for example [T] and [D]. The point of articulation is dental, but the manner<br />
of articulation is fricative, not stop. You should easily be able to feel the air passing<br />
between the tongue-tip and the back of the teeth, and the loose contact between them.<br />
(With voicing added in the case of [ð] of course.)<br />
Consonants<br />
45